ION
-
 KAIST's Im Mi-hee wins Korea's L'Oréal-UNESCO Women in Science Award
<At the 24th L'Oréal-UNESCO For Women in Science Awards ceremony, winners and officials take a commemorative photo. From left: Yoon Byeong-soon, Acting Secretary General of the Korean National Commission for UNESCO; Hwang Eun-sook, Chairperson of the Women’s Bioscience Forum; Lim Mi-hee, Professor at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and recipient of the Academic Promotion Award; Kang Mi-kyung, Assistant Professor at Korea University and recipient of the Fellowship Award; Lee Jeong-hyun, Assistant Professor at Kongju National University; Jeon Ji-hye, Assistant Professor at Gyeongsang National University; Jo Yu-na, Research Professor at Pusan National University; and Samuel du Retail, CEO of L'Oréal Korea./Courtesy of L'Oréal Korea>
Im Mi-hee, a professor at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) Department of Chemistry, received the Academic Promotion Award at the 24th Korean L'Oréal-UNESCO Women in Science Awards ceremony.
L'Oréal Korea, the Korean National Commission for UNESCO, and the Women’s Bioscience Forum held the 24th Korean L'Oréal-UNESCO Women in Science Awards ceremony on the 16th and noted that Im Mi-hee was selected for this year’s Academic Promotion Award.
Professor Im was recognized for her research on the causes of Alzheimer's disease at the molecular level and her efforts in the discovery of intracellular proteins that promote the toxicity of Alzheimer’s-inducing factors. Professor Im is a full member of the Korean Academy of Science and Technology (KAST) and has received several awards including the Hanseong Science Award, this year's Women in Science and Technology Award, and the RIGAKU-ACCC Award (Asia's top woman scientist).
The fellowship section, awarded to four emerging women scientists, includes Kang Mi-kyung, an assistant professor at Korea University’s Department of Health and Environmental Sciences; Jeon Ji-hye, an assistant professor at Gyeongsang National University’s Department of Life Sciences; Jo Yu-na, a research professor at Pusan National University’s College of Medicine; and Lee Jeong-hyun, an assistant professor at Kongju National University’s Department of Environmental Education.
The recipients of the Academic Promotion Award and fellowships will receive a certificate and a trophy, along with research funding of 30 million won and 7 million won, respectively.
Samuel du Retail, the representative of L'Oréal Korea, said, “The L'Oréal Group continues to support the empowerment of women scientists and the improvement of research environments worldwide under the philosophy that 'the world needs science, and science needs women.' We will actively support more female talents to shine at the center of scientific and technological advancement in the future.”
2025.07.18 View 46
KAIST's Im Mi-hee wins Korea's L'Oréal-UNESCO Women in Science Award
<At the 24th L'Oréal-UNESCO For Women in Science Awards ceremony, winners and officials take a commemorative photo. From left: Yoon Byeong-soon, Acting Secretary General of the Korean National Commission for UNESCO; Hwang Eun-sook, Chairperson of the Women’s Bioscience Forum; Lim Mi-hee, Professor at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and recipient of the Academic Promotion Award; Kang Mi-kyung, Assistant Professor at Korea University and recipient of the Fellowship Award; Lee Jeong-hyun, Assistant Professor at Kongju National University; Jeon Ji-hye, Assistant Professor at Gyeongsang National University; Jo Yu-na, Research Professor at Pusan National University; and Samuel du Retail, CEO of L'Oréal Korea./Courtesy of L'Oréal Korea>
Im Mi-hee, a professor at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) Department of Chemistry, received the Academic Promotion Award at the 24th Korean L'Oréal-UNESCO Women in Science Awards ceremony.
L'Oréal Korea, the Korean National Commission for UNESCO, and the Women’s Bioscience Forum held the 24th Korean L'Oréal-UNESCO Women in Science Awards ceremony on the 16th and noted that Im Mi-hee was selected for this year’s Academic Promotion Award.
Professor Im was recognized for her research on the causes of Alzheimer's disease at the molecular level and her efforts in the discovery of intracellular proteins that promote the toxicity of Alzheimer’s-inducing factors. Professor Im is a full member of the Korean Academy of Science and Technology (KAST) and has received several awards including the Hanseong Science Award, this year's Women in Science and Technology Award, and the RIGAKU-ACCC Award (Asia's top woman scientist).
The fellowship section, awarded to four emerging women scientists, includes Kang Mi-kyung, an assistant professor at Korea University’s Department of Health and Environmental Sciences; Jeon Ji-hye, an assistant professor at Gyeongsang National University’s Department of Life Sciences; Jo Yu-na, a research professor at Pusan National University’s College of Medicine; and Lee Jeong-hyun, an assistant professor at Kongju National University’s Department of Environmental Education.
The recipients of the Academic Promotion Award and fellowships will receive a certificate and a trophy, along with research funding of 30 million won and 7 million won, respectively.
Samuel du Retail, the representative of L'Oréal Korea, said, “The L'Oréal Group continues to support the empowerment of women scientists and the improvement of research environments worldwide under the philosophy that 'the world needs science, and science needs women.' We will actively support more female talents to shine at the center of scientific and technological advancement in the future.”
2025.07.18 View 46 -
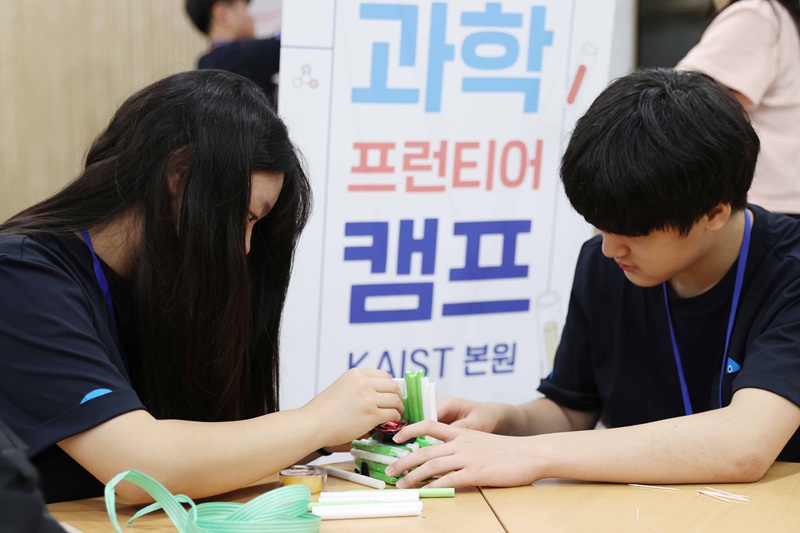 KAIST Holds '2025 KAIST Science Frontier Camp' for Multicultural Youth
<2025 KAIST Science Frontier Camp Activities>
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 18th of July that it hosted the '2025 KAIST Science Frontier Camp' for multicultural youth from the 15th for three days and two nights at the Creative Learning Building on its main campus in Daejeon.
This event was organized in accordance with the 'Multicultural Talent Nurturing Agreement' signed by KAIST and GS Caltex in 2024. It marks the first year of a mid-to-long-term project in which 100 million KRW in development funds will be contributed annually for four years. The Global Institute for Talented Education organized the camp, and approximately 30 middle school students from multicultural families affiliated with the 'Hanmaum Educational Volunteer Group' (Director, Honorary Professor Byung Kyu Choi), a mentoring and volunteer organization for multicultural students, participated.
The camp participants enjoyed developing their scientific thinking skills and problem-solving abilities, and broadening their understanding of STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) career paths through a variety of science activity programs, including: △'Black Box: Record the Egg's Last Moment!' △'Find the Best Strategy! Heuristic Algorithm Challenge' △'Future Society and AI, Finding Career Directions' △'Distance Dominates the World!' and △'Career Talk Concert.'
During the opening ceremony, Director Byung Kyu Choi delivered a congratulatory speech. Additionally, Yong Hyun Kim, Dean of Admissions at KAIST, gave a special lecture titled 'La La Land KAIST – A Story of Chasing the Dream of a Young Scientist,' sharing honest stories about careers and dreams as a scientist.
Gi Jung Yoo, a freshman from the Division of Undeclared Majors who participated in the camp as a student mentor, shared that he had a very meaningful time mentoring the participating students, who are future STEM hopefuls, sharing vivid experiences as well as insights on metric functions. He added his hope that more students would be given such opportunities.
< Students Actively Taking Part in the Camp Activities>
Si Jong Kwak, Director of the Global Institute for Talented Education, stated, "We hope this will be a practical way to help students foster their interest in science, learn the joy of discussion and communication, and design their future."
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee remarked, "This camp was a valuable opportunity for students from diverse cultural backgrounds to gain confidence through science and envision their future." He added, "KAIST will continue to dedicate efforts to nurturing multicultural talent and contribute to creating a sustainable society."
Since 2024, KAIST has introduced and selected multicultural students through its Equal Opportunity Admission track. Utilizing the development funds from GS Caltex, KAIST also established the 'GS Caltex Multicultural Excellence Scholarship Program.' Through this scholarship program, undergraduate students from multicultural families receive living expenses each semester, allowing them to focus more stably on their studies. As the number of applicants for the Equal Opportunity Admission track is increasing every year, more multicultural students are expected to benefit from scholarships in the future.
Additionally, in May, both organizations invited Ms. Si Si Wu Fong, a foreign employee at GS Caltex, to give a special lecture titled 'Working Life for Foreigners in Korea' to support foreign students' career exploration. Foreign students who attended the lecture reported positive feedback, stating that they gained practical career information and were motivated to pursue employment in STEM fields in Korea.
KAIST plans to continue strengthening its efforts to nurture multicultural talent, increase understanding of the upcoming multicultural society, and help spread social values.
<At the 2025 KAIST Science Frontier Camp>
2025.07.18 View 65
KAIST Holds '2025 KAIST Science Frontier Camp' for Multicultural Youth
<2025 KAIST Science Frontier Camp Activities>
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 18th of July that it hosted the '2025 KAIST Science Frontier Camp' for multicultural youth from the 15th for three days and two nights at the Creative Learning Building on its main campus in Daejeon.
This event was organized in accordance with the 'Multicultural Talent Nurturing Agreement' signed by KAIST and GS Caltex in 2024. It marks the first year of a mid-to-long-term project in which 100 million KRW in development funds will be contributed annually for four years. The Global Institute for Talented Education organized the camp, and approximately 30 middle school students from multicultural families affiliated with the 'Hanmaum Educational Volunteer Group' (Director, Honorary Professor Byung Kyu Choi), a mentoring and volunteer organization for multicultural students, participated.
The camp participants enjoyed developing their scientific thinking skills and problem-solving abilities, and broadening their understanding of STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) career paths through a variety of science activity programs, including: △'Black Box: Record the Egg's Last Moment!' △'Find the Best Strategy! Heuristic Algorithm Challenge' △'Future Society and AI, Finding Career Directions' △'Distance Dominates the World!' and △'Career Talk Concert.'
During the opening ceremony, Director Byung Kyu Choi delivered a congratulatory speech. Additionally, Yong Hyun Kim, Dean of Admissions at KAIST, gave a special lecture titled 'La La Land KAIST – A Story of Chasing the Dream of a Young Scientist,' sharing honest stories about careers and dreams as a scientist.
Gi Jung Yoo, a freshman from the Division of Undeclared Majors who participated in the camp as a student mentor, shared that he had a very meaningful time mentoring the participating students, who are future STEM hopefuls, sharing vivid experiences as well as insights on metric functions. He added his hope that more students would be given such opportunities.
