Ro
-
 Machine Learning-Based Algorithm to Speed up DNA Sequencing
The algorithm presents the first full-fledged, short-read alignment software that leverages learned indices for solving the exact match search problem for efficient seeding
The human genome consists of a complete set of DNA, which is about 6.4 billion letters long. Because of its size, reading the whole genome sequence at once is challenging. So scientists use DNA sequencers to produce hundreds of millions of DNA sequence fragments, or short reads, up to 300 letters long. Then the DNA sequencer assembles all the short reads like a giant jigsaw puzzle to reconstruct the entire genome sequence. Even with very fast computers, this job can take hours to complete.
A research team at KAIST has achieved up to 3.45x faster speeds by developing the first short-read alignment software that uses a recent advance in machine-learning called a learned index.
The research team reported their findings on March 7, 2022 in the journal Bioinformatics. The software has been released as open source and can be found on github (https://github.com/kaist-ina/BWA-MEME).
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) is a state-of-the-art DNA sequencing method. Projects are underway with the goal of producing genome sequencing at population scale. Modern NGS hardware is capable of generating billions of short reads in a single run. Then the short reads have to be aligned with the reference DNA sequence. With large-scale DNA sequencing operations running hundreds of next-generation sequences, the need for an efficient short read alignment tool has become even more critical. Accelerating the DNA sequence alignment would be a step toward achieving the goal of population-scale sequencing. However, existing algorithms are limited in their performance because of their frequent memory accesses.
BWA-MEM2 is a popular short-read alignment software package currently used to sequence the DNA. However, it has its limitations. The state-of-the-art alignment has two phases – seeding and extending. During the seeding phase, searches find exact matches of short reads in the reference DNA sequence. During the extending phase, the short reads from the seeding phase are extended. In the current process, bottlenecks occur in the seeding phase. Finding the exact matches slows the process.
The researchers set out to solve the problem of accelerating the DNA sequence alignment. To speed the process, they applied machine learning techniques to create an algorithmic improvement. Their algorithm, BWA-MEME (BWA-MEM emulated) leverages learned indices to solve the exact match search problem. The original software compared one character at a time for an exact match search. The team’s new algorithm achieves up to 3.45x faster speeds in seeding throughput over BWA-MEM2 by reducing the number of instructions by 4.60x and memory accesses by 8.77x. “Through this study, it has been shown that full genome big data analysis can be performed faster and less costly than conventional methods by applying machine learning technology,” said Professor Dongsu Han from the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST.
The researchers’ ultimate goal was to develop efficient software that scientists from academia and industry could use on a daily basis for analyzing big data in genomics. “With the recent advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning, we see so many opportunities for designing better software for genomic data analysis. The potential is there for accelerating existing analysis as well as enabling new types of analysis, and our goal is to develop such software,” added Han.
Whole genome sequencing has traditionally been used for discovering genomic mutations and identifying the root causes of diseases, which leads to the discovery and development of new drugs and cures. There could be many potential applications. Whole genome sequencing is used not only for research, but also for clinical purposes. “The science and technology for analyzing genomic data is making rapid progress to make it more accessible for scientists and patients. This will enhance our understanding about diseases and develop a better cure for patients of various diseases.”
The research was funded by the National Research Foundation of the Korean government’s Ministry of Science and ICT.
-PublicationYoungmok Jung, Dongsu Han, “BWA-MEME:BWA-MEM emulated with a machine learning approach,” Bioinformatics, Volume 38, Issue 9, May 2022
(https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac137)
-ProfileProfessor Dongsu HanSchool of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
2022.05.10 View 11087
Machine Learning-Based Algorithm to Speed up DNA Sequencing
The algorithm presents the first full-fledged, short-read alignment software that leverages learned indices for solving the exact match search problem for efficient seeding
The human genome consists of a complete set of DNA, which is about 6.4 billion letters long. Because of its size, reading the whole genome sequence at once is challenging. So scientists use DNA sequencers to produce hundreds of millions of DNA sequence fragments, or short reads, up to 300 letters long. Then the DNA sequencer assembles all the short reads like a giant jigsaw puzzle to reconstruct the entire genome sequence. Even with very fast computers, this job can take hours to complete.
A research team at KAIST has achieved up to 3.45x faster speeds by developing the first short-read alignment software that uses a recent advance in machine-learning called a learned index.
The research team reported their findings on March 7, 2022 in the journal Bioinformatics. The software has been released as open source and can be found on github (https://github.com/kaist-ina/BWA-MEME).
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) is a state-of-the-art DNA sequencing method. Projects are underway with the goal of producing genome sequencing at population scale. Modern NGS hardware is capable of generating billions of short reads in a single run. Then the short reads have to be aligned with the reference DNA sequence. With large-scale DNA sequencing operations running hundreds of next-generation sequences, the need for an efficient short read alignment tool has become even more critical. Accelerating the DNA sequence alignment would be a step toward achieving the goal of population-scale sequencing. However, existing algorithms are limited in their performance because of their frequent memory accesses.
BWA-MEM2 is a popular short-read alignment software package currently used to sequence the DNA. However, it has its limitations. The state-of-the-art alignment has two phases – seeding and extending. During the seeding phase, searches find exact matches of short reads in the reference DNA sequence. During the extending phase, the short reads from the seeding phase are extended. In the current process, bottlenecks occur in the seeding phase. Finding the exact matches slows the process.
The researchers set out to solve the problem of accelerating the DNA sequence alignment. To speed the process, they applied machine learning techniques to create an algorithmic improvement. Their algorithm, BWA-MEME (BWA-MEM emulated) leverages learned indices to solve the exact match search problem. The original software compared one character at a time for an exact match search. The team’s new algorithm achieves up to 3.45x faster speeds in seeding throughput over BWA-MEM2 by reducing the number of instructions by 4.60x and memory accesses by 8.77x. “Through this study, it has been shown that full genome big data analysis can be performed faster and less costly than conventional methods by applying machine learning technology,” said Professor Dongsu Han from the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST.
The researchers’ ultimate goal was to develop efficient software that scientists from academia and industry could use on a daily basis for analyzing big data in genomics. “With the recent advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning, we see so many opportunities for designing better software for genomic data analysis. The potential is there for accelerating existing analysis as well as enabling new types of analysis, and our goal is to develop such software,” added Han.
Whole genome sequencing has traditionally been used for discovering genomic mutations and identifying the root causes of diseases, which leads to the discovery and development of new drugs and cures. There could be many potential applications. Whole genome sequencing is used not only for research, but also for clinical purposes. “The science and technology for analyzing genomic data is making rapid progress to make it more accessible for scientists and patients. This will enhance our understanding about diseases and develop a better cure for patients of various diseases.”
The research was funded by the National Research Foundation of the Korean government’s Ministry of Science and ICT.
-PublicationYoungmok Jung, Dongsu Han, “BWA-MEME:BWA-MEM emulated with a machine learning approach,” Bioinformatics, Volume 38, Issue 9, May 2022
(https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac137)
-ProfileProfessor Dongsu HanSchool of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
2022.05.10 View 11087 -
 VP Sang Yup Lee Receives Honorary Doctorate from DTU
Vice President for Research, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee at the Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering, was awarded an honorary doctorate from the Technical University of Denmark (DTU) during the DTU Commemoration Day 2022 on April 29. The event drew distinguished guests, students, and faculty including HRH The Crown Prince Frederik Andre Henrik Christian and DTU President Anders Bjarklev.
Professor Lee was recognized for his exceptional scholarship in the field of systems metabolic engineering, which led to the development of microcell factories capable of producing a wide range of fuels, chemicals, materials, and natural compounds, many for the first time.
