Ro
-
 Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee Honored with Charles D. Scott Award
Vice President for Research Sang Yup Lee received the 2021 Charles D. Scott Award from the Society for Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology. Distinguished Professor Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST is the first Asian awardee.
The Charles D. Scott Award, initiated in 1995, recognizes individuals who have made significant contributions to enable and further the use of biotechnology to produce fuels and chemicals. The award is named in honor of Dr. Charles D. Scott, who founded the Symposium on Biomaterials, Fuels, and Chemicals and chaired the conference for its first ten years.
Professor Lee has pioneered systems metabolic engineering and developed various micro-organisms capable of producing a wide range of fuels, chemicals, materials, and natural compounds, many of them for the first time. Some of the breakthroughs include the microbial production of gasoline, diacids, diamines, PLA and PLGA polymers, and several natural products.
More recently, his team has developed a microbial strain capable of the mass production of succinic acid, a monomer for manufacturing polyester, with the highest production efficiency to date, as well as a Corynebacterium glutamicum strain capable of producing high-level glutaric acid. They also engineered for the first time a bacterium capable of producing carminic acid, a natural red colorant that is widely used for food and cosmetics.
Professor Lee is one of the Highly Cited Researchers (HCR), ranked in the top 1% by citations in their field by Clarivate Analytics for four consecutive years from 2017. He is the first Korean fellow ever elected into the National Academy of Inventors in the US and one of 13 scholars elected as an International Member of both the National Academy of Sciences and the National Academy of Engineering in the USA.
The awards ceremony will take place during the Symposium on Biomaterials, Fuels, and Chemicals held online from April 26.
2021.04.27 View 11548
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee Honored with Charles D. Scott Award
Vice President for Research Sang Yup Lee received the 2021 Charles D. Scott Award from the Society for Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology. Distinguished Professor Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST is the first Asian awardee.
The Charles D. Scott Award, initiated in 1995, recognizes individuals who have made significant contributions to enable and further the use of biotechnology to produce fuels and chemicals. The award is named in honor of Dr. Charles D. Scott, who founded the Symposium on Biomaterials, Fuels, and Chemicals and chaired the conference for its first ten years.
Professor Lee has pioneered systems metabolic engineering and developed various micro-organisms capable of producing a wide range of fuels, chemicals, materials, and natural compounds, many of them for the first time. Some of the breakthroughs include the microbial production of gasoline, diacids, diamines, PLA and PLGA polymers, and several natural products.
More recently, his team has developed a microbial strain capable of the mass production of succinic acid, a monomer for manufacturing polyester, with the highest production efficiency to date, as well as a Corynebacterium glutamicum strain capable of producing high-level glutaric acid. They also engineered for the first time a bacterium capable of producing carminic acid, a natural red colorant that is widely used for food and cosmetics.
Professor Lee is one of the Highly Cited Researchers (HCR), ranked in the top 1% by citations in their field by Clarivate Analytics for four consecutive years from 2017. He is the first Korean fellow ever elected into the National Academy of Inventors in the US and one of 13 scholars elected as an International Member of both the National Academy of Sciences and the National Academy of Engineering in the USA.
The awards ceremony will take place during the Symposium on Biomaterials, Fuels, and Chemicals held online from April 26.
2021.04.27 View 11548 -
 Microbial Production of a Natural Red Colorant Carminic Acid
Metabolic engineering and computer-simulated enzyme engineering led to the production of carminic acid, a natural red colorant, from bacteria for the first time
A research group at KAIST has engineered a bacterium capable of producing a natural red colorant, carminic acid, which is widely used for food and cosmetics. The research team reported the complete biosynthesis of carminic acid from glucose in engineered Escherichia coli. The strategies will be useful for the design and construction of biosynthetic pathways involving unknown enzymes and consequently the production of diverse industrially important natural products for the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries.
Carminic acid is a natural red colorant widely being used for products such as strawberry milk and lipstick. However, carminic acid has been produced by farming cochineals, a scale insect which only grows in the region around Peru and Canary Islands, followed by complicated multi-step purification processes. Moreover, carminic acid often contains protein contaminants that cause allergies so many people are unwilling to consume products made of insect-driven colorants. On that account, manufacturers around the world are using alternative red colorants despite the fact that carminic acid is one of the most stable natural red colorants.
These challenges inspired the metabolic engineering research group at KAIST to address this issue. Its members include postdoctoral researchers Dongsoo Yang and Woo Dae Jang, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering. This study entitled “Production of carminic acid by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli” was published online in the Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS) on April 2.
This research reports for the first time the development of a bacterial strain capable of producing carminic acid from glucose via metabolic engineering and computer simulation-assisted enzyme engineering. The research group optimized the type II polyketide synthase machinery to efficiently produce the precursor of carminic acid, flavokermesic acid.
Since the enzymes responsible for the remaining two reactions were neither discovered nor functional, biochemical reaction analysis was performed to identify enzymes that can convert flavokermesic acid into carminic acid. Then, homology modeling and docking simulations were performed to enhance the activities of the two identified enzymes. The team could confirm that the final engineered strain could produce carminic acid directly from glucose. The C-glucosyltransferase developed in this study was found to be generally applicable for other natural products as showcased by the successful production of an additional product, aloesin, which is found in aloe leaves.
“The most important part of this research is that unknown enzymes for the production of target natural products were identified and improved by biochemical reaction analyses and computer simulation-assisted enzyme engineering,” says Dr. Dongsoo Yang. He explained the development of a generally applicable C-glucosyltransferase is also useful since C-glucosylation is a relatively unexplored reaction in bacteria including Escherichia coli. Using the C-glucosyltransferase developed in this study, both carminic acid and aloesin were successfully produced from glucose.