< Students Actively Taking Part in the Camp Activities>
Si Jong Kwak, Director of the Global Institute for Talented Education, stated, "We hope this will be a practical way to help students foster their interest in science, learn the joy of discussion and communication, and design their future."
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee remarked, "This camp was a valuable opportunity for students from diverse cultural backgrounds to gain confidence through science and envision their future." He added, "KAIST will continue to dedicate efforts to nurturing multicultural talent and contribute to creating a sustainable society."
Since 2024, KAIST has introduced and selected multicultural students through its Equal Opportunity Admission track. Utilizing the development funds from GS Caltex, KAIST also established the 'GS Caltex Multicultural Excellence Scholarship Program.' Through this scholarship program, undergraduate students from multicultural families receive living expenses each semester, allowing them to focus more stably on their studies. As the number of applicants for the Equal Opportunity Admission track is increasing every year, more multicultural students are expected to benefit from scholarships in the future.
Additionally, in May, both organizations invited Ms. Si Si Wu Fong, a foreign employee at GS Caltex, to give a special lecture titled 'Working Life for Foreigners in Korea' to support foreign students' career exploration. Foreign students who attended the lecture reported positive feedback, stating that they gained practical career information and were motivated to pursue employment in STEM fields in Korea.
KAIST plans to continue strengthening its efforts to nurture multicultural talent, increase understanding of the upcoming multicultural society, and help spread social values.
<At the 2025 KAIST Science Frontier Camp>
2025.07.18 View 65 -
 KAIST reveals for the first time the mechanism by which alcohol triggers liver inflammation
<(From left)Dr. Keungmo Yang, Professor Won-Il Jeong, Ph.D candidate Kyurae Kim>
Excessive alcohol consumption causes alcoholic liver disease, and about 20% of these cases progress to alcohol-associated steatohepatitis (ASH), which can lead to liver cirrhosis and liver failure. Early diagnosis and treatment are therefore extremely important. A KAIST research team has identified a new molecular mechanism in which alcohol-damaged liver cells increase reactive oxygen species (ROS), leading to cell death and inflammatory responses. In addition, they discovered that Kupffer cells, immune cells residing in the liver, act as a “dual-function regulator” that can either promote or suppress inflammation through interactions with liver cells.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 17th that a research team led by Professor Won-Il Jeong from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering, in collaboration with Professor Won Kim’s team at Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, has uncovered the molecular pathway of liver damage and inflammation caused by alcohol consumption. This finding offers new clues for the diagnosis and treatment of alcohol-associated liver disease (ALD).
Professor Won-Il Jeong’s research team found that during chronic alcohol intake, expression of the vesicular glutamate transporter VGLUT3 increases, leading to glutamate accumulation in hepatocytes. Subsequent binge drinking causes rapid changes in intracellular calcium levels, which then triggers glutamate* secretion. The secreted glutamate stimulates the glutamate receptor mGluR5 on liver-resident macrophages (Kupffer cells), which induces ROS production and activates a pathological pathway resulting in hepatocyte death and inflammation.
*Glutamate: A type of amino acid involved in intercellular signaling, protein synthesis, and energy metabolism in various tissues including the brain and liver. In excess, it can cause overexcitation and death of nerve cells.
<Figure1. Glutamate accumulation in perivenous hepatocytes through vesicular glutamate transporter 3 after 2-week EtOH intake and its release by binge drinking>
A particularly groundbreaking aspect of this study is that damaged hepatocytes and Kupffer cells can form a "pseudosynapse"—a structure similar to a synapse which is previously thought to occur only in the brain—enabling them to exchange signals. This is the first time such a phenomenon has been identified in the liver.
This pseudosynapse forms when hepatocytes expand (ballooning) due to alcohol, becoming physically attached to Kupffer cells. Simply put, the damaged hepatocytes don’t just die—they send distress signals to nearby immune cells, prompting a response.
This discovery proposes a new paradigm: even in peripheral organs, direct structural contact between cells can allow signal transmission. It also shows that damaged hepatocytes can actively stimulate macrophages and induce regeneration through cell death, revealing the liver’s “autonomous recovery function.”
The team also confirmed in animal models that genetic or pharmacological inhibition of VGLUT3, mGluR5, or the ROS-producing enzyme NOX2 reduces alcohol-induced liver damage. They also confirmed that the same mechanism observed in animal models was present in human patients with ALD by analyzing blood and liver tissue samples.
<Figure2. Binge drinking rapidly alters the intracellular calcium levels to release glutamates and activate mGluR5 of Kupffer cells>
Professor Won-Il Jeong of KAIST said, “These findings may serve as new molecular targets for early diagnosis and treatment of ASH in the future.”
This study was jointly led by Dr. Keungmo Yang (now at Yeouido St. Mary’s Hospital) and Kyurae Kim, a doctoral candidate at KAIST, who served as co–first authors. It was conducted in collaboration with Professor Won Kim’s team at Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center and was published in the journal Nature Communications on July 1.
※ Article Title: Binge drinking triggers VGLUT3-mediated glutamate secretion and subsequent hepatic inflammation by activating mGluR5/NOX2 in Kupffer cells ※ DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-60820-3
This study was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation of Korea's Global Leader Program, Mid-Career Researcher Program, and the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program.
2025.07.17 View 124
KAIST reveals for the first time the mechanism by which alcohol triggers liver inflammation
<(From left)Dr. Keungmo Yang, Professor Won-Il Jeong, Ph.D candidate Kyurae Kim>
Excessive alcohol consumption causes alcoholic liver disease, and about 20% of these cases progress to alcohol-associated steatohepatitis (ASH), which can lead to liver cirrhosis and liver failure. Early diagnosis and treatment are therefore extremely important. A KAIST research team has identified a new molecular mechanism in which alcohol-damaged liver cells increase reactive oxygen species (ROS), leading to cell death and inflammatory responses. In addition, they discovered that Kupffer cells, immune cells residing in the liver, act as a “dual-function regulator” that can either promote or suppress inflammation through interactions with liver cells.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 17th that a research team led by Professor Won-Il Jeong from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering, in collaboration with Professor Won Kim’s team at Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, has uncovered the molecular pathway of liver damage and inflammation caused by alcohol consumption. This finding offers new clues for the diagnosis and treatment of alcohol-associated liver disease (ALD).
Professor Won-Il Jeong’s research team found that during chronic alcohol intake, expression of the vesicular glutamate transporter VGLUT3 increases, leading to glutamate accumulation in hepatocytes. Subsequent binge drinking causes rapid changes in intracellular calcium levels, which then triggers glutamate* secretion. The secreted glutamate stimulates the glutamate receptor mGluR5 on liver-resident macrophages (Kupffer cells), which induces ROS production and activates a pathological pathway resulting in hepatocyte death and inflammation.
*Glutamate: A type of amino acid involved in intercellular signaling, protein synthesis, and energy metabolism in various tissues including the brain and liver. In excess, it can cause overexcitation and death of nerve cells.
<Figure1. Glutamate accumulation in perivenous hepatocytes through vesicular glutamate transporter 3 after 2-week EtOH intake and its release by binge drinking>
A particularly groundbreaking aspect of this study is that damaged hepatocytes and Kupffer cells can form a "pseudosynapse"—a structure similar to a synapse which is previously thought to occur only in the brain—enabling them to exchange signals. This is the first time such a phenomenon has been identified in the liver.
This pseudosynapse forms when hepatocytes expand (ballooning) due to alcohol, becoming physically attached to Kupffer cells. Simply put, the damaged hepatocytes don’t just die—they send distress signals to nearby immune cells, prompting a response.
This discovery proposes a new paradigm: even in peripheral organs, direct structural contact between cells can allow signal transmission. It also shows that damaged hepatocytes can actively stimulate macrophages and induce regeneration through cell death, revealing the liver’s “autonomous recovery function.”
The team also confirmed in animal models that genetic or pharmacological inhibition of VGLUT3, mGluR5, or the ROS-producing enzyme NOX2 reduces alcohol-induced liver damage. They also confirmed that the same mechanism observed in animal models was present in human patients with ALD by analyzing blood and liver tissue samples.
<Figure2. Binge drinking rapidly alters the intracellular calcium levels to release glutamates and activate mGluR5 of Kupffer cells>
Professor Won-Il Jeong of KAIST said, “These findings may serve as new molecular targets for early diagnosis and treatment of ASH in the future.”
This study was jointly led by Dr. Keungmo Yang (now at Yeouido St. Mary’s Hospital) and Kyurae Kim, a doctoral candidate at KAIST, who served as co–first authors. It was conducted in collaboration with Professor Won Kim’s team at Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center and was published in the journal Nature Communications on July 1.
※ Article Title: Binge drinking triggers VGLUT3-mediated glutamate secretion and subsequent hepatic inflammation by activating mGluR5/NOX2 in Kupffer cells ※ DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-60820-3
This study was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation of Korea's Global Leader Program, Mid-Career Researcher Program, and the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program.
2025.07.17 View 124 -
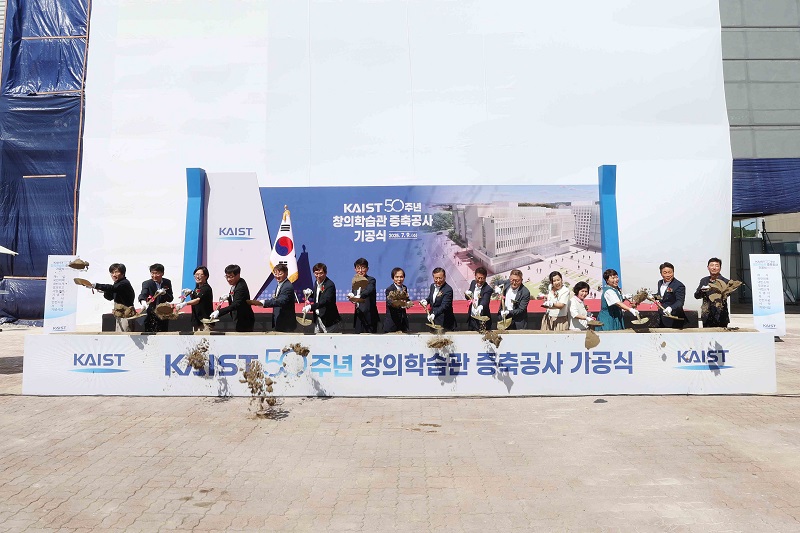 KAIST Kicks Off the Expansion of its Creative Learning Building, a 50th Anniversary Donation Landmark
KAIST announced on July 10th that it held a groundbreaking ceremony on July 9th for the expansion of its Creative Learning Building. This project, which celebrates the university's 50th anniversary, will become a significant donation-funded landmark and marks the official start of its construction.
<(From left) President Kwang Hyung Lee, Former President Sung-Chul Shin>
The groundbreaking ceremony was attended by key donors who graced the occasion, including KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee, former President Sung-Chul Shin, Alumni Association President Yoon-Tae Lee, as well as parents and faculty member.
The Creative Learning Building serves as a primary space where KAIST undergraduate and graduate students attend lectures, functioning as a central hub for a variety of classes and talks. It also houses student support departments, including the Student Affairs Office, establishing itself as a student-centric complex that integrates educational, counseling, and welfare functions.
This expansion is more than just an increase in educational facilities; it's being developed as a "donation landmark" embodying KAIST's identity and future vision. Designed with a focus on creative convergence education, this project aims to create a new educational hub that organically combines education, exchange, and welfare functions
The campaign included over 230 participants, including KAIST alumni Byung-gyu Chang, Chairman of Krafton, former Alumni Association President Ki-chul Cha, Dr. Kun-mo Chung (former Minister of Science and Technology), as well as faculty members, parents, and current students. They collectively raised 6.5 billion KRW in donations. The total cost for this expansion project is 9 billion KRW, encompassing a gross floor area of 3,222.92㎡ across five above-ground floors, with completion targeted for September 2026.