Professor Lee said in his acceptance speech that KAIST’s continued partnership with DTU in the field of biotechnology will lead to significant contributions in the global efforts to respond to climate change and promote green growth.
DTU CPO and CSO Dina Petronovic Nielson, who heads DTU Biosustain, also lauded Professor Lee saying, “It is not only a great honor for Professor Lee to be induced at DTU but also great honor for DTU to have him.”
Professor Lee also gave commemorative lectures at DTU Biosustain in Lingby and the Bio Innovation Research Institute at the Novo Nordisk Foundation in Copenhagen while in Denmark.
DTU, one of the leading science and technology universities in Europe, has been awarding honorary doctorates since 1921, including to Nobel laureate in chemistry Professor Frances Arnold at Caltech. Professor Lee is the first Korean to receive an honorary doctorate from DTU.
2022.05.03 View 12828
VP Sang Yup Lee Receives Honorary Doctorate from DTU
Vice President for Research, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee at the Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering, was awarded an honorary doctorate from the Technical University of Denmark (DTU) during the DTU Commemoration Day 2022 on April 29. The event drew distinguished guests, students, and faculty including HRH The Crown Prince Frederik Andre Henrik Christian and DTU President Anders Bjarklev.
Professor Lee was recognized for his exceptional scholarship in the field of systems metabolic engineering, which led to the development of microcell factories capable of producing a wide range of fuels, chemicals, materials, and natural compounds, many for the first time.
Professor Lee said in his acceptance speech that KAIST’s continued partnership with DTU in the field of biotechnology will lead to significant contributions in the global efforts to respond to climate change and promote green growth.
DTU CPO and CSO Dina Petronovic Nielson, who heads DTU Biosustain, also lauded Professor Lee saying, “It is not only a great honor for Professor Lee to be induced at DTU but also great honor for DTU to have him.”
Professor Lee also gave commemorative lectures at DTU Biosustain in Lingby and the Bio Innovation Research Institute at the Novo Nordisk Foundation in Copenhagen while in Denmark.
DTU, one of the leading science and technology universities in Europe, has been awarding honorary doctorates since 1921, including to Nobel laureate in chemistry Professor Frances Arnold at Caltech. Professor Lee is the first Korean to receive an honorary doctorate from DTU.
2022.05.03 View 12828 -
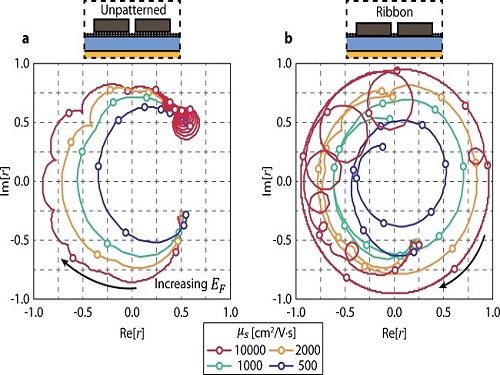 A New Strategy for Active Metasurface Design Provides a Full 360° Phase Tunable Metasurface
The new strategy displays an unprecedented upper limit of dynamic phase modulation with no significant variations in optical amplitude
An international team of researchers led by Professor Min Seok Jang of KAIST and Professor Victor W. Brar of the University of Wisconsin-Madison has demonstrated a widely applicable methodology enabling a full 360° active phase modulation for metasurfaces while maintaining significant levels of uniform light amplitude. This strategy can be fundamentally applied to any spectral region with any structures and resonances that fit the bill.
Metasurfaces are optical components with specialized functionalities indispensable for real-life applications ranging from LIDAR and spectroscopy to futuristic technologies such as invisibility cloaks and holograms. They are known for their compact and micro/nano-sized nature, which enables them to be integrated into electronic computerized systems with sizes that are ever decreasing as predicted by Moore’s law.
In order to allow for such innovations, metasurfaces must be capable of manipulating the impinging light, doing so by manipulating either the light’s amplitude or phase (or both) and emitting it back out. However, dynamically modulating the phase with the full circle range has been a notoriously difficult task, with very few works managing to do so by sacrificing a substantial amount of amplitude control.
Challenged by these limitations, the team proposed a general methodology that enables metasurfaces to implement a dynamic phase modulation with the complete 360° phase range, all the while uniformly maintaining significant levels of amplitude.
The underlying reason for the difficulty achieving such a feat is that there is a fundamental trade-off regarding dynamically controlling the optical phase of light. Metasurfaces generally perform such a function through optical resonances, an excitation of electrons inside the metasurface structure that harmonically oscillate together with the incident light. In order to be able to modulate through the entire range of 0-360°, the optical resonance frequency (the center of the spectrum) must be tuned by a large amount while the linewidth (the width of the spectrum) is kept to a minimum. However, to electrically tune the optical resonance frequency of the metasurface on demand, there needs to be a controllable influx and outflux of electrons into the metasurface and this inevitably leads to a larger linewidth of the aforementioned optical resonance.
The problem is further compounded by the fact that the phase and the amplitude of optical resonances are closely correlated in a complex, non-linear fashion, making it very difficult to hold substantial control over the amplitude while changing the phase.
The team’s work circumvented both problems by using two optical resonances, each with specifically designated properties. One resonance provides the decoupling between the phase and amplitude so that the phase is able to be tuned while significant and uniform levels of amplitude are maintained, as well as providing a narrow linewidth.
The other resonance provides the capability of being sufficiently tuned to a large degree so that the complete full circle range of phase modulation is achievable. The quintessence of the work is then to combine the different properties of the two resonances through a phenomenon called avoided crossing, so that the interactions between the two resonances lead to an amalgamation of the desired traits that achieves and even surpasses the full 360° phase modulation with uniform amplitude.
Professor Jang said, “Our research proposes a new methodology in dynamic phase modulation that breaks through the conventional limits and trade-offs, while being broadly applicable in diverse types of metasurfaces. We hope that this idea helps researchers implement and realize many key applications of metasurfaces, such as LIDAR and holograms, so that the nanophotonics industry keeps growing and provides a brighter technological future.”
The research paper authored by Ju Young Kim and Juho Park, et al., and titled "Full 2π Tunable Phase Modulation Using Avoided Crossing of Resonances" was published in Nature Communications on April 19. The research was funded by the Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center of Samsung Electronics.
-Publication:Ju Young Kim, Juho Park, Gregory R. Holdman, Jacob T. Heiden, Shinho Kim, Victor W. Brar, and Min Seok Jang, “Full 2π Tunable Phase Modulation Using Avoided Crossing ofResonances” Nature Communications on April 19 (2022). doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-29721-7
-ProfileProfessor Min Seok JangSchool of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
2022.05.02 View 9444
A New Strategy for Active Metasurface Design Provides a Full 360° Phase Tunable Metasurface
The new strategy displays an unprecedented upper limit of dynamic phase modulation with no significant variations in optical amplitude
An international team of researchers led by Professor Min Seok Jang of KAIST and Professor Victor W. Brar of the University of Wisconsin-Madison has demonstrated a widely applicable methodology enabling a full 360° active phase modulation for metasurfaces while maintaining significant levels of uniform light amplitude. This strategy can be fundamentally applied to any spectral region with any structures and resonances that fit the bill.
Metasurfaces are optical components with specialized functionalities indispensable for real-life applications ranging from LIDAR and spectroscopy to futuristic technologies such as invisibility cloaks and holograms. They are known for their compact and micro/nano-sized nature, which enables them to be integrated into electronic computerized systems with sizes that are ever decreasing as predicted by Moore’s law.
In order to allow for such innovations, metasurfaces must be capable of manipulating the impinging light, doing so by manipulating either the light’s amplitude or phase (or both) and emitting it back out. However, dynamically modulating the phase with the full circle range has been a notoriously difficult task, with very few works managing to do so by sacrificing a substantial amount of amplitude control.
Challenged by these limitations, the team proposed a general methodology that enables metasurfaces to implement a dynamic phase modulation with the complete 360° phase range, all the while uniformly maintaining significant levels of amplitude.
The underlying reason for the difficulty achieving such a feat is that there is a fundamental trade-off regarding dynamically controlling the optical phase of light. Metasurfaces generally perform such a function through optical resonances, an excitation of electrons inside the metasurface structure that harmonically oscillate together with the incident light. In order to be able to modulate through the entire range of 0-360°, the optical resonance frequency (the center of the spectrum) must be tuned by a large amount while the linewidth (the width of the spectrum) is kept to a minimum. However, to electrically tune the optical resonance frequency of the metasurface on demand, there needs to be a controllable influx and outflux of electrons into the metasurface and this inevitably leads to a larger linewidth of the aforementioned optical resonance.
The problem is further compounded by the fact that the phase and the amplitude of optical resonances are closely correlated in a complex, non-linear fashion, making it very difficult to hold substantial control over the amplitude while changing the phase.
The team’s work circumvented both problems by using two optical resonances, each with specifically designated properties. One resonance provides the decoupling between the phase and amplitude so that the phase is able to be tuned while significant and uniform levels of amplitude are maintained, as well as providing a narrow linewidth.
The other resonance provides the capability of being sufficiently tuned to a large degree so that the complete full circle range of phase modulation is achievable. The quintessence of the work is then to combine the different properties of the two resonances through a phenomenon called avoided crossing, so that the interactions between the two resonances lead to an amalgamation of the desired traits that achieves and even surpasses the full 360° phase modulation with uniform amplitude.
Professor Jang said, “Our research proposes a new methodology in dynamic phase modulation that breaks through the conventional limits and trade-offs, while being broadly applicable in diverse types of metasurfaces. We hope that this idea helps researchers implement and realize many key applications of metasurfaces, such as LIDAR and holograms, so that the nanophotonics industry keeps growing and provides a brighter technological future.”
The research paper authored by Ju Young Kim and Juho Park, et al., and titled "Full 2π Tunable Phase Modulation Using Avoided Crossing of Resonances" was published in Nature Communications on April 19. The research was funded by the Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center of Samsung Electronics.
-Publication:Ju Young Kim, Juho Park, Gregory R. Holdman, Jacob T. Heiden, Shinho Kim, Victor W. Brar, and Min Seok Jang, “Full 2π Tunable Phase Modulation Using Avoided Crossing ofResonances” Nature Communications on April 19 (2022). doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-29721-7
-ProfileProfessor Min Seok JangSchool of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
2022.05.02 View 9444 -
 LightPC Presents a Resilient System Using Only Non-Volatile Memory
Lightweight Persistence Centric System (LightPC) ensures both data and execution persistence for energy-efficient full system persistence
A KAIST research team has developed hardware and software technology that ensures both data and execution persistence. The Lightweight Persistence Centric System (LightPC) makes the systems resilient against power failures by utilizing only non-volatile memory as the main memory.
“We mounted non-volatile memory on a system board prototype and created an operating system to verify the effectiveness of LightPC,” said Professor Myoungsoo Jung. The team confirmed that LightPC validated its execution while powering up and down in the middle of execution, showing up to eight times more memory, 4.3 times faster application execution, and 73% lower power consumption compared to traditional systems.
Professor Jung said that LightPC can be utilized in a variety of fields such as data centers and high-performance computing to provide large-capacity memory, high performance, low power consumption, and service reliability.
In general, power failures on legacy systems can lead to the loss of data stored in the DRAM-based main memory. Unlike volatile memory such as DRAM, non-volatile memory can retain its data without power. Although non-volatile memory has the characteristics of lower power consumption and larger capacity than DRAM, non-volatile memory is typically used for the task of secondary storage due to its lower write performance. For this reason, nonvolatile memory is often used with DRAM. However, modern systems employing non-volatile memory-based main memory experience unexpected performance degradation due to the complicated memory microarchitecture.
To enable both data and execution persistent in legacy systems, it is necessary to transfer the data from the volatile memory to the non-volatile memory. Checkpointing is one possible solution. It periodically transfers the data in preparation for a sudden power failure. While this technology is essential for ensuring high mobility and reliability for users, checkpointing also has fatal drawbacks. It takes additional time and power to move data and requires a data recovery process as well as restarting the system.
In order to address these issues, the research team developed a processor and memory controller to raise the performance of non-volatile memory-only memory. LightPC matches the performance of DRAM by minimizing the internal volatile memory components from non-volatile memory, exposing the non-volatile memory (PRAM) media to the host, and increasing parallelism to service on-the-fly requests as soon as possible.
The team also presented operating system technology that quickly makes execution states of running processes persistent without the need for a checkpointing process. The operating system prevents all modifications to execution states and data by keeping all program executions idle before transferring data in order to support consistency within a period much shorter than the standard power hold-up time of about 16 minutes. For consistency, when the power is recovered, the computer almost immediately revives itself and re-executes all the offline processes immediately without the need for a boot process.
The researchers will present their work (LightPC: Hardware and Software Co-Design for Energy-Efficient Full System Persistence) at the International Symposium on Computer Architecture (ISCA) 2022 in New York in June. More information is available at the CAMELab website (http://camelab.org).
-Profile: Professor Myoungsoo Jung Computer Architecture and Memory Systems Laboratory (CAMEL)http://camelab.org School of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
2022.04.25 View 24861
LightPC Presents a Resilient System Using Only Non-Volatile Memory
Lightweight Persistence Centric System (LightPC) ensures both data and execution persistence for energy-efficient full system persistence
A KAIST research team has developed hardware and software technology that ensures both data and execution persistence. The Lightweight Persistence Centric System (LightPC) makes the systems resilient against power failures by utilizing only non-volatile memory as the main memory.
“We mounted non-volatile memory on a system board prototype and created an operating system to verify the effectiveness of LightPC,” said Professor Myoungsoo Jung. The team confirmed that LightPC validated its execution while powering up and down in the middle of execution, showing up to eight times more memory, 4.3 times faster application execution, and 73% lower power consumption compared to traditional systems.
Professor Jung said that LightPC can be utilized in a variety of fields such as data centers and high-performance computing to provide large-capacity memory, high performance, low power consumption, and service reliability.
In general, power failures on legacy systems can lead to the loss of data stored in the DRAM-based main memory. Unlike volatile memory such as DRAM, non-volatile memory can retain its data without power. Although non-volatile memory has the characteristics of lower power consumption and larger capacity than DRAM, non-volatile memory is typically used for the task of secondary storage due to its lower write performance. For this reason, nonvolatile memory is often used with DRAM. However, modern systems employing non-volatile memory-based main memory experience unexpected performance degradation due to the complicated memory microarchitecture.
To enable both data and execution persistent in legacy systems, it is necessary to transfer the data from the volatile memory to the non-volatile memory. Checkpointing is one possible solution. It periodically transfers the data in preparation for a sudden power failure. While this technology is essential for ensuring high mobility and reliability for users, checkpointing also has fatal drawbacks. It takes additional time and power to move data and requires a data recovery process as well as restarting the system.
In order to address these issues, the research team developed a processor and memory controller to raise the performance of non-volatile memory-only memory. LightPC matches the performance of DRAM by minimizing the internal volatile memory components from non-volatile memory, exposing the non-volatile memory (PRAM) media to the host, and increasing parallelism to service on-the-fly requests as soon as possible.