2025.07.10 View 149
KAIST Kicks Off the Expansion of its Creative Learning Building, a 50th Anniversary Donation Landmark
KAIST announced on July 10th that it held a groundbreaking ceremony on July 9th for the expansion of its Creative Learning Building. This project, which celebrates the university's 50th anniversary, will become a significant donation-funded landmark and marks the official start of its construction.
<(From left) President Kwang Hyung Lee, Former President Sung-Chul Shin>
The groundbreaking ceremony was attended by key donors who graced the occasion, including KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee, former President Sung-Chul Shin, Alumni Association President Yoon-Tae Lee, as well as parents and faculty member.
The Creative Learning Building serves as a primary space where KAIST undergraduate and graduate students attend lectures, functioning as a central hub for a variety of classes and talks. It also houses student support departments, including the Student Affairs Office, establishing itself as a student-centric complex that integrates educational, counseling, and welfare functions.
This expansion is more than just an increase in educational facilities; it's being developed as a "donation landmark" embodying KAIST's identity and future vision. Designed with a focus on creative convergence education, this project aims to create a new educational hub that organically combines education, exchange, and welfare functions
The campaign included over 230 participants, including KAIST alumni Byung-gyu Chang, Chairman of Krafton, former Alumni Association President Ki-chul Cha, Dr. Kun-mo Chung (former Minister of Science and Technology), as well as faculty members, parents, and current students. They collectively raised 6.5 billion KRW in donations. The total cost for this expansion project is 9 billion KRW, encompassing a gross floor area of 3,222.92㎡ across five above-ground floors, with completion targeted for September 2026.
2025.07.10 View 149 -
 KAIST Presents a Breakthrough in Overcoming Drug Resistance in Cancer – Hope for Treating Intractable Diseases like Diabetes
<(From the left) Prof. Hyun Uk Kim, Ph.D candiate Hae Deok Jung, Ph.D candidate Jina Lim, Prof.Yoosik Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering>
One of the biggest obstacles in cancer treatment is drug resistance in cancer cells. Conventional efforts have focused on identifying new drug targets to eliminate these resistant cells, but such approaches can often lead to even stronger resistance. Now, researchers at KAIST have developed a computational framework to predict key metabolic genes that can re-sensitize resistant cancer cells to treatment. This technique holds promise not only for a variety of cancer therapies but also for treating metabolic diseases such as diabetes.
On the 7th of July, KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced that a research team led by Professors Hyun Uk Kim and Yoosik Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering had developed a computational framework that predicts metabolic gene targets to re-sensitize drug-resistant breast cancer cells. This was achieved using a metabolic network model capable of simulating human metabolism.
Focusing on metabolic alterations—key characteristics in the formation of drug resistance—the researchers developed a metabolism-based approach to identify gene targets that could enhance drug responsiveness by regulating the metabolism of drug-resistant breast cancer cells.
< Computational framework that can identify metabolic gene targets to revert the metabolic state of the drug-resistant cells to that of the drug-sensitive parental cells>
The team first constructed cell-specific metabolic network models by integrating proteomic data obtained from two different types of drug-resistant MCF7 breast cancer cell lines: one resistant to doxorubicin and the other to paclitaxel. They then performed gene knockout simulations* on all of the metabolic genes and analyzed the results.
*Gene knockout simulation: A computational method to predict changes in a biological network by virtually removing specific genes.
As a result, they discovered that suppressing certain genes could make previously resistant cancer cells responsive to anticancer drugs again. Specifically, they identified GOT1 as a target in doxorubicin-resistant cells, GPI in paclitaxel-resistant cells, and SLC1A5 as a common target for both drugs.
The predictions were experimentally validated by suppressing proteins encoded by these genes, which led to the re-sensitization of the drug-resistant cancer cells.
Furthermore, consistent re-sensitization effects were also observed when the same proteins were inhibited in other types of breast cancer cells that had developed resistance to the same drugs.
Professor Yoosik Kim remarked, “Cellular metabolism plays a crucial role in various intractable diseases including infectious and degenerative conditions. This new technology, which predicts metabolic regulation switches, can serve as a foundational tool not only for treating drug-resistant breast cancer but also for a wide range of diseases that currently lack effective therapies.”
Professor Hyun Uk Kim, who led the study, emphasized, “The significance of this research lies in our ability to accurately predict key metabolic genes that can make resistant cancer cells responsive to treatment again—using only computer simulations and minimal experimental data. This framework can be widely applied to discover new therapeutic targets in various cancers and metabolic diseases.”
The study, in which Ph.D. candidates JinA Lim and Hae Deok Jung from KAIST participated as co-first authors, was published online on June 25 in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), a leading multidisciplinary journal that covers top-tier research in life sciences, physics, engineering, and social sciences.
※ Title: Genome-scale knockout simulation and clustering analysis of drug-resistant breast cancer cells reveal drug sensitization targets ※ DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2425384122 ※ Authors: JinA Lim (KAIST, co-first author), Hae Deok Jung (KAIST, co-first author), Han Suk Ryu (Seoul National University Hospital, corresponding author), Yoosik Kim (KAIST, corresponding author), Hyun Uk Kim (KAIST, corresponding author), and five others.
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI).
2025.07.08 View 393
KAIST Presents a Breakthrough in Overcoming Drug Resistance in Cancer – Hope for Treating Intractable Diseases like Diabetes
<(From the left) Prof. Hyun Uk Kim, Ph.D candiate Hae Deok Jung, Ph.D candidate Jina Lim, Prof.Yoosik Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering>
One of the biggest obstacles in cancer treatment is drug resistance in cancer cells. Conventional efforts have focused on identifying new drug targets to eliminate these resistant cells, but such approaches can often lead to even stronger resistance. Now, researchers at KAIST have developed a computational framework to predict key metabolic genes that can re-sensitize resistant cancer cells to treatment. This technique holds promise not only for a variety of cancer therapies but also for treating metabolic diseases such as diabetes.
On the 7th of July, KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced that a research team led by Professors Hyun Uk Kim and Yoosik Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering had developed a computational framework that predicts metabolic gene targets to re-sensitize drug-resistant breast cancer cells. This was achieved using a metabolic network model capable of simulating human metabolism.
Focusing on metabolic alterations—key characteristics in the formation of drug resistance—the researchers developed a metabolism-based approach to identify gene targets that could enhance drug responsiveness by regulating the metabolism of drug-resistant breast cancer cells.
< Computational framework that can identify metabolic gene targets to revert the metabolic state of the drug-resistant cells to that of the drug-sensitive parental cells>
The team first constructed cell-specific metabolic network models by integrating proteomic data obtained from two different types of drug-resistant MCF7 breast cancer cell lines: one resistant to doxorubicin and the other to paclitaxel. They then performed gene knockout simulations* on all of the metabolic genes and analyzed the results.
*Gene knockout simulation: A computational method to predict changes in a biological network by virtually removing specific genes.
As a result, they discovered that suppressing certain genes could make previously resistant cancer cells responsive to anticancer drugs again. Specifically, they identified GOT1 as a target in doxorubicin-resistant cells, GPI in paclitaxel-resistant cells, and SLC1A5 as a common target for both drugs.
The predictions were experimentally validated by suppressing proteins encoded by these genes, which led to the re-sensitization of the drug-resistant cancer cells.
Furthermore, consistent re-sensitization effects were also observed when the same proteins were inhibited in other types of breast cancer cells that had developed resistance to the same drugs.
Professor Yoosik Kim remarked, “Cellular metabolism plays a crucial role in various intractable diseases including infectious and degenerative conditions. This new technology, which predicts metabolic regulation switches, can serve as a foundational tool not only for treating drug-resistant breast cancer but also for a wide range of diseases that currently lack effective therapies.”
Professor Hyun Uk Kim, who led the study, emphasized, “The significance of this research lies in our ability to accurately predict key metabolic genes that can make resistant cancer cells responsive to treatment again—using only computer simulations and minimal experimental data. This framework can be widely applied to discover new therapeutic targets in various cancers and metabolic diseases.”
The study, in which Ph.D. candidates JinA Lim and Hae Deok Jung from KAIST participated as co-first authors, was published online on June 25 in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), a leading multidisciplinary journal that covers top-tier research in life sciences, physics, engineering, and social sciences.
※ Title: Genome-scale knockout simulation and clustering analysis of drug-resistant breast cancer cells reveal drug sensitization targets ※ DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2425384122 ※ Authors: JinA Lim (KAIST, co-first author), Hae Deok Jung (KAIST, co-first author), Han Suk Ryu (Seoul National University Hospital, corresponding author), Yoosik Kim (KAIST, corresponding author), Hyun Uk Kim (KAIST, corresponding author), and five others.
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI).
2025.07.08 View 393 -
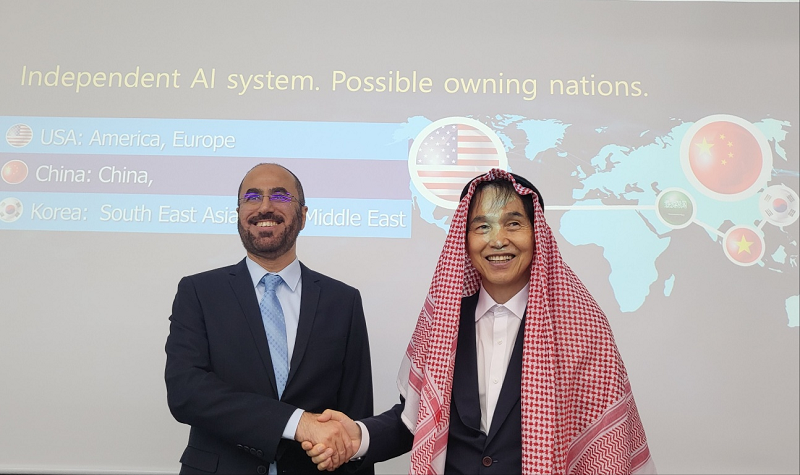 King Saud University and KAIST discussed Strategic AI Partnership
<From left> President Abdulla Al-Salman(King Saud University), President Kwang Hyung Lee(KAIST)
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) and King Saud University (President Abdulla Al-Salman) held a meeting on July 3 at the KAIST Campus in Seoul and agreed to pursue strategic cooperation in AI and digital platform development. The global AI landscape is increasingly polarized between closed models developed by the U.S. and China’s nationally focused technology ecosystems. In this context, many neutral countries have consistently called for an alternative third model that promotes both technological diversity and open access. President Lee has previously advocated for a "Tripartite Platform Strategy" (三分之計), proposing an international collaboration framework based on open-source principles to be free from binary digital power structures and foster cooperative coexistence.
This KAIST-KSU collaboration represents a step toward developing a new, inclusive AI model. The collaboration aims to establish an innovative multilateral framework, especially within the MENA, Japan, Korea, and Southeast Asia, by building an open-source-based AI alliance. Both institutions bring complementary strengths to the table. Saudi Arabia possesses large-scale capital and digital infrastructure, while Korea leads in core AI and semiconductor technologies, applied research, and talent cultivation.
Together, the two nations aim to establish a sustainable collaboration model that creates a virtuous cycle of investment, technology, and talent. This initiative is expected to contribute to the development of an open AI platform and promote diversity in the global AI ecosystem.