The team also presented operating system technology that quickly makes execution states of running processes persistent without the need for a checkpointing process. The operating system prevents all modifications to execution states and data by keeping all program executions idle before transferring data in order to support consistency within a period much shorter than the standard power hold-up time of about 16 minutes. For consistency, when the power is recovered, the computer almost immediately revives itself and re-executes all the offline processes immediately without the need for a boot process.
The researchers will present their work (LightPC: Hardware and Software Co-Design for Energy-Efficient Full System Persistence) at the International Symposium on Computer Architecture (ISCA) 2022 in New York in June. More information is available at the CAMELab website (http://camelab.org).
-Profile: Professor Myoungsoo Jung Computer Architecture and Memory Systems Laboratory (CAMEL)http://camelab.org School of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
2022.04.25 View 24861 -
 Quantum Technology: the Next Game Changer?
The 6th KAIST Global Strategy Institute Forum explores how quantum technology has evolved into a new growth engine for the future
The participants of the 6th KAIST Global Strategy Institute (GSI) Forum on April 20 agreed that the emerging technology of quantum computing will be a game changer of the future. As KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee said in his opening remarks, the future is quantum and that future is rapidly approaching. Keynote speakers and panelists presented their insights on the disruptive innovations we are already experiencing.
The three keynote speakers included Dr. Jerry M. Chow, IBM fellow and director of quantum infrastructure, Professor John Preskill from Caltech, and Professor Jungsang Kim from Duke University. They discussed the academic impact and industrial applications of quantum technology, and its prospects for the future.
Dr. Chow leads IBM Quantum’s hardware system development efforts, focusing on research and system deployment. Professor Preskill is one of the leading quantum information science and quantum computation scholars. He coined the term “quantum supremacy.” Professor Kim is the co-founder and CTO of IonQ Inc., which develops general-purpose trapped ion quantum computers and software to generate, optimize, and execute quantum circuits.
Two leading quantum scholars from KAIST, Professor June-Koo Kevin Rhee and Professor Youngik Sohn, and Professor Andreas Heinrich from the IBS Center for Quantum Nanoscience also participated in the forum as panelists. Professor Rhee is the founder of the nation’s first quantum computing software company and leads the AI Quantum Computing IT Research Center at KAIST.
During the panel session, Professor Rhee said that although it is undeniable the quantum computing will be a game changer, there are several challenges. For instance, the first actual quantum computer is NISQ (Noisy intermediate-scale quantum era), which is still incomplete. However, it is expected to outperform a supercomputer. Until then, it is important to advance the accuracy of quantum computation in order to offer super computation speeds.
Professor Sohn, who worked at PsiQuantum, detailed how quantum computers will affect our society. He said that PsiQuantum is developing silicon photonics that will control photons. We can’t begin to imagine how silicon photonics will transform our society. Things will change slowly but the scale would be massive.
The keynote speakers presented how quantum cryptography communications and its sensing technology will serve as disruptive innovations. Dr. Chow stressed that to realize the potential growth and innovation, additional R&D is needed. More research groups and scholars should be nurtured. Only then will the rich R&D resources be able to create breakthroughs in quantum-related industries. Lastly, the commercialization of quantum computing must be advanced, which will enable the provision of diverse services. In addition, more technological and industrial infrastructure must be built to better accommodate quantum computing.
Professor Preskill believes that quantum computing will benefit humanity. He cited two basic reasons for his optimistic prediction: quantum complexity and quantum error corrections. He explained why quantum computing is so powerful: quantum computer can easily solve the problems classically considered difficult, such as factorization. In addition, quantum computer has the potential to efficiently simulate all of the physical processes taking place in nature.
Despite such dramatic advantages, why does it seem so difficult? Professor Preskill believes this is because we want qubits (quantum bits or ‘qubits’ are the basic unit of quantum information) to interact very strongly with each other. Because computations can fail, we don’t want qubits to interact with the environment unless we can control and predict them.
As for quantum computing in the NISQ era, he said that NISQ will be an exciting tool for exploring physics. Professor Preskill does not believe that NISQ will change the world alone, rather it is a step forward toward more powerful quantum technologies in the future. He added that a potentially transformable, scalable quantum computer could still be decades away.
Professor Preskill said that a large number of qubits, higher accuracy, and better quality will require a significant investment. He said if we expand with better ideas, we can make a better system. In the longer term, quantum technology will bring significant benefits to the technological sectors and society in the fields of materials, physics, chemistry, and energy production.
Professor Kim from Duke University presented on the practical applications of quantum computing, especially in the startup environment. He said that although there is no right answer for the early applications of quantum computing, developing new approaches to solve difficult problems and raising the accessibility of the technology will be important for ensuring the growth of technology-based startups.
2022.04.21 View 14061
Quantum Technology: the Next Game Changer?
The 6th KAIST Global Strategy Institute Forum explores how quantum technology has evolved into a new growth engine for the future
The participants of the 6th KAIST Global Strategy Institute (GSI) Forum on April 20 agreed that the emerging technology of quantum computing will be a game changer of the future. As KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee said in his opening remarks, the future is quantum and that future is rapidly approaching. Keynote speakers and panelists presented their insights on the disruptive innovations we are already experiencing.
The three keynote speakers included Dr. Jerry M. Chow, IBM fellow and director of quantum infrastructure, Professor John Preskill from Caltech, and Professor Jungsang Kim from Duke University. They discussed the academic impact and industrial applications of quantum technology, and its prospects for the future.
Dr. Chow leads IBM Quantum’s hardware system development efforts, focusing on research and system deployment. Professor Preskill is one of the leading quantum information science and quantum computation scholars. He coined the term “quantum supremacy.” Professor Kim is the co-founder and CTO of IonQ Inc., which develops general-purpose trapped ion quantum computers and software to generate, optimize, and execute quantum circuits.
Two leading quantum scholars from KAIST, Professor June-Koo Kevin Rhee and Professor Youngik Sohn, and Professor Andreas Heinrich from the IBS Center for Quantum Nanoscience also participated in the forum as panelists. Professor Rhee is the founder of the nation’s first quantum computing software company and leads the AI Quantum Computing IT Research Center at KAIST.
During the panel session, Professor Rhee said that although it is undeniable the quantum computing will be a game changer, there are several challenges. For instance, the first actual quantum computer is NISQ (Noisy intermediate-scale quantum era), which is still incomplete. However, it is expected to outperform a supercomputer. Until then, it is important to advance the accuracy of quantum computation in order to offer super computation speeds.
Professor Sohn, who worked at PsiQuantum, detailed how quantum computers will affect our society. He said that PsiQuantum is developing silicon photonics that will control photons. We can’t begin to imagine how silicon photonics will transform our society. Things will change slowly but the scale would be massive.
The keynote speakers presented how quantum cryptography communications and its sensing technology will serve as disruptive innovations. Dr. Chow stressed that to realize the potential growth and innovation, additional R&D is needed. More research groups and scholars should be nurtured. Only then will the rich R&D resources be able to create breakthroughs in quantum-related industries. Lastly, the commercialization of quantum computing must be advanced, which will enable the provision of diverse services. In addition, more technological and industrial infrastructure must be built to better accommodate quantum computing.
Professor Preskill believes that quantum computing will benefit humanity. He cited two basic reasons for his optimistic prediction: quantum complexity and quantum error corrections. He explained why quantum computing is so powerful: quantum computer can easily solve the problems classically considered difficult, such as factorization. In addition, quantum computer has the potential to efficiently simulate all of the physical processes taking place in nature.
Despite such dramatic advantages, why does it seem so difficult? Professor Preskill believes this is because we want qubits (quantum bits or ‘qubits’ are the basic unit of quantum information) to interact very strongly with each other. Because computations can fail, we don’t want qubits to interact with the environment unless we can control and predict them.