During the meeting, the two sides discussed key areas of future cooperation, including:
· Joint development of open-source AI technologies and digital platforms
· Launch of a KAIST-KSU dual graduate degree program
· Expansion of exchange programs for students, faculty, and researchers
· Collaborative research in basic science and STEM disciplines
In particular, the two institutions discussed to establish a joint AI research center to co-develop open AI models and explore practical industrial applications. The goal is to broaden access to AI technology and create an inclusive innovation environment for more countries and institutions.
President Abdulla Al-Salman stated, "Under Saudi Vision 2030, we are driving innovation in science and technology through new leadership, openness, and strategic investment. This partnership with KAIST will serve as a critical foundation for building a competitive AI ecosystem in the Middle East."
President Kwang Hyung Lee emphasized, "By combining Saudi Arabia's leadership, market, and investment capacity with KAIST's technological innovation and the rich talent pools from both countries, we will significantly contribute to diversifying the global AI ecosystem."
Both leaders further noted, "Through joint research leading to an independent AI model, our two institutions could establish a new axis beyond the existing US-China digital order—realizing a 'Tripartite AI Strategy' that will propel us into global markets extending far beyond the MENA and ASEAN regions."
KAIST and KSU plan to formalize this agreement by signing an MOU in the near future, followed by concrete actions such as launching the joint research institute and global talent development programs. This collaboration was initiated under the Korea Foundation’s Distinguished Guests Invitation Program, overseen by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, and is expected to grow into a long-term strategic partnership with continued support from KF.
About King Saud University (KSU)
Founded in 1957, KSU is Saudi Arabia’s first and leading national university. As a top research-oriented institution in the Middle East, it has achieved international recognition in fields such as AI, energy, and biotechnology. It plays a central role in nurturing talent and driving innovation aligned with Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030, and is expanding global partnerships to further strengthen its research capabilities.
About the Korea Foundation (KF)
Established in 1991 under the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, the Korea Foundation is a public diplomacy institution dedicated to strengthening international understanding and friendship with Korea. KF plays a key role in expanding Korea’s soft power through academic and cultural exchange, people-to-people networks, and global Korean studies programs. Its Distinguished Guests Invitation Program fosters strategic partnerships with global leaders in government, academia, and industry.
2025.07.04 View 502
King Saud University and KAIST discussed Strategic AI Partnership
<From left> President Abdulla Al-Salman(King Saud University), President Kwang Hyung Lee(KAIST)
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) and King Saud University (President Abdulla Al-Salman) held a meeting on July 3 at the KAIST Campus in Seoul and agreed to pursue strategic cooperation in AI and digital platform development. The global AI landscape is increasingly polarized between closed models developed by the U.S. and China’s nationally focused technology ecosystems. In this context, many neutral countries have consistently called for an alternative third model that promotes both technological diversity and open access. President Lee has previously advocated for a "Tripartite Platform Strategy" (三分之計), proposing an international collaboration framework based on open-source principles to be free from binary digital power structures and foster cooperative coexistence.
This KAIST-KSU collaboration represents a step toward developing a new, inclusive AI model. The collaboration aims to establish an innovative multilateral framework, especially within the MENA, Japan, Korea, and Southeast Asia, by building an open-source-based AI alliance. Both institutions bring complementary strengths to the table. Saudi Arabia possesses large-scale capital and digital infrastructure, while Korea leads in core AI and semiconductor technologies, applied research, and talent cultivation.
Together, the two nations aim to establish a sustainable collaboration model that creates a virtuous cycle of investment, technology, and talent. This initiative is expected to contribute to the development of an open AI platform and promote diversity in the global AI ecosystem.
During the meeting, the two sides discussed key areas of future cooperation, including:
· Joint development of open-source AI technologies and digital platforms
· Launch of a KAIST-KSU dual graduate degree program
· Expansion of exchange programs for students, faculty, and researchers
· Collaborative research in basic science and STEM disciplines
In particular, the two institutions discussed to establish a joint AI research center to co-develop open AI models and explore practical industrial applications. The goal is to broaden access to AI technology and create an inclusive innovation environment for more countries and institutions.
President Abdulla Al-Salman stated, "Under Saudi Vision 2030, we are driving innovation in science and technology through new leadership, openness, and strategic investment. This partnership with KAIST will serve as a critical foundation for building a competitive AI ecosystem in the Middle East."
President Kwang Hyung Lee emphasized, "By combining Saudi Arabia's leadership, market, and investment capacity with KAIST's technological innovation and the rich talent pools from both countries, we will significantly contribute to diversifying the global AI ecosystem."
Both leaders further noted, "Through joint research leading to an independent AI model, our two institutions could establish a new axis beyond the existing US-China digital order—realizing a 'Tripartite AI Strategy' that will propel us into global markets extending far beyond the MENA and ASEAN regions."
KAIST and KSU plan to formalize this agreement by signing an MOU in the near future, followed by concrete actions such as launching the joint research institute and global talent development programs. This collaboration was initiated under the Korea Foundation’s Distinguished Guests Invitation Program, overseen by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, and is expected to grow into a long-term strategic partnership with continued support from KF.
About King Saud University (KSU)
Founded in 1957, KSU is Saudi Arabia’s first and leading national university. As a top research-oriented institution in the Middle East, it has achieved international recognition in fields such as AI, energy, and biotechnology. It plays a central role in nurturing talent and driving innovation aligned with Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030, and is expanding global partnerships to further strengthen its research capabilities.
About the Korea Foundation (KF)
Established in 1991 under the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, the Korea Foundation is a public diplomacy institution dedicated to strengthening international understanding and friendship with Korea. KF plays a key role in expanding Korea’s soft power through academic and cultural exchange, people-to-people networks, and global Korean studies programs. Its Distinguished Guests Invitation Program fosters strategic partnerships with global leaders in government, academia, and industry.
2025.07.04 View 502 -
 New and Highly Efficient Recycling Technology to Turn Used Tires into Raw Materials for Rubber and Nylon
< (From left) Kyungmin Choi (MS-Ph.D. integrated course, Department of Chemistry), Dr. Beomsoon Park, Professor Soon Hyeok Hong, Dr. Kyoungil Cho >
Approximately 1.5 billions of tires are discarded globally every year, and this is identified as one of the major causes of serious environmental pollution. The research team at the Department of Chemistry at KAIST has achieved a breakthrough by selectively converting waste tires into high-purity cyclic alkenes, valuable chemical building blocks used in the production of rubber and nylon fibers. This advance marks a new milestone in chemical recycling technology for waste tires.
The team, led by Professor Soon Hyeok Hong, has developed a dual-catalyst-based reaction system that overcomes the long-standing challenges associated with recycling vulcanized rubber materials.
Tires are composed of complex blends of synthetic and natural rubber, and their physical strength and durability are reinforced with additives such as silica, carbon black, and antioxidants. In particular, cross-linking between rubber chains is formed through the vulcanization process, giving them a structure resistant to heat and pressure, which is one of the main reasons why chemical recycling of waste tires is difficult.
Until now, waste tire recycling has mainly relied on pyrolysis or mechanical recycling methods. The pyrolysis method is a technology that decomposes polymer chains at high temperatures of 350-800°C to convert them into fuel oil, but it clearly has limitations such as high energy consumption, low selectivity, and the production of low-quality hydrocarbon mixtures.
To solve these problems, the research team developed a method to convert waste rubber into useful chemicals using dual catalysis. The first catalyst helps to break down rubber molecules by changing their bonding structure, and the second catalyst creates cyclic compounds through a ring-closing reaction.
This process shows high selectivity of up to 92% and a yield of 82%. The produced cyclopentene can be recycled into rubber, and cyclohexene can be used as a raw material for nylon fibers, making them industrially very valuable.
The research team successfully applied the developed system to discarded waste tires, achieving selective conversion into high-purity cyclic alkenes. Unlike the existing pyrolysis method, this is evaluated as a new turning point in the field of waste tire recycling as it can produce high-value chemicals through low-temperature precision catalytic reactions.
In addition, this catalytic platform is compatible with a wide range of synthetic and waste rubbers, positioning it as a promising foundation for scalable, circular solutions in the polymer and materials industries.
< Figure 1. Development of a Catalytic Method for Chemical Recycling of Waste Rubber >
Professor Hong stated, "This research offers an innovative solution for the chemical recycling of waste tires. We aim to develop next-generation high-efficiency catalysts and lay the groundwork for commercialization to enhance economic feasibility. Ultimately, our goal is to contribute to solving the broader waste plastic problem through fundamental chemistry."
This research, in which Beomsoon Park, Kyoungil Cho, and Kyungmin Choi participated, was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea and was published online in the internationally renowned academic journal ‘Chem’ on June 18th.
※Paper Title: Catalytic and Selective Chemical Recycling of Post-Consumer Rubbers into Cycloalkenes
※DOI: 10.1016/j.chempr.2025.102625
2025.06.26 View 1890
New and Highly Efficient Recycling Technology to Turn Used Tires into Raw Materials for Rubber and Nylon
< (From left) Kyungmin Choi (MS-Ph.D. integrated course, Department of Chemistry), Dr. Beomsoon Park, Professor Soon Hyeok Hong, Dr. Kyoungil Cho >
Approximately 1.5 billions of tires are discarded globally every year, and this is identified as one of the major causes of serious environmental pollution. The research team at the Department of Chemistry at KAIST has achieved a breakthrough by selectively converting waste tires into high-purity cyclic alkenes, valuable chemical building blocks used in the production of rubber and nylon fibers. This advance marks a new milestone in chemical recycling technology for waste tires.
The team, led by Professor Soon Hyeok Hong, has developed a dual-catalyst-based reaction system that overcomes the long-standing challenges associated with recycling vulcanized rubber materials.
Tires are composed of complex blends of synthetic and natural rubber, and their physical strength and durability are reinforced with additives such as silica, carbon black, and antioxidants. In particular, cross-linking between rubber chains is formed through the vulcanization process, giving them a structure resistant to heat and pressure, which is one of the main reasons why chemical recycling of waste tires is difficult.
Until now, waste tire recycling has mainly relied on pyrolysis or mechanical recycling methods. The pyrolysis method is a technology that decomposes polymer chains at high temperatures of 350-800°C to convert them into fuel oil, but it clearly has limitations such as high energy consumption, low selectivity, and the production of low-quality hydrocarbon mixtures.
To solve these problems, the research team developed a method to convert waste rubber into useful chemicals using dual catalysis. The first catalyst helps to break down rubber molecules by changing their bonding structure, and the second catalyst creates cyclic compounds through a ring-closing reaction.
This process shows high selectivity of up to 92% and a yield of 82%. The produced cyclopentene can be recycled into rubber, and cyclohexene can be used as a raw material for nylon fibers, making them industrially very valuable.
The research team successfully applied the developed system to discarded waste tires, achieving selective conversion into high-purity cyclic alkenes. Unlike the existing pyrolysis method, this is evaluated as a new turning point in the field of waste tire recycling as it can produce high-value chemicals through low-temperature precision catalytic reactions.
In addition, this catalytic platform is compatible with a wide range of synthetic and waste rubbers, positioning it as a promising foundation for scalable, circular solutions in the polymer and materials industries.
< Figure 1. Development of a Catalytic Method for Chemical Recycling of Waste Rubber >
Professor Hong stated, "This research offers an innovative solution for the chemical recycling of waste tires. We aim to develop next-generation high-efficiency catalysts and lay the groundwork for commercialization to enhance economic feasibility. Ultimately, our goal is to contribute to solving the broader waste plastic problem through fundamental chemistry."
This research, in which Beomsoon Park, Kyoungil Cho, and Kyungmin Choi participated, was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea and was published online in the internationally renowned academic journal ‘Chem’ on June 18th.
※Paper Title: Catalytic and Selective Chemical Recycling of Post-Consumer Rubbers into Cycloalkenes
※DOI: 10.1016/j.chempr.2025.102625
2025.06.26 View 1890 -
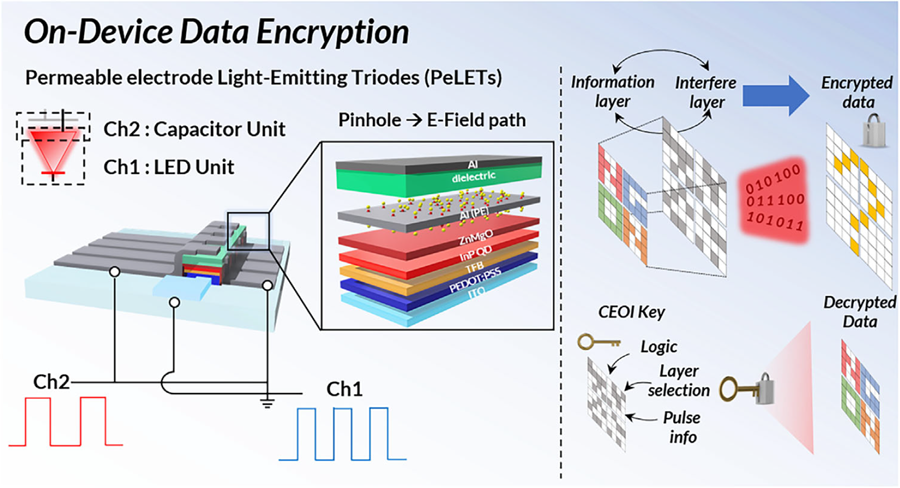 KAIST's Li-Fi - Achieves 100 Times Faster Speed and Enhanced Security of Wi-Fi
- KAIST-KRISS Develop 'On-Device Encryption Optical Transmitter' Based on Eco-Friendly Quantum Dots
- New Li-Fi Platform Technology Achieves High Performance with 17.4% Device Efficiency and 29,000 nit Brightness, Simultaneously Improving Transmission Speed and Security
- Presents New Methodology for High-Speed and Encrypted Communication Through Single-Device-Based Dual-Channel Optical Modulation
< Photo 1. (Front row from left) Seungmin Shin, First Author; Professor Himchan Cho; (Back row from left) Hyungdoh Lee, Seungwoo Lee, Wonbeom Lee; (Top left) Dr. Kyung-geun Lim >
Li-Fi (Light Fidelity) is a wireless communication technology that utilizes the visible light spectrum (400-800 THz), similar to LED light, offering speeds up to 100 times faster than existing Wi-Fi (up to 224 Gbps). While it has fewer limitations in available frequency allocation and less radio interference, it is relatively vulnerable to security breaches as anyone can access it. Korean researchers have now proposed a new Li-Fi platform that overcomes the limitations of conventional optical communication devices and can simultaneously enhance both transmission speed and security.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 24th that Professor Himchan Cho's research team from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, in collaboration with Dr. Kyung-geun Lim of the Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science (KRISS, President Ho-Seong Lee) under the National Research Council of Science & Technology (NST, Chairman Young-Sik Kim), has developed 'on-device encryption optical communication device' technology for the utilization of 'Li-Fi,' which is attracting attention as a next-generation ultra-high-speed data communication.
Professor Cho's team created high-efficiency light-emitting triode devices using eco-friendly quantum dots (low-toxicity and sustainable materials). The device developed by the research team is a mechanism that generates light using an electric field. Specifically, the electric field is concentrated in 'tiny holes (pinholes) in the permeable electrode' and transmitted beyond the electrode. This device utilizes this principle to simultaneously process two input data streams.
Using this principle, the research team developed a technology called 'on-device encryption optical transmitter.' The core of this technology is that the device itself converts information into light and simultaneously encrypts it. This means that enhanced security data transmission is possible without the need for complex, separate equipment.
External Quantum Efficiency (EQE) is an indicator of how efficiently electricity is converted into light, with a general commercialization standard of about 20%. The newly developed device recorded an EQE of 17.4%, and its luminance was 29,000 nit, significantly exceeding the maximum brightness of a smartphone OLED screen, which is 2,000 nit, demonstrating a brightness more than 10 times higher.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the device structure developed by the research team and encrypted communication >
Furthermore, to more accurately understand how this device converts information into light, the research team used a method called 'transient electroluminescence analysis.' They analyzed the light-emitting characteristics generated by the device when voltage was instantaneously applied for very short durations (hundreds of nanoseconds = billionths of a second). Through this analysis, they investigated the movement of charges within the device at hundreds of nanoseconds, elucidating the operating mechanism of dual-channel optical modulation implemented within a single device.
Professor Himchan Cho of KAIST stated, "This research overcomes the limitations of existing optical communication devices and proposes a new communication platform that can both increase transmission speed and enhance security."
< Photo 2. Professor Himchan Cho, Department of Materials Science and Engineering >
He added, "This technology, which strengthens security without additional equipment and simultaneously enables encryption and transmission, can be widely applied in various fields where security is crucial in the future."
This research, with Seungmin Shin, a Ph.D. candidate at KAIST's Department of Materials Science and Engineering, participating as the first author, and Professor Himchan Cho and Dr. Kyung-geun Lim of KRISS as co-corresponding authors, was published in the international journal 'Advanced Materials' on May 30th and was selected as an inside front cover paper.※ Paper Title: High-Efficiency Quantum Dot Permeable electrode Light-Emitting Triodes for Visible-Light Communications and On-Device Data Encryption※ DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202503189
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea, the National Research Council of Science & Technology (NST), and the Korea Institute for Advancement of Technology.
2025.06.24 View 1987
KAIST's Li-Fi - Achieves 100 Times Faster Speed and Enhanced Security of Wi-Fi
- KAIST-KRISS Develop 'On-Device Encryption Optical Transmitter' Based on Eco-Friendly Quantum Dots
- New Li-Fi Platform Technology Achieves High Performance with 17.4% Device Efficiency and 29,000 nit Brightness, Simultaneously Improving Transmission Speed and Security
- Presents New Methodology for High-Speed and Encrypted Communication Through Single-Device-Based Dual-Channel Optical Modulation
< Photo 1. (Front row from left) Seungmin Shin, First Author; Professor Himchan Cho; (Back row from left) Hyungdoh Lee, Seungwoo Lee, Wonbeom Lee; (Top left) Dr. Kyung-geun Lim >
Li-Fi (Light Fidelity) is a wireless communication technology that utilizes the visible light spectrum (400-800 THz), similar to LED light, offering speeds up to 100 times faster than existing Wi-Fi (up to 224 Gbps). While it has fewer limitations in available frequency allocation and less radio interference, it is relatively vulnerable to security breaches as anyone can access it. Korean researchers have now proposed a new Li-Fi platform that overcomes the limitations of conventional optical communication devices and can simultaneously enhance both transmission speed and security.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 24th that Professor Himchan Cho's research team from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, in collaboration with Dr. Kyung-geun Lim of the Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science (KRISS, President Ho-Seong Lee) under the National Research Council of Science & Technology (NST, Chairman Young-Sik Kim), has developed 'on-device encryption optical communication device' technology for the utilization of 'Li-Fi,' which is attracting attention as a next-generation ultra-high-speed data communication.
Professor Cho's team created high-efficiency light-emitting triode devices using eco-friendly quantum dots (low-toxicity and sustainable materials). The device developed by the research team is a mechanism that generates light using an electric field. Specifically, the electric field is concentrated in 'tiny holes (pinholes) in the permeable electrode' and transmitted beyond the electrode. This device utilizes this principle to simultaneously process two input data streams.
Using this principle, the research team developed a technology called 'on-device encryption optical transmitter.' The core of this technology is that the device itself converts information into light and simultaneously encrypts it. This means that enhanced security data transmission is possible without the need for complex, separate equipment.
External Quantum Efficiency (EQE) is an indicator of how efficiently electricity is converted into light, with a general commercialization standard of about 20%. The newly developed device recorded an EQE of 17.4%, and its luminance was 29,000 nit, significantly exceeding the maximum brightness of a smartphone OLED screen, which is 2,000 nit, demonstrating a brightness more than 10 times higher.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the device structure developed by the research team and encrypted communication >
Furthermore, to more accurately understand how this device converts information into light, the research team used a method called 'transient electroluminescence analysis.' They analyzed the light-emitting characteristics generated by the device when voltage was instantaneously applied for very short durations (hundreds of nanoseconds = billionths of a second). Through this analysis, they investigated the movement of charges within the device at hundreds of nanoseconds, elucidating the operating mechanism of dual-channel optical modulation implemented within a single device.
Professor Himchan Cho of KAIST stated, "This research overcomes the limitations of existing optical communication devices and proposes a new communication platform that can both increase transmission speed and enhance security."
< Photo 2. Professor Himchan Cho, Department of Materials Science and Engineering >
He added, "This technology, which strengthens security without additional equipment and simultaneously enables encryption and transmission, can be widely applied in various fields where security is crucial in the future."
This research, with Seungmin Shin, a Ph.D. candidate at KAIST's Department of Materials Science and Engineering, participating as the first author, and Professor Himchan Cho and Dr. Kyung-geun Lim of KRISS as co-corresponding authors, was published in the international journal 'Advanced Materials' on May 30th and was selected as an inside front cover paper.※ Paper Title: High-Efficiency Quantum Dot Permeable electrode Light-Emitting Triodes for Visible-Light Communications and On-Device Data Encryption※ DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202503189
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea, the National Research Council of Science & Technology (NST), and the Korea Institute for Advancement of Technology.
2025.06.24 View 1987 -
 KAIST to Lead the Way in Nurturing Talent and Driving S&T Innovation for a G3 AI Powerhouse
* Focusing on nurturing talent and dedicating to R&D to become a G3 AI powerhouse (Top 3 AI Nations).
* Leading the realization of an "AI-driven Basic Society for All" and developing technologies that leverage AI to overcome the crisis in Korea's manufacturing sector.
* 50 years ago, South Korea emerged as a scientific and technological powerhouse from the ashes, with KAIST at its core, contributing to the development of scientific and technological talent, innovative technology, national industrial growth, and the creation of a startup innovation ecosystem.
As public interest in AI and science and technology has significantly grown with the inauguration of the new government, KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced its plan, on June 24th, to transform into an "AI-centric, Value-Creating Science and Technology University" that leads national innovation based on science and technology and spearheads solutions to global challenges.
At a time when South Korea is undergoing a major transition to a technology-driven society, KAIST, drawing on its half-century of experience as a "Starter Kit" for national development, is preparing to leap beyond being a mere educational and research institution to become a global innovation hub that creates new social value.
In particular, KAIST has presented a vision for realizing an "AI-driven Basic Society" where all citizens can utilize AI without alienation, enabling South Korea to ascend to the top three AI nations (G3). To achieve this, through the "National AI Research Hub" project (headed by Kee Eung Kim), led by KAIST representing South Korea, the institution is dedicated to enhancing industrial competitiveness and effectively solving social problems based on AI technology.
< KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee >
KAIST's research achievements in the AI field are garnering international attention. In the top three machine learning conferences (ICML, NeurIPS, ICLR), KAIST ranked 5th globally and 1st in Asia over the past five years (2020-2024). During the same period, based on the number of papers published in top conferences in machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision (ICML, NeurIPS, ICLR, ACL, EMNLP, NAACL, CVPR, ICCV, ECCV), KAIST ranked 5th globally and 4th in Asia. Furthermore, KAIST has consistently demonstrated unparalleled research capabilities, ranking 1st globally in the average number of papers accepted at ISSCC (International Solid-State Circuits Conference), the world's most prestigious academic conference on semiconductor integrated circuits, for 19 years (2006-2024).