As for quantum computing in the NISQ era, he said that NISQ will be an exciting tool for exploring physics. Professor Preskill does not believe that NISQ will change the world alone, rather it is a step forward toward more powerful quantum technologies in the future. He added that a potentially transformable, scalable quantum computer could still be decades away.
Professor Preskill said that a large number of qubits, higher accuracy, and better quality will require a significant investment. He said if we expand with better ideas, we can make a better system. In the longer term, quantum technology will bring significant benefits to the technological sectors and society in the fields of materials, physics, chemistry, and energy production.
Professor Kim from Duke University presented on the practical applications of quantum computing, especially in the startup environment. He said that although there is no right answer for the early applications of quantum computing, developing new approaches to solve difficult problems and raising the accessibility of the technology will be important for ensuring the growth of technology-based startups.
2022.04.21 View 14061 -
 Professor Hyunjoo Jenny Lee to Co-Chair IEEE MEMS 2025
Professor Hyunjoo Jenny Lee from the School of Electrical Engineering has been appointed General Chair of the 38th IEEE MEMS 2025 (International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems). Professor Lee, who is 40, is the conference’s youngest General Chair to date and will work jointly with Professor Sheng-Shian Li of Taiwan’s National Tsing Hua University as co-chairs in 2025.
IEEE MEMS is a top-tier international conference on microelectromechanical systems and it serves as a core academic showcase for MEMS research and technology in areas such as microsensors and actuators.
With over 800 MEMS paper submissions each year, the conference only accepts and publishes about 250 of them after a rigorous review process recognized for its world-class prestige. Of all the submissions, fewer than 10% are chosen for oral presentations.
2022.04.18 View 8977
Professor Hyunjoo Jenny Lee to Co-Chair IEEE MEMS 2025
Professor Hyunjoo Jenny Lee from the School of Electrical Engineering has been appointed General Chair of the 38th IEEE MEMS 2025 (International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems). Professor Lee, who is 40, is the conference’s youngest General Chair to date and will work jointly with Professor Sheng-Shian Li of Taiwan’s National Tsing Hua University as co-chairs in 2025.
IEEE MEMS is a top-tier international conference on microelectromechanical systems and it serves as a core academic showcase for MEMS research and technology in areas such as microsensors and actuators.
With over 800 MEMS paper submissions each year, the conference only accepts and publishes about 250 of them after a rigorous review process recognized for its world-class prestige. Of all the submissions, fewer than 10% are chosen for oral presentations.
2022.04.18 View 8977 -
 Professor June-Koo Rhee’s Team Wins the QHack Open Hackathon Science Challenge
The research team consisting of three master students Ju-Young Ryu, Jeung-rak Lee, and Eyel Elala in Professor June-Koo Rhee’s group from the KAIST IRTC of Quantum Computing for AI has won the first place at the QHack 2022 Open Hackathon Science Challenge.
The QHack 2022 Open Hackathon is one of the world’s prestigious quantum software hackathon events held by US Xanadu, in which 250 people from 100 countries participate. Major sponsors such as IBM Quantum, AWS, CERN QTI, and Google Quantum AI proposed challenging problems, and a winning team is selected judged on team projects in each of the 13 challenges.
The KAIST team supervised by Professor Rhee received the First Place prize on the Science Challenge which was organized by the CERN QTI of the European Communities. The team will be awarded an opportunity to tour CERN’s research lab in Europe for one week along with an online internship.
The students on the team presented a method for “Leaning Based Error Mitigation for VQE,” in which they implemented an LBEM protocol to lower the error in quantum computing, and leveraged the protocol in the VQU algorithm which is used to calculate the ground state energy of a given molecule.
Their research successfully demonstrated the ability to effectively mitigate the error in IBM Quantum hardware and the virtual error model. In conjunction, Professor June-Koo (Kevin) Rhee founded a quantum computing venture start-up, Qunova Computing(https://qunovacomputing.com), with technology tranfer from the KAIST ITRC of Quantum Computing for AI. Qunova Computing is one of the frontier of the quantum software industry in Korea.
2022.04.08 View 8228
Professor June-Koo Rhee’s Team Wins the QHack Open Hackathon Science Challenge
The research team consisting of three master students Ju-Young Ryu, Jeung-rak Lee, and Eyel Elala in Professor June-Koo Rhee’s group from the KAIST IRTC of Quantum Computing for AI has won the first place at the QHack 2022 Open Hackathon Science Challenge.
The QHack 2022 Open Hackathon is one of the world’s prestigious quantum software hackathon events held by US Xanadu, in which 250 people from 100 countries participate. Major sponsors such as IBM Quantum, AWS, CERN QTI, and Google Quantum AI proposed challenging problems, and a winning team is selected judged on team projects in each of the 13 challenges.
The KAIST team supervised by Professor Rhee received the First Place prize on the Science Challenge which was organized by the CERN QTI of the European Communities. The team will be awarded an opportunity to tour CERN’s research lab in Europe for one week along with an online internship.
The students on the team presented a method for “Leaning Based Error Mitigation for VQE,” in which they implemented an LBEM protocol to lower the error in quantum computing, and leveraged the protocol in the VQU algorithm which is used to calculate the ground state energy of a given molecule.
Their research successfully demonstrated the ability to effectively mitigate the error in IBM Quantum hardware and the virtual error model. In conjunction, Professor June-Koo (Kevin) Rhee founded a quantum computing venture start-up, Qunova Computing(https://qunovacomputing.com), with technology tranfer from the KAIST ITRC of Quantum Computing for AI. Qunova Computing is one of the frontier of the quantum software industry in Korea.
2022.04.08 View 8228 -
 Professor Lik-Hang Lee Offers Metaverse Course for Hong Kong Productivity Council
Professor Lik-Hang Lee from the Department of Industrial System Engineering will offer a metaverse course in partnership with the Hong Kong Productivity Council (HKPC) from the Spring 2022 semester to Hong Kong-based professionals.
“The Metaverse Course for Professionals” aims to nurture world-class talents of the metaverse in response to surging demand for virtual worlds and virtual-physical blended environments. The HKPC’s R&D scientists, consultants, software engineers, and related professionals will attend the course. They will receive a professional certificate on managing and developing metaverse skills upon the completion of this intensive course.
The course will provide essential skills and knowledge about the parallel virtual universe and how to leverage digitalization and industrialization in the metaverse era. The course includes comprehensive modules, such as designing and implementing virtual-physical blended environments, metaverse technology and ecosystems, immersive smart cities, token economies, and intelligent industrialization in the metaverse era.
Professor Lee believes in the decades to come that we will see rising numbers of virtual worlds in cyberspace known as the ‘Immersive Internet’ that will be characterized by high levels of immersiveness, user interactivity, and user-machine collaborations.
“Consumers in virtual worlds will create novel content as well as personalized products and services, becoming as catalyst for ‘hyperpersonalization’ in the next industrial revolution,” he said.
Professor Lee said he will continue offering world-class education related to the metaverse to students in KAIST and professionals from various industrial sectors, as his Augmented Reality and Media Lab will focus on a variety of metaverse topics such as metaverse campuses and industrial metaverses.
The HKPC has worked to address innovative solutions for Hong Kong industries and enterprises since 1967, helping them achieve optimized resource utilization, effectiveness, and cost reduction as well as enhanced productivity and competitiveness in both local and international markets. The HKPC has advocated for facilitating Hong Kong’s reindustrialization powered by Industry 4.0 and e-commerce 4.0 with a strong emphasis on R&D, IoT, AI, digital manufacturing.
The Augmented Reality and Media Lab led by Professor Lee will continue its close partnerships with HKPC and its other partners to help build the epicentre of the metaverse in the region. Furthermore, the lab will fully leverage its well-established research niches in user-centric, virtual-physical cyberspace (https://www.lhlee.com/projects-8 ) to serve upcoming projects related to industrial metaverses, which aligns with the departmental focus on smart factories and artificial intelligence.
2022.04.06 View 9916
Professor Lik-Hang Lee Offers Metaverse Course for Hong Kong Productivity Council
Professor Lik-Hang Lee from the Department of Industrial System Engineering will offer a metaverse course in partnership with the Hong Kong Productivity Council (HKPC) from the Spring 2022 semester to Hong Kong-based professionals.
“The Metaverse Course for Professionals” aims to nurture world-class talents of the metaverse in response to surging demand for virtual worlds and virtual-physical blended environments. The HKPC’s R&D scientists, consultants, software engineers, and related professionals will attend the course. They will receive a professional certificate on managing and developing metaverse skills upon the completion of this intensive course.
The course will provide essential skills and knowledge about the parallel virtual universe and how to leverage digitalization and industrialization in the metaverse era. The course includes comprehensive modules, such as designing and implementing virtual-physical blended environments, metaverse technology and ecosystems, immersive smart cities, token economies, and intelligent industrialization in the metaverse era.
Professor Lee believes in the decades to come that we will see rising numbers of virtual worlds in cyberspace known as the ‘Immersive Internet’ that will be characterized by high levels of immersiveness, user interactivity, and user-machine collaborations.
“Consumers in virtual worlds will create novel content as well as personalized products and services, becoming as catalyst for ‘hyperpersonalization’ in the next industrial revolution,” he said.
Professor Lee said he will continue offering world-class education related to the metaverse to students in KAIST and professionals from various industrial sectors, as his Augmented Reality and Media Lab will focus on a variety of metaverse topics such as metaverse campuses and industrial metaverses.
The HKPC has worked to address innovative solutions for Hong Kong industries and enterprises since 1967, helping them achieve optimized resource utilization, effectiveness, and cost reduction as well as enhanced productivity and competitiveness in both local and international markets. The HKPC has advocated for facilitating Hong Kong’s reindustrialization powered by Industry 4.0 and e-commerce 4.0 with a strong emphasis on R&D, IoT, AI, digital manufacturing.
The Augmented Reality and Media Lab led by Professor Lee will continue its close partnerships with HKPC and its other partners to help build the epicentre of the metaverse in the region. Furthermore, the lab will fully leverage its well-established research niches in user-centric, virtual-physical cyberspace (https://www.lhlee.com/projects-8 ) to serve upcoming projects related to industrial metaverses, which aligns with the departmental focus on smart factories and artificial intelligence.
2022.04.06 View 9916 -
 Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang Named the 2022 Ho-Am Laureate
Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang from the Department of Chemistry was named the awardee of the Ho-Am Prize in the fields of chemistry and life sciences. The award has recognized the most distinguished scholars, individuals, and organizations in physics and mathematics, chemistry and life sciences, engineering, medicine, arts, and community service in honor of the late founder of Samsung Group Byong-Chul Lee, whose penname is Ho-Am. The awards ceremony will be held on May 31 and awardees will receive 300 million KRW in prize money.
Professor Chang became the fourth KAIST Ho-Am laureate following Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee in engineering in 2014, Distinguished Professor Jun Ho Oh in engineering in 2016, and Distinguished Professor Gou Young Koh in medicine in 2018.
Professor Chang is a renowned chemist who has made pioneering research in the area of transition metal catalysis for organic transformations. Professor Chang is also one of the Highly Cited Researchers who rank in the top 1% of citations by field and publication year in the Web of Science citation index. He has made the list seven years in a row from 2016.
Professor Chang has developed a range of new and impactful C-H bond functionalization reactions. By using his approaches, value-added molecules can be readily produced from chemical feedstocks, representatively hydrocarbons and (hetero)arenes. His research team elucidated fundamental key mechanistic aspects in the course of the essential C-H bond activation process of unreactive starting materials. He was able to utilize the obtained mechanistic understanding for the subsequent catalyst design to develop more efficient and highly (stereo)selective catalytic reactions.
Among the numerous contributions he made, the design of new mechanistic approaches toward metal nitrenoid transfers are of especially high impact to the chemical community. Indeed, a series of important transition metal catalyst systems were developed by Professor Chang to enable the direct and selective C-H amidation of unreactive organic compounds, thereby producing aminated compounds that have important applicability in synthetic, medicinal, and materials science. He has also pioneered in the area of asymmetric C-H amination chemistry by creatively devising various types of chiral transition metal catalyst systems, and his team proved for the first time that chiral lactam compounds can be obtained at an excellent level of stereoselectivity.
Another significant contribution of Professor. Chang was the introduction of dioxazolones as a robust but highly reactive source of acyl nitrenoids for the catalytic C-H amidation reactions, and this reagent is now broadly utilized in synthetic chemistry worldwide.
Professor Chang also leads a research group in the Center for Catalytic Hydrocarbon Functionalizations at the Institute for Basic Science.
2022.04.06 View 9627
Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang Named the 2022 Ho-Am Laureate
Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang from the Department of Chemistry was named the awardee of the Ho-Am Prize in the fields of chemistry and life sciences. The award has recognized the most distinguished scholars, individuals, and organizations in physics and mathematics, chemistry and life sciences, engineering, medicine, arts, and community service in honor of the late founder of Samsung Group Byong-Chul Lee, whose penname is Ho-Am. The awards ceremony will be held on May 31 and awardees will receive 300 million KRW in prize money.
Professor Chang became the fourth KAIST Ho-Am laureate following Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee in engineering in 2014, Distinguished Professor Jun Ho Oh in engineering in 2016, and Distinguished Professor Gou Young Koh in medicine in 2018.
Professor Chang is a renowned chemist who has made pioneering research in the area of transition metal catalysis for organic transformations. Professor Chang is also one of the Highly Cited Researchers who rank in the top 1% of citations by field and publication year in the Web of Science citation index. He has made the list seven years in a row from 2016.
Professor Chang has developed a range of new and impactful C-H bond functionalization reactions. By using his approaches, value-added molecules can be readily produced from chemical feedstocks, representatively hydrocarbons and (hetero)arenes. His research team elucidated fundamental key mechanistic aspects in the course of the essential C-H bond activation process of unreactive starting materials. He was able to utilize the obtained mechanistic understanding for the subsequent catalyst design to develop more efficient and highly (stereo)selective catalytic reactions.
Among the numerous contributions he made, the design of new mechanistic approaches toward metal nitrenoid transfers are of especially high impact to the chemical community. Indeed, a series of important transition metal catalyst systems were developed by Professor Chang to enable the direct and selective C-H amidation of unreactive organic compounds, thereby producing aminated compounds that have important applicability in synthetic, medicinal, and materials science. He has also pioneered in the area of asymmetric C-H amination chemistry by creatively devising various types of chiral transition metal catalyst systems, and his team proved for the first time that chiral lactam compounds can be obtained at an excellent level of stereoselectivity.
Another significant contribution of Professor. Chang was the introduction of dioxazolones as a robust but highly reactive source of acyl nitrenoids for the catalytic C-H amidation reactions, and this reagent is now broadly utilized in synthetic chemistry worldwide.
Professor Chang also leads a research group in the Center for Catalytic Hydrocarbon Functionalizations at the Institute for Basic Science.