KAIST is continuously expanding its research into core AI technologies, including hyper-scale AI models (Korean LLM), neuromorphic semiconductors, and low-power AI processors, as well as various application areas such as autonomous driving, urban air mobility (UAM), precision medicine, and explainable AI (XAI).
In the manufacturing sector, KAIST's AI technologies are also driving on-site innovation. Professor Young Jae Jang's team has enhanced productivity in advanced manufacturing fields like semiconductors and displays through digital twins utilizing manufacturing site data and AI-based prediction technology. Professor Song Min Kim's team developed ultra-low power wireless tag technology capable of tracking locations with sub-centimeter precision, accelerating the implementation of smart factories. Technologies such as industrial process optimization and equipment failure prediction developed by INEEJI Co., Ltd., founded by Professor Jaesik Choi, are being rapidly applied in real industrial settings, yielding results. INEEJI was designated as a national strategic technology in the 'Explainable AI (XAI)' field by the government in March.
< Researchers performing data analysis for AI research >
Practical applications are also emerging in the robotics sector, which is closely linked to AI. Professor Jemin Hwangbo's team from the Department of Mechanical Engineering garnered attention by newly developing RAIBO 2, a quadrupedal robot usable in high-risk environments such as disaster relief and rough terrain exploration. Professor Kyoung Chul Kong's team and Angel Robotics Co., Ltd. developed the WalkOn Suit exoskeleton robot, significantly improving the quality of life for individuals with complete lower body paralysis or walking disabilities.
Additionally, remarkable research is ongoing in future core technology areas such as AI semiconductors, quantum cryptography communication, ultra-small satellites, hydrogen fuel cells, next-generation batteries, and biomimetic sensors. Notably, space exploration technology based on small satellites, asteroid exploration projects, energy harvesting, and high-speed charging technologies are gaining attention.
Particularly in advanced bio and life sciences, KAIST is collaborating with Germany's Merck company on various research initiatives, including synthetic biology and mRNA. KAIST is also contributing to the construction of a 430 billion won Merck Bio-Center in Daejeon, thereby stimulating the local economy and creating jobs.
Based on these cutting-edge research capabilities, KAIST continues to expand its influence not only within the industry but also on the global stage. It has established strategic partnerships with leading universities worldwide, including MIT, Stanford University, and New York University (NYU). Notably, KAIST and NYU have established a joint campus in New York to strengthen human exchange and collaborative research. Active industry-academia collaborations with global companies such as Google, Intel, and TSMC are also ongoing, playing a pivotal role in future technology development and the creation of an innovation ecosystem.
These activities also lead to a strong startup ecosystem that drives South Korean industries. The flow of startups, which began with companies like Qnix Computer, Nexon, and Naver, has expanded to a total of 1,914 companies to date. Their cumulative assets amount to 94 trillion won, with sales reaching 36 trillion won and employing approximately 60,000 people. Over 90% of these are technology-based startups originating from faculty and student labs, demonstrating a model that makes a tangible economic contribution based on science and technology.
< Students at work >
Having consistently generated diverse achievements, KAIST has already produced approximately 80,000 "KAISTians" who have created innovation through challenge and failure, and is currently recruiting new talent to continue driving innovation that transforms South Korea and the world.
President Kwang Hyung Lee emphasized, "KAIST will establish itself as a global leader in science and technology, designing the future of South Korea and humanity and creating tangible value." He added, "We will focus on talent nurturing and research and development to realize the new government's national agenda of becoming a G3 AI powerhouse."
He further stated, "KAIST's vision for the AI field, in which it places particular emphasis, is to strive for a society where everyone can freely utilize AI. We will contribute to significantly boosting productivity by recovering manufacturing competitiveness through AI and actively disseminating physical AI, AI robots, and AI mobility technologies to industrial sites."
2025.06.24 View 1525
KAIST to Lead the Way in Nurturing Talent and Driving S&T Innovation for a G3 AI Powerhouse
* Focusing on nurturing talent and dedicating to R&D to become a G3 AI powerhouse (Top 3 AI Nations).
* Leading the realization of an "AI-driven Basic Society for All" and developing technologies that leverage AI to overcome the crisis in Korea's manufacturing sector.
* 50 years ago, South Korea emerged as a scientific and technological powerhouse from the ashes, with KAIST at its core, contributing to the development of scientific and technological talent, innovative technology, national industrial growth, and the creation of a startup innovation ecosystem.
As public interest in AI and science and technology has significantly grown with the inauguration of the new government, KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced its plan, on June 24th, to transform into an "AI-centric, Value-Creating Science and Technology University" that leads national innovation based on science and technology and spearheads solutions to global challenges.
At a time when South Korea is undergoing a major transition to a technology-driven society, KAIST, drawing on its half-century of experience as a "Starter Kit" for national development, is preparing to leap beyond being a mere educational and research institution to become a global innovation hub that creates new social value.
In particular, KAIST has presented a vision for realizing an "AI-driven Basic Society" where all citizens can utilize AI without alienation, enabling South Korea to ascend to the top three AI nations (G3). To achieve this, through the "National AI Research Hub" project (headed by Kee Eung Kim), led by KAIST representing South Korea, the institution is dedicated to enhancing industrial competitiveness and effectively solving social problems based on AI technology.
< KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee >
KAIST's research achievements in the AI field are garnering international attention. In the top three machine learning conferences (ICML, NeurIPS, ICLR), KAIST ranked 5th globally and 1st in Asia over the past five years (2020-2024). During the same period, based on the number of papers published in top conferences in machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision (ICML, NeurIPS, ICLR, ACL, EMNLP, NAACL, CVPR, ICCV, ECCV), KAIST ranked 5th globally and 4th in Asia. Furthermore, KAIST has consistently demonstrated unparalleled research capabilities, ranking 1st globally in the average number of papers accepted at ISSCC (International Solid-State Circuits Conference), the world's most prestigious academic conference on semiconductor integrated circuits, for 19 years (2006-2024).
KAIST is continuously expanding its research into core AI technologies, including hyper-scale AI models (Korean LLM), neuromorphic semiconductors, and low-power AI processors, as well as various application areas such as autonomous driving, urban air mobility (UAM), precision medicine, and explainable AI (XAI).
In the manufacturing sector, KAIST's AI technologies are also driving on-site innovation. Professor Young Jae Jang's team has enhanced productivity in advanced manufacturing fields like semiconductors and displays through digital twins utilizing manufacturing site data and AI-based prediction technology. Professor Song Min Kim's team developed ultra-low power wireless tag technology capable of tracking locations with sub-centimeter precision, accelerating the implementation of smart factories. Technologies such as industrial process optimization and equipment failure prediction developed by INEEJI Co., Ltd., founded by Professor Jaesik Choi, are being rapidly applied in real industrial settings, yielding results. INEEJI was designated as a national strategic technology in the 'Explainable AI (XAI)' field by the government in March.
< Researchers performing data analysis for AI research >
Practical applications are also emerging in the robotics sector, which is closely linked to AI. Professor Jemin Hwangbo's team from the Department of Mechanical Engineering garnered attention by newly developing RAIBO 2, a quadrupedal robot usable in high-risk environments such as disaster relief and rough terrain exploration. Professor Kyoung Chul Kong's team and Angel Robotics Co., Ltd. developed the WalkOn Suit exoskeleton robot, significantly improving the quality of life for individuals with complete lower body paralysis or walking disabilities.
Additionally, remarkable research is ongoing in future core technology areas such as AI semiconductors, quantum cryptography communication, ultra-small satellites, hydrogen fuel cells, next-generation batteries, and biomimetic sensors. Notably, space exploration technology based on small satellites, asteroid exploration projects, energy harvesting, and high-speed charging technologies are gaining attention.
Particularly in advanced bio and life sciences, KAIST is collaborating with Germany's Merck company on various research initiatives, including synthetic biology and mRNA. KAIST is also contributing to the construction of a 430 billion won Merck Bio-Center in Daejeon, thereby stimulating the local economy and creating jobs.
Based on these cutting-edge research capabilities, KAIST continues to expand its influence not only within the industry but also on the global stage. It has established strategic partnerships with leading universities worldwide, including MIT, Stanford University, and New York University (NYU). Notably, KAIST and NYU have established a joint campus in New York to strengthen human exchange and collaborative research. Active industry-academia collaborations with global companies such as Google, Intel, and TSMC are also ongoing, playing a pivotal role in future technology development and the creation of an innovation ecosystem.
These activities also lead to a strong startup ecosystem that drives South Korean industries. The flow of startups, which began with companies like Qnix Computer, Nexon, and Naver, has expanded to a total of 1,914 companies to date. Their cumulative assets amount to 94 trillion won, with sales reaching 36 trillion won and employing approximately 60,000 people. Over 90% of these are technology-based startups originating from faculty and student labs, demonstrating a model that makes a tangible economic contribution based on science and technology.
< Students at work >
Having consistently generated diverse achievements, KAIST has already produced approximately 80,000 "KAISTians" who have created innovation through challenge and failure, and is currently recruiting new talent to continue driving innovation that transforms South Korea and the world.
President Kwang Hyung Lee emphasized, "KAIST will establish itself as a global leader in science and technology, designing the future of South Korea and humanity and creating tangible value." He added, "We will focus on talent nurturing and research and development to realize the new government's national agenda of becoming a G3 AI powerhouse."
He further stated, "KAIST's vision for the AI field, in which it places particular emphasis, is to strive for a society where everyone can freely utilize AI. We will contribute to significantly boosting productivity by recovering manufacturing competitiveness through AI and actively disseminating physical AI, AI robots, and AI mobility technologies to industrial sites."
2025.06.24 View 1525 -
 Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee Wins 2025 Global Metabolic Engineering Award
< Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee (Senior Vice President for Research) from the Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering >
KAIST announced on the 20th that Professor Sang Yup Lee, who serves as the Vice President for Research and a Distinguished Professor at our university, has been awarded the '2025 Gregory N. Stephanopoulos Award for Metabolic Engineering' by the International Metabolic Engineering Society (IMES). Professor Lee delivered his award lecture at the 16th Metabolic Engineering Conference (ME16), held in Copenhagen, Denmark, from June 15th to 19th.
This award was established through contributions from the American Institute of Chemical Engineers (AIChE) Foundation, as well as fellow colleagues and acquaintances, to honor the achievements of Dr. Gregory Stephanopoulos, widely recognized as one of the pioneers of metabolic engineering. Presented biennially, the award recognizes scientists who have successfully commercialized fundamental research in metabolic engineering or have made outstanding contributions to the quantitative analysis, design, and modeling of metabolic pathways.
Professor Sang Yup Lee boasts an impressive record of over 770 journal papers and more than 860 patents. His groundbreaking research in metabolic engineering and biochemical engineering is highly acclaimed globally.
Throughout his 31 years as a professor at KAIST, Professor Lee has developed various metabolic engineering-based technologies and strategies. These advancements have been transferred to industries, facilitating the production of bulk chemicals, polymers, natural products, pharmaceuticals, and health functional foods. He has also founded companies and actively engages in advisory roles with various enterprises.
The International Metabolic Engineering Society (IMES) defines metabolic engineering as the manipulation of metabolic pathways in microorganisms or cells to produce useful substances (such as pharmaceuticals, biofuels, and chemical products). It utilizes tools like systems biology, synthetic biology, and computational modeling with the aim of enhancing the economic viability and sustainability of bio-based processes.