2022.04.06 View 9627 -
 Mathematicians Identify a Key Source of Cell-to-Cell Variability in Cell Signaling
Systematic inferences identify a major source of heterogeneity in cell signaling dynamics
Why do genetically identical cells respond differently to the same external stimuli, such as antibiotics? This long-standing mystery has been solved by KAIST and IBS mathematicians who have developed a new framework for analyzing cell responses to some stimuli. The team found that the cell-to-cell variability in antibiotic stress response increases as the effective length of the cell signaling pathway (i.e., the number of rate-limiting steps) increases. This finding could identify more effective chemotherapies to overcome the fractional killing of cancer cells caused by cell-to-cell variability.
Cells in the human body contain signal transduction systems that respond to various external stimuli such as antibiotics and changes in osmotic pressure. When an external stimulus is detected, various biochemical reactions occur sequentially. This leads to the expression of relevant genes, allowing the cells to respond to the perturbed external environment. Furthermore, signal transduction leads to a drug response (e.g., antibiotic resistance genes are expressed when antibiotic drugs are given).
However, even when the same external stimuli are detected, the responses of individual cells are greatly heterogeneous. This leads to the emergence of persister cells that are highly resistant to drugs. To identify potential sources of this cell-to cell variability, many studies have been conducted. However, most of the intermediate signal transduction reactions are unobservable with current experimental techniques.
A group of researchers including Dae Wook Kim and Hyukpyo Hong and led by Professor Jae Kyoung Kim from the KAIST Department of Mathematical Sciences and IBS Biomedical Mathematics Group solved the mystery by exploiting queueing theory and Bayesian inference methodology. They proposed a queueing process that describes the signal transduction system in cells. Based on this, they developed Bayesian inference computational software using MBI (the Moment-based Bayesian Inference method). This enables the analysis of the signal transduction system without a direct observation of the intermediate steps. This study was published in Science Advances.
By analyzing experimental data from Escherichia coli using MBI, the research team found that cell-to-cell variability increases as the number of rate-limiting steps in the signaling pathway increases.
The rate-limiting steps denote the slowest steps (i.e., bottlenecks) in sequential biochemical reaction steps composing cell signaling pathways and thus dominates most of the signaling time. As the number of the rate-limiting steps increases, the intensity of the transduced signal becomes greatly heterogeneous even in a population of genetically identical cells. This finding is expected to provide a new paradigm for studying the heterogeneous antibiotic resistance of cells, which is a big challenge in cancer medicine.
Professor Kim said, “As a mathematician, I am excited to help advance the understanding of cell-to-cell variability in response to external stimuli. I hope this finding facilitates the development of more effective chemotherapies.”
This work was supported by the Samsung Science and Technology Foundation, the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Institute for Basic Science.
-Publication:Dae Wook Kim, Hyukpyo Hong, and Jae Kyoung Kim (2022) “Systematic inference identifies a major source of heterogeneity in cell signaling dynamics: the rate-limiting step number,”Science Advances March 18, 2022 (DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abl4598)
-Profile:Professor Jae Kyoung Kimhttp://mathsci.kaist.ac.kr/~jaekkim
jaekkim@kaist.ac.kr@umichkim on TwitterDepartment of Mathematical SciencesKAIST
2022.03.29 View 12326
Mathematicians Identify a Key Source of Cell-to-Cell Variability in Cell Signaling
Systematic inferences identify a major source of heterogeneity in cell signaling dynamics
Why do genetically identical cells respond differently to the same external stimuli, such as antibiotics? This long-standing mystery has been solved by KAIST and IBS mathematicians who have developed a new framework for analyzing cell responses to some stimuli. The team found that the cell-to-cell variability in antibiotic stress response increases as the effective length of the cell signaling pathway (i.e., the number of rate-limiting steps) increases. This finding could identify more effective chemotherapies to overcome the fractional killing of cancer cells caused by cell-to-cell variability.
Cells in the human body contain signal transduction systems that respond to various external stimuli such as antibiotics and changes in osmotic pressure. When an external stimulus is detected, various biochemical reactions occur sequentially. This leads to the expression of relevant genes, allowing the cells to respond to the perturbed external environment. Furthermore, signal transduction leads to a drug response (e.g., antibiotic resistance genes are expressed when antibiotic drugs are given).
However, even when the same external stimuli are detected, the responses of individual cells are greatly heterogeneous. This leads to the emergence of persister cells that are highly resistant to drugs. To identify potential sources of this cell-to cell variability, many studies have been conducted. However, most of the intermediate signal transduction reactions are unobservable with current experimental techniques.
A group of researchers including Dae Wook Kim and Hyukpyo Hong and led by Professor Jae Kyoung Kim from the KAIST Department of Mathematical Sciences and IBS Biomedical Mathematics Group solved the mystery by exploiting queueing theory and Bayesian inference methodology. They proposed a queueing process that describes the signal transduction system in cells. Based on this, they developed Bayesian inference computational software using MBI (the Moment-based Bayesian Inference method). This enables the analysis of the signal transduction system without a direct observation of the intermediate steps. This study was published in Science Advances.
By analyzing experimental data from Escherichia coli using MBI, the research team found that cell-to-cell variability increases as the number of rate-limiting steps in the signaling pathway increases.
The rate-limiting steps denote the slowest steps (i.e., bottlenecks) in sequential biochemical reaction steps composing cell signaling pathways and thus dominates most of the signaling time. As the number of the rate-limiting steps increases, the intensity of the transduced signal becomes greatly heterogeneous even in a population of genetically identical cells. This finding is expected to provide a new paradigm for studying the heterogeneous antibiotic resistance of cells, which is a big challenge in cancer medicine.
Professor Kim said, “As a mathematician, I am excited to help advance the understanding of cell-to-cell variability in response to external stimuli. I hope this finding facilitates the development of more effective chemotherapies.”
This work was supported by the Samsung Science and Technology Foundation, the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Institute for Basic Science.
-Publication:Dae Wook Kim, Hyukpyo Hong, and Jae Kyoung Kim (2022) “Systematic inference identifies a major source of heterogeneity in cell signaling dynamics: the rate-limiting step number,”Science Advances March 18, 2022 (DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abl4598)
-Profile:Professor Jae Kyoung Kimhttp://mathsci.kaist.ac.kr/~jaekkim
jaekkim@kaist.ac.kr@umichkim on TwitterDepartment of Mathematical SciencesKAIST
2022.03.29 View 12326 -
 Baemin CEO Endows a Scholarship in Honor of the Late Professor Chwa
CEO Beom-Jun Kim of Woowa Brothers also known as ‘Baemin,’ a leading meal delivery app company, made a donation of 100 million KRW in honor of the late Professor Kyong-Yong Chwa from the School of Computing who passed away last year. The fund will be established for the “Kyong-Yong Chwa - Beom-Jun Kim Scholarship” to provide scholarships for four students over five years.
Kim finished his BS in 1997 and MS in 1999 at the School of Computing and Professor Chwa was his advisor. The late Professor Chwa was a pioneering scholar who brought the concept of computer algorithms to Korea. After graduating from Seoul National University in electric engineering, Professor Chwa earned his PhD at Northwestern University and began teaching at KAIST in 1980. Professor Chwa served as the President of the Korean Institute of Information Scientists and Engineers and a fellow emeritus at the Korean Academy of Science and Technology.
Professor Chwa encouraged younger students to participate in international computer programming contests. Under his wing, Team Korea, which was comprised of four high school students, including Kim, placed fourth in the International Olympiad Informatics (IOI). Kim, who participated in the contest as high school junior, won an individual gold medal in the fourth IOI competition in 1992. Since then, Korean students have actively participated in many competitions including the International Collegiate Programming Contest (ICPC) hosted by the Association for Computing Machinery.