Furthermore, Professor Lee previously received the Merck Metabolic Engineering Award, a prominent international award in the field, in 2008. In 2018, he was honored with the Eni Award, often referred to as the Nobel Prize in energy, presented by the President of Italy.
Professor Sang Yup Lee remarked, "Metabolic engineering is a discipline that leads the current and future of biotechnology. It is a tremendous honor to receive this meaningful award at a time when the transition to a bio-based economy is accelerating. Together with my students and fellow researchers, we have generated numerous patents and transferred technologies to industry, and also established startups in the fields of biofuels, wound healing, and cosmetics. I will continue to pursue research that encompasses both fundamental research and technological commercialization."
The 'International Metabolic Engineering Society (IMES)' is a specialized society under the American Institute of Chemical Engineers. Its mission is to enable the production of various bio-based products, including pharmaceuticals, food additives, chemicals, and fuels, through metabolic engineering. The society hosts the Metabolic Engineering Conference biennially, offering researchers opportunities for knowledge exchange and collaboration.
2025.06.20 View 1668
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee Wins 2025 Global Metabolic Engineering Award
< Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee (Senior Vice President for Research) from the Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering >
KAIST announced on the 20th that Professor Sang Yup Lee, who serves as the Vice President for Research and a Distinguished Professor at our university, has been awarded the '2025 Gregory N. Stephanopoulos Award for Metabolic Engineering' by the International Metabolic Engineering Society (IMES). Professor Lee delivered his award lecture at the 16th Metabolic Engineering Conference (ME16), held in Copenhagen, Denmark, from June 15th to 19th.
This award was established through contributions from the American Institute of Chemical Engineers (AIChE) Foundation, as well as fellow colleagues and acquaintances, to honor the achievements of Dr. Gregory Stephanopoulos, widely recognized as one of the pioneers of metabolic engineering. Presented biennially, the award recognizes scientists who have successfully commercialized fundamental research in metabolic engineering or have made outstanding contributions to the quantitative analysis, design, and modeling of metabolic pathways.
Professor Sang Yup Lee boasts an impressive record of over 770 journal papers and more than 860 patents. His groundbreaking research in metabolic engineering and biochemical engineering is highly acclaimed globally.
Throughout his 31 years as a professor at KAIST, Professor Lee has developed various metabolic engineering-based technologies and strategies. These advancements have been transferred to industries, facilitating the production of bulk chemicals, polymers, natural products, pharmaceuticals, and health functional foods. He has also founded companies and actively engages in advisory roles with various enterprises.
The International Metabolic Engineering Society (IMES) defines metabolic engineering as the manipulation of metabolic pathways in microorganisms or cells to produce useful substances (such as pharmaceuticals, biofuels, and chemical products). It utilizes tools like systems biology, synthetic biology, and computational modeling with the aim of enhancing the economic viability and sustainability of bio-based processes.
Furthermore, Professor Lee previously received the Merck Metabolic Engineering Award, a prominent international award in the field, in 2008. In 2018, he was honored with the Eni Award, often referred to as the Nobel Prize in energy, presented by the President of Italy.
Professor Sang Yup Lee remarked, "Metabolic engineering is a discipline that leads the current and future of biotechnology. It is a tremendous honor to receive this meaningful award at a time when the transition to a bio-based economy is accelerating. Together with my students and fellow researchers, we have generated numerous patents and transferred technologies to industry, and also established startups in the fields of biofuels, wound healing, and cosmetics. I will continue to pursue research that encompasses both fundamental research and technological commercialization."
The 'International Metabolic Engineering Society (IMES)' is a specialized society under the American Institute of Chemical Engineers. Its mission is to enable the production of various bio-based products, including pharmaceuticals, food additives, chemicals, and fuels, through metabolic engineering. The society hosts the Metabolic Engineering Conference biennially, offering researchers opportunities for knowledge exchange and collaboration.
2025.06.20 View 1668 -
 KAIST Develops Glare-Free, Heat-Blocking 'Smart Window'... Applicable to Buildings and Vehicles
• Professor Hong Chul Moon of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering develops RECM, a next-generation smart window technology, expecting cooling energy savings and effective indoor thermal management.
• When using the developed RECM, a significantly superior temperature reduction effect is observed compared to conventional windows.
• With a 'pedestrian-friendly smart window' design that eliminates glare by suppressing external reflections, it is expected to be adapted in architectural structures, transportation, and more.
< (From left) First author Hoy Jung Jo, Professor Hong Chul Moon >
In the building sector, which accounts for approximately 40% of global energy consumption, heat ingress through windows has been identified as a primary cause of wasted heating and cooling energy. Our research team has successfully developed a 'pedestrian-friendly smart window' technology capable of not only reducing heating and cooling energy in urban buildings but also resolving the persistent issue of 'light pollution' in urban living.
On the 17th of June, Professor Hong Chul Moon's research team at KAIST's Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering announced the development of a 'smart window technology' that allows users to control the light and heat entering through windows according to their intent, and effectively neutralize glare from external sources.
Recently, 'active smart window' technology, which enables free adjustment of light and heat based on user operation, has garnered significant attention. Unlike conventional windows that passively react to changes in temperature or light, this is a next-generation window system that can be controlled in real-time via electrical signals.
The next-generation smart window technology developed by the research team, RECM (Reversible Electrodeposition and Electrochromic Mirror), is a smart window system based on a single-structured *electrochromic device that can actively control the transmittance of visible light and near-infrared (heat).
*Electrochromic device: A device whose optical properties change in response to an electrical signal.
In particular, by effectively suppressing the glare phenomenon caused by external reflected light—a problem previously identified in traditional metal *deposition smart windows—through the combined application of electrochromic materials, a 'pedestrian-friendly smart window' suitable for building facades has been realized.
*Deposition: A process involving the electrochemical reaction to coat metal ions, such as Ag+, onto an electrode surface in solid form.
The RECM system developed in this study operates in three modes depending on voltage control.
Mode I (Transparent Mode) is advantageous for allowing sunlight to enter the indoor space during winter, as it transmits both light and heat like ordinary glass.
In Mode II (Colored Mode), *Prussian Blue (PB) and **DHV+• chemical species are formed through a redox (oxidation-reduction) reaction, causing the window to turn a deep blue color. In this state, light is absorbed, and only a portion of the heat is transmitted, allowing for privacy while enabling appropriate indoor temperature control.
*Prussian Blue: An electrochromic material that transitions between colorless and blue upon electrical stimulation.
**DHV+•: A radical state colored molecule generated upon electrical stimulation.
Mode III (Colored and Deposition Mode) involves the reduction and deposition of silver (Ag+) ions on the electrode surface, reflecting both light and heat. Concurrently, the colored material absorbs the reflected light, effectively blocking glare for external pedestrians.
The research team validated the practical indoor temperature reduction effect of the RECM technology through experiments utilizing a miniature model house. When a conventional glass window was installed, the indoor temperature rose to 58.7°C within 45 minutes. Conversely, when RECM was operated in Mode III, the temperature reached 31.5°C, demonstrating a temperature reduction effect of approximately 27.2°C.
Furthermore, since each state transition is achievable solely by electrical signals, it is regarded as an active smart technology capable of instantaneous response according to season, time, and intended use.
< Figure 1. Operation mechanism of the RECM smart window. The RECM system can switch among three states—transparent, colored, and colored & deposition—via electrical stimulation. At -1.6 V, DHV•+ and Prussian Blue (PB) are formed, blocking visible light to provide privacy protection and heat blocking. At -2.0 V, silver (Ag) is deposited on the electrode surface, reflecting light and heat, while DHV•+ and Prussian Blue absorb reflected light, effectively suppressing external glare. Through this mechanism, it functions as an active smart window that simultaneously controls light, heat, and glare. >
Professor Hong Chul Moon of KAIST, the corresponding author of this study, stated, "This research goes beyond existing smart window technologies limited to visible light control, presenting a truly smart window platform that comprehensively considers not only active indoor thermal control but also the visual safety of pedestrians." He added, "Various applications are anticipated, from urban buildings to vehicles and trains."
< Figure 2. Analysis of glare suppression effect of conventional reflective smart windows and RECM. This figure presents the results comparing the glare phenomenon occurring during silver (Ag) deposition between conventional reflective smart windows and RECM Mode III. Conventional reflective devices resulted in strong reflected light on the desk surface due to their high reflectivity. In contrast, RECM Mode III, where the colored material absorbed reflected light, showed a 33% reduction in reflected light intensity, and no reflected light was observed from outside. This highlights the RECM system's distinctiveness and practicality as a 'pedestrian-friendly smart window' optimized for dense urban environments, extending beyond just heat blocking. >
The findings of this research were published on June 13, 2025, in Volume 10, Issue 6 of 'ACS Energy Letters'. The listed authors for this publication are Hoy Jung Jo, Yeon Jae Jang, Hyeon-Don Kim, Kwang-Seop Kim, and Hong Chul Moon.
※ Paper Title: Glare-Free, Energy-Efficient Smart Windows: A Pedestrian-Friendly System with Dynamically Tunable Light and Heat Regulation
※ DOI: 10.1021/acsenergylett.5c00637
< Figure 3. Temperature reduction performance verification in a miniature model house. The actual heat blocking effect was evaluated by applying RECM devices to a model building. Under identical conditions, the indoor temperature with ordinary glass rose to 58.7°C, whereas with RECM in Mode III, it reached 31.5°C, demonstrating a maximum temperature reduction effect of 27.2°C. The indoor temperature difference was also visually confirmed through thermal images, which proves the potential for indoor temperature control in urban buildings. >
This research was supported by the Nano & Material Technology Development Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the internal research program of the Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials.
2025.06.20 View 3578
KAIST Develops Glare-Free, Heat-Blocking 'Smart Window'... Applicable to Buildings and Vehicles
• Professor Hong Chul Moon of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering develops RECM, a next-generation smart window technology, expecting cooling energy savings and effective indoor thermal management.
• When using the developed RECM, a significantly superior temperature reduction effect is observed compared to conventional windows.
• With a 'pedestrian-friendly smart window' design that eliminates glare by suppressing external reflections, it is expected to be adapted in architectural structures, transportation, and more.
< (From left) First author Hoy Jung Jo, Professor Hong Chul Moon >
In the building sector, which accounts for approximately 40% of global energy consumption, heat ingress through windows has been identified as a primary cause of wasted heating and cooling energy. Our research team has successfully developed a 'pedestrian-friendly smart window' technology capable of not only reducing heating and cooling energy in urban buildings but also resolving the persistent issue of 'light pollution' in urban living.
On the 17th of June, Professor Hong Chul Moon's research team at KAIST's Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering announced the development of a 'smart window technology' that allows users to control the light and heat entering through windows according to their intent, and effectively neutralize glare from external sources.
Recently, 'active smart window' technology, which enables free adjustment of light and heat based on user operation, has garnered significant attention. Unlike conventional windows that passively react to changes in temperature or light, this is a next-generation window system that can be controlled in real-time via electrical signals.
The next-generation smart window technology developed by the research team, RECM (Reversible Electrodeposition and Electrochromic Mirror), is a smart window system based on a single-structured *electrochromic device that can actively control the transmittance of visible light and near-infrared (heat).
*Electrochromic device: A device whose optical properties change in response to an electrical signal.
In particular, by effectively suppressing the glare phenomenon caused by external reflected light—a problem previously identified in traditional metal *deposition smart windows—through the combined application of electrochromic materials, a 'pedestrian-friendly smart window' suitable for building facades has been realized.
*Deposition: A process involving the electrochemical reaction to coat metal ions, such as Ag+, onto an electrode surface in solid form.
The RECM system developed in this study operates in three modes depending on voltage control.
Mode I (Transparent Mode) is advantageous for allowing sunlight to enter the indoor space during winter, as it transmits both light and heat like ordinary glass.
In Mode II (Colored Mode), *Prussian Blue (PB) and **DHV+• chemical species are formed through a redox (oxidation-reduction) reaction, causing the window to turn a deep blue color. In this state, light is absorbed, and only a portion of the heat is transmitted, allowing for privacy while enabling appropriate indoor temperature control.
*Prussian Blue: An electrochromic material that transitions between colorless and blue upon electrical stimulation.
**DHV+•: A radical state colored molecule generated upon electrical stimulation.
Mode III (Colored and Deposition Mode) involves the reduction and deposition of silver (Ag+) ions on the electrode surface, reflecting both light and heat. Concurrently, the colored material absorbs the reflected light, effectively blocking glare for external pedestrians.
The research team validated the practical indoor temperature reduction effect of the RECM technology through experiments utilizing a miniature model house. When a conventional glass window was installed, the indoor temperature rose to 58.7°C within 45 minutes. Conversely, when RECM was operated in Mode III, the temperature reached 31.5°C, demonstrating a temperature reduction effect of approximately 27.2°C.
Furthermore, since each state transition is achievable solely by electrical signals, it is regarded as an active smart technology capable of instantaneous response according to season, time, and intended use.
< Figure 1. Operation mechanism of the RECM smart window. The RECM system can switch among three states—transparent, colored, and colored & deposition—via electrical stimulation. At -1.6 V, DHV•+ and Prussian Blue (PB) are formed, blocking visible light to provide privacy protection and heat blocking. At -2.0 V, silver (Ag) is deposited on the electrode surface, reflecting light and heat, while DHV•+ and Prussian Blue absorb reflected light, effectively suppressing external glare. Through this mechanism, it functions as an active smart window that simultaneously controls light, heat, and glare. >
Professor Hong Chul Moon of KAIST, the corresponding author of this study, stated, "This research goes beyond existing smart window technologies limited to visible light control, presenting a truly smart window platform that comprehensively considers not only active indoor thermal control but also the visual safety of pedestrians." He added, "Various applications are anticipated, from urban buildings to vehicles and trains."
< Figure 2. Analysis of glare suppression effect of conventional reflective smart windows and RECM. This figure presents the results comparing the glare phenomenon occurring during silver (Ag) deposition between conventional reflective smart windows and RECM Mode III. Conventional reflective devices resulted in strong reflected light on the desk surface due to their high reflectivity. In contrast, RECM Mode III, where the colored material absorbed reflected light, showed a 33% reduction in reflected light intensity, and no reflected light was observed from outside. This highlights the RECM system's distinctiveness and practicality as a 'pedestrian-friendly smart window' optimized for dense urban environments, extending beyond just heat blocking. >
The findings of this research were published on June 13, 2025, in Volume 10, Issue 6 of 'ACS Energy Letters'. The listed authors for this publication are Hoy Jung Jo, Yeon Jae Jang, Hyeon-Don Kim, Kwang-Seop Kim, and Hong Chul Moon.
※ Paper Title: Glare-Free, Energy-Efficient Smart Windows: A Pedestrian-Friendly System with Dynamically Tunable Light and Heat Regulation
※ DOI: 10.1021/acsenergylett.5c00637
< Figure 3. Temperature reduction performance verification in a miniature model house. The actual heat blocking effect was evaluated by applying RECM devices to a model building. Under identical conditions, the indoor temperature with ordinary glass rose to 58.7°C, whereas with RECM in Mode III, it reached 31.5°C, demonstrating a maximum temperature reduction effect of 27.2°C. The indoor temperature difference was also visually confirmed through thermal images, which proves the potential for indoor temperature control in urban buildings. >
This research was supported by the Nano & Material Technology Development Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the internal research program of the Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials.
2025.06.20 View 3578 -
 ‘InnoCORE Research Group’ Launched to Lead AI Convergence Innovation
KAIST announced on the 16th of June that it has launched the ‘InnoCORE (Innovation-Core) Research Group,’ which will lead advanced strategic research in AI convergence (AI+S&T), in cooperation with the Ministry of Science and ICT (Minister Yoo Sang-im, hereinafter referred to as MSIT) and DGIST, GIST, and UNIST*. Through this, the group plans to actively recruit up to 200 world-class postdoctoral researchers.
DGIST (Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science & Technology), GIST (Gwangju Institute of Science & Technology), UNIST (Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology)
The ‘InnoCORE Research Group’ aims to foster core research personnel who will lead innovation in the field of AI convergence, focusing on nurturing and attracting high-level research talent in AI+Science & Technology. This is a strategic response to prevent brain drain of domestic talent and attract excellent overseas talent amidst the accelerating global competition for AI talent.
Through this initiative, our university plans to accelerate AI-based science and technology innovation and disseminate research achievements across industries and the economy by supporting top domestic and international postdoctoral researchers to dedicate themselves to developing AI convergence technologies in an advanced collaborative research environment.
The InnoCORE project for advanced AI+S&T convergence research and global talent attraction is jointly promoted by four science and technology institutes, including KAIST. It is structured around AI core technologies (such as hyper-scale language models, AI semiconductors) and AI convergence technologies (such as bio, manufacturing, energy, and aerospace).
As the leading institution, our university operates the following four research groups:
Hyper-scale Language Model Innovation Research Group: Advancement of LLM technology and research on generative AI, multimodal AI, and ensuring reliability.
AI-based Intelligent Design-Manufacturing Integration Research Group: Establishment of an AI platform for the entire lifecycle of the manufacturing industry and innovation in design and processes.
AI-Innovation Drug Research Group: Securing AI-based drug development technologies across the entire lifecycle and overcoming intractable diseases.
AI-Transformed Aerospace Research Group: AI transformation of aerospace systems throughout their lifecycle and development of new technologies such as autonomous flight and space communication.
< Poster on the InnoCORE Global Jobfair for Recruitment of Postdoctoral Researchers >
In addition, a total of eight research groups are formed to promote global collaborative convergence research, including those led by DGIST, GIST, and UNIST: ▲Bio-Integrated Physical AI, ▲Early Diagnosis of Brain Diseases AI+Nano Convergence, ▲Intelligent Hydrogen Technology Innovation, and ▲AI-Space Solar Power Research Group.
Starting in 2025, the four science and technology institutes, including KAIST, will officially begin recruiting 400 postdoctoral researchers in the AI+S&T fields. Selected postdoctoral researchers will be guaranteed high-level treatment with an annual salary of over 90 million KRW, and additional support through matching with companies and research projects is also planned.
In particular, global recruitment fairs will be held in major US regions to expand the attraction of excellent overseas talent. Local recruitment fairs will be held in Boston (Harvard, MIT), New York (NYU), and Silicon Valley (Stanford) in June, along with promotions through global academic journals such as Nature and Science, and LinkedIn.
KAIST plans to provide multiple mentor programs, global joint research opportunities, and excellent infrastructure (such as supercomputers, semiconductor fabs, and AI research platforms) within the research groups to enable postdoctoral researchers to collaborate with experts from various academic and industrial fields.
President Kwang Hyung Lee emphasized, “Through this InnoCORE project, KAIST will leap forward as a Global Hub for AI+S&T convergence research. Young researchers from around the world will challenge themselves and grow at KAIST, and our country will play a pivotal role in establishing itself as a leading nation in global AI convergence research and industry. To achieve this, we will spare no effort in providing the best research environment and active support.”
KAIST plans to actively pursue the InnoCORE project to secure global competitiveness in AI convergence research and contribute to the development of advanced industries. The eight selected research groups will finalize their detailed research plans by the end of June and commence full-scale research in July.
2025.06.19 View 2102
‘InnoCORE Research Group’ Launched to Lead AI Convergence Innovation
KAIST announced on the 16th of June that it has launched the ‘InnoCORE (Innovation-Core) Research Group,’ which will lead advanced strategic research in AI convergence (AI+S&T), in cooperation with the Ministry of Science and ICT (Minister Yoo Sang-im, hereinafter referred to as MSIT) and DGIST, GIST, and UNIST*. Through this, the group plans to actively recruit up to 200 world-class postdoctoral researchers.
DGIST (Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science & Technology), GIST (Gwangju Institute of Science & Technology), UNIST (Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology)
The ‘InnoCORE Research Group’ aims to foster core research personnel who will lead innovation in the field of AI convergence, focusing on nurturing and attracting high-level research talent in AI+Science & Technology. This is a strategic response to prevent brain drain of domestic talent and attract excellent overseas talent amidst the accelerating global competition for AI talent.
Through this initiative, our university plans to accelerate AI-based science and technology innovation and disseminate research achievements across industries and the economy by supporting top domestic and international postdoctoral researchers to dedicate themselves to developing AI convergence technologies in an advanced collaborative research environment.
The InnoCORE project for advanced AI+S&T convergence research and global talent attraction is jointly promoted by four science and technology institutes, including KAIST. It is structured around AI core technologies (such as hyper-scale language models, AI semiconductors) and AI convergence technologies (such as bio, manufacturing, energy, and aerospace).
As the leading institution, our university operates the following four research groups:
Hyper-scale Language Model Innovation Research Group: Advancement of LLM technology and research on generative AI, multimodal AI, and ensuring reliability.
AI-based Intelligent Design-Manufacturing Integration Research Group: Establishment of an AI platform for the entire lifecycle of the manufacturing industry and innovation in design and processes.
AI-Innovation Drug Research Group: Securing AI-based drug development technologies across the entire lifecycle and overcoming intractable diseases.
AI-Transformed Aerospace Research Group: AI transformation of aerospace systems throughout their lifecycle and development of new technologies such as autonomous flight and space communication.
< Poster on the InnoCORE Global Jobfair for Recruitment of Postdoctoral Researchers >
In addition, a total of eight research groups are formed to promote global collaborative convergence research, including those led by DGIST, GIST, and UNIST: ▲Bio-Integrated Physical AI, ▲Early Diagnosis of Brain Diseases AI+Nano Convergence, ▲Intelligent Hydrogen Technology Innovation, and ▲AI-Space Solar Power Research Group.
Starting in 2025, the four science and technology institutes, including KAIST, will officially begin recruiting 400 postdoctoral researchers in the AI+S&T fields. Selected postdoctoral researchers will be guaranteed high-level treatment with an annual salary of over 90 million KRW, and additional support through matching with companies and research projects is also planned.
In particular, global recruitment fairs will be held in major US regions to expand the attraction of excellent overseas talent. Local recruitment fairs will be held in Boston (Harvard, MIT), New York (NYU), and Silicon Valley (Stanford) in June, along with promotions through global academic journals such as Nature and Science, and LinkedIn.
KAIST plans to provide multiple mentor programs, global joint research opportunities, and excellent infrastructure (such as supercomputers, semiconductor fabs, and AI research platforms) within the research groups to enable postdoctoral researchers to collaborate with experts from various academic and industrial fields.
President Kwang Hyung Lee emphasized, “Through this InnoCORE project, KAIST will leap forward as a Global Hub for AI+S&T convergence research. Young researchers from around the world will challenge themselves and grow at KAIST, and our country will play a pivotal role in establishing itself as a leading nation in global AI convergence research and industry. To achieve this, we will spare no effort in providing the best research environment and active support.”
KAIST plans to actively pursue the InnoCORE project to secure global competitiveness in AI convergence research and contribute to the development of advanced industries. The eight selected research groups will finalize their detailed research plans by the end of June and commence full-scale research in July.
2025.06.19 View 2102