Kim said, “I feel fortunate to have met so many good friends and distinguished professors. With them, I had opportunities to grow. I would like to provide such opportunities to my juniors at KAIST. Professor Chwa was a larger than life figure in the field of computer programming. He was always caring and supported us with a warm heart. I want this donation to help carry on his legacy for our students and for them to seek greater challenges and bigger dreams.”
2022.03.25 View 10020
Baemin CEO Endows a Scholarship in Honor of the Late Professor Chwa
CEO Beom-Jun Kim of Woowa Brothers also known as ‘Baemin,’ a leading meal delivery app company, made a donation of 100 million KRW in honor of the late Professor Kyong-Yong Chwa from the School of Computing who passed away last year. The fund will be established for the “Kyong-Yong Chwa - Beom-Jun Kim Scholarship” to provide scholarships for four students over five years.
Kim finished his BS in 1997 and MS in 1999 at the School of Computing and Professor Chwa was his advisor. The late Professor Chwa was a pioneering scholar who brought the concept of computer algorithms to Korea. After graduating from Seoul National University in electric engineering, Professor Chwa earned his PhD at Northwestern University and began teaching at KAIST in 1980. Professor Chwa served as the President of the Korean Institute of Information Scientists and Engineers and a fellow emeritus at the Korean Academy of Science and Technology.
Professor Chwa encouraged younger students to participate in international computer programming contests. Under his wing, Team Korea, which was comprised of four high school students, including Kim, placed fourth in the International Olympiad Informatics (IOI). Kim, who participated in the contest as high school junior, won an individual gold medal in the fourth IOI competition in 1992. Since then, Korean students have actively participated in many competitions including the International Collegiate Programming Contest (ICPC) hosted by the Association for Computing Machinery.
Kim said, “I feel fortunate to have met so many good friends and distinguished professors. With them, I had opportunities to grow. I would like to provide such opportunities to my juniors at KAIST. Professor Chwa was a larger than life figure in the field of computer programming. He was always caring and supported us with a warm heart. I want this donation to help carry on his legacy for our students and for them to seek greater challenges and bigger dreams.”
2022.03.25 View 10020 -
 Tomographic Measurement of Dielectric Tensors
Dielectric tensor tomography allows the direct measurement of the 3D dielectric tensors of optically anisotropic structures
A research team reported the direct measurement of dielectric tensors of anisotropic structures including the spatial variations of principal refractive indices and directors. The group also demonstrated quantitative tomographic measurements of various nematic liquid-crystal structures and their fast 3D nonequilibrium dynamics using a 3D label-free tomographic method. The method was described in Nature Materials.
Light-matter interactions are described by the dielectric tensor. Despite their importance in basic science and applications, it has not been possible to measure 3D dielectric tensors directly. The main challenge was due to the vectorial nature of light scattering from a 3D anisotropic structure. Previous approaches only addressed 3D anisotropic information indirectly and were limited to two-dimensional, qualitative, strict sample conditions or assumptions.
The research team developed a method enabling the tomographic reconstruction of 3D dielectric tensors without any preparation or assumptions. A sample is illuminated with a laser beam with various angles and circularly polarization states. Then, the light fields scattered from a sample are holographically measured and converted into vectorial diffraction components. Finally, by inversely solving a vectorial wave equation, the 3D dielectric tensor is reconstructed.
Professor YongKeun Park said, “There were a greater number of unknowns in direct measuring than with the conventional approach. We applied our approach to measure additional holographic images by slightly tilting the incident angle.”
He said that the slightly tilted illumination provides an additional orthogonal polarization, which makes the underdetermined problem become the determined problem. “Although scattered fields are dependent on the illumination angle, the Fourier differentiation theorem enables the extraction of the same dielectric tensor for the slightly tilted illumination,” Professor Park added.
His team’s method was validated by reconstructing well-known liquid crystal (LC) structures, including the twisted nematic, hybrid aligned nematic, radial, and bipolar configurations. Furthermore, the research team demonstrated the experimental measurements of the non-equilibrium dynamics of annihilating, nucleating, and merging LC droplets, and the LC polymer network with repeating 3D topological defects.
“This is the first experimental measurement of non-equilibrium dynamics and 3D topological defects in LC structures in a label-free manner. Our method enables the exploration of inaccessible nematic structures and interactions in non-equilibrium dynamics,” first author Dr. Seungwoo Shin explained.
-PublicationSeungwoo Shin, Jonghee Eun, Sang Seok Lee, Changjae Lee, Herve Hugonnet, Dong Ki Yoon, Shin-Hyun Kim, Jongwoo Jeong, YongKeun Park, “Tomographic Measurement ofDielectric Tensors at Optical Frequency,” Nature Materials March 02, 2022 (https://doi.org/10/1038/s41563-022-01202-8)
-ProfileProfessor YongKeun ParkBiomedical Optics Laboratory (http://bmol.kaist.ac.kr)Department of PhysicsCollege of Natural SciencesKAIST
2022.03.22 View 10203
Tomographic Measurement of Dielectric Tensors
Dielectric tensor tomography allows the direct measurement of the 3D dielectric tensors of optically anisotropic structures
A research team reported the direct measurement of dielectric tensors of anisotropic structures including the spatial variations of principal refractive indices and directors. The group also demonstrated quantitative tomographic measurements of various nematic liquid-crystal structures and their fast 3D nonequilibrium dynamics using a 3D label-free tomographic method. The method was described in Nature Materials.
Light-matter interactions are described by the dielectric tensor. Despite their importance in basic science and applications, it has not been possible to measure 3D dielectric tensors directly. The main challenge was due to the vectorial nature of light scattering from a 3D anisotropic structure. Previous approaches only addressed 3D anisotropic information indirectly and were limited to two-dimensional, qualitative, strict sample conditions or assumptions.
The research team developed a method enabling the tomographic reconstruction of 3D dielectric tensors without any preparation or assumptions. A sample is illuminated with a laser beam with various angles and circularly polarization states. Then, the light fields scattered from a sample are holographically measured and converted into vectorial diffraction components. Finally, by inversely solving a vectorial wave equation, the 3D dielectric tensor is reconstructed.
Professor YongKeun Park said, “There were a greater number of unknowns in direct measuring than with the conventional approach. We applied our approach to measure additional holographic images by slightly tilting the incident angle.”
He said that the slightly tilted illumination provides an additional orthogonal polarization, which makes the underdetermined problem become the determined problem. “Although scattered fields are dependent on the illumination angle, the Fourier differentiation theorem enables the extraction of the same dielectric tensor for the slightly tilted illumination,” Professor Park added.
His team’s method was validated by reconstructing well-known liquid crystal (LC) structures, including the twisted nematic, hybrid aligned nematic, radial, and bipolar configurations. Furthermore, the research team demonstrated the experimental measurements of the non-equilibrium dynamics of annihilating, nucleating, and merging LC droplets, and the LC polymer network with repeating 3D topological defects.
“This is the first experimental measurement of non-equilibrium dynamics and 3D topological defects in LC structures in a label-free manner. Our method enables the exploration of inaccessible nematic structures and interactions in non-equilibrium dynamics,” first author Dr. Seungwoo Shin explained.
-PublicationSeungwoo Shin, Jonghee Eun, Sang Seok Lee, Changjae Lee, Herve Hugonnet, Dong Ki Yoon, Shin-Hyun Kim, Jongwoo Jeong, YongKeun Park, “Tomographic Measurement ofDielectric Tensors at Optical Frequency,” Nature Materials March 02, 2022 (https://doi.org/10/1038/s41563-022-01202-8)
-ProfileProfessor YongKeun ParkBiomedical Optics Laboratory (http://bmol.kaist.ac.kr)Department of PhysicsCollege of Natural SciencesKAIST
2022.03.22 View 10203