“A sustainable and insect-free method of producing carminic acid was achieved for the first time in this study. Unknown or inefficient enzymes have always been a major problem in natural product biosynthesis, and here we suggest one effective solution for solving this problem. As maintaining good health in the aging society is becoming increasingly important, we expect that the technology and strategies developed here will play pivotal roles in producing other valuable natural products of medical or nutritional importance,” said Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee.
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries of the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) through the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea and the KAIST Cross-Generation Collaborative Lab project; Sang Yup Lee and Dongsoo Yang were also supported by Novo Nordisk Foundation in Denmark.
Publication:
Dongsoo Yang, Woo Dae Jang, and Sang Yup Lee. Production of carminic acid by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli. at the Journal of the American Chemical Society. https://doi.org.10.1021/jacs.0c12406
Profile:
Sang Yup Lee, PhD
Distinguished Professor
leesy@kaist.ac.kr
http://mbel.kaist.ac.kr
Metabolic &Biomolecular Engineering National Research Laboratory
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
KAIST
2021.04.06 View 14441
Microbial Production of a Natural Red Colorant Carminic Acid
Metabolic engineering and computer-simulated enzyme engineering led to the production of carminic acid, a natural red colorant, from bacteria for the first time
A research group at KAIST has engineered a bacterium capable of producing a natural red colorant, carminic acid, which is widely used for food and cosmetics. The research team reported the complete biosynthesis of carminic acid from glucose in engineered Escherichia coli. The strategies will be useful for the design and construction of biosynthetic pathways involving unknown enzymes and consequently the production of diverse industrially important natural products for the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries.
Carminic acid is a natural red colorant widely being used for products such as strawberry milk and lipstick. However, carminic acid has been produced by farming cochineals, a scale insect which only grows in the region around Peru and Canary Islands, followed by complicated multi-step purification processes. Moreover, carminic acid often contains protein contaminants that cause allergies so many people are unwilling to consume products made of insect-driven colorants. On that account, manufacturers around the world are using alternative red colorants despite the fact that carminic acid is one of the most stable natural red colorants.
These challenges inspired the metabolic engineering research group at KAIST to address this issue. Its members include postdoctoral researchers Dongsoo Yang and Woo Dae Jang, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering. This study entitled “Production of carminic acid by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli” was published online in the Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS) on April 2.
This research reports for the first time the development of a bacterial strain capable of producing carminic acid from glucose via metabolic engineering and computer simulation-assisted enzyme engineering. The research group optimized the type II polyketide synthase machinery to efficiently produce the precursor of carminic acid, flavokermesic acid.
Since the enzymes responsible for the remaining two reactions were neither discovered nor functional, biochemical reaction analysis was performed to identify enzymes that can convert flavokermesic acid into carminic acid. Then, homology modeling and docking simulations were performed to enhance the activities of the two identified enzymes. The team could confirm that the final engineered strain could produce carminic acid directly from glucose. The C-glucosyltransferase developed in this study was found to be generally applicable for other natural products as showcased by the successful production of an additional product, aloesin, which is found in aloe leaves.
“The most important part of this research is that unknown enzymes for the production of target natural products were identified and improved by biochemical reaction analyses and computer simulation-assisted enzyme engineering,” says Dr. Dongsoo Yang. He explained the development of a generally applicable C-glucosyltransferase is also useful since C-glucosylation is a relatively unexplored reaction in bacteria including Escherichia coli. Using the C-glucosyltransferase developed in this study, both carminic acid and aloesin were successfully produced from glucose.
“A sustainable and insect-free method of producing carminic acid was achieved for the first time in this study. Unknown or inefficient enzymes have always been a major problem in natural product biosynthesis, and here we suggest one effective solution for solving this problem. As maintaining good health in the aging society is becoming increasingly important, we expect that the technology and strategies developed here will play pivotal roles in producing other valuable natural products of medical or nutritional importance,” said Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee.
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries of the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) through the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea and the KAIST Cross-Generation Collaborative Lab project; Sang Yup Lee and Dongsoo Yang were also supported by Novo Nordisk Foundation in Denmark.
Publication:
Dongsoo Yang, Woo Dae Jang, and Sang Yup Lee. Production of carminic acid by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli. at the Journal of the American Chemical Society. https://doi.org.10.1021/jacs.0c12406
Profile:
Sang Yup Lee, PhD
Distinguished Professor
leesy@kaist.ac.kr
http://mbel.kaist.ac.kr
Metabolic &Biomolecular Engineering National Research Laboratory
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
KAIST
2021.04.06 View 14441 -
 Professor Mu-Hyun Baik Honored with the POSCO TJ Park Prize
Professor Mu-Hyun Baik at the Department of Chemistry was honored to be the recipient of the 2021 POSCO TJ Park Prize in Science. The POSCO TJ Park Foundation awards every year the individual or organization which made significant contribution in science, education, community development, philanthropy, and technology.
Professor Baik, a renowned computational chemist in analyzing complicated chemical reactions to understand how molecules behave and how they change. Professor Baik was awarded in recognition of his pioneering research in designing numerous organometallic catalysts with using computational molecular modelling. In 2016, he published in Science on the catalytic borylation of methane that showed how chemical reactions can be carried out using the natural gas methane as a substrate.
In 2020, he reported in Science that electrodes can be used as functional groups with adjustable inductive effects to change the chemical reactivity of molecules that are attached to them, closely mimicking the inductive effect of conventional functional groups. This constitutes a potentially powerful new way of controlling chemical reactions, offering an alternative to preparing derivatives to install electron-withdrawing functional groups.
Joined at KAIST in 2015, Professor Baik also serves as associate director at the Center for Catalytic Hydrocarbon Functionalization at the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) since 2015. Among the many recognitions and awards that he received include the Kavli Fellowship by the Kavli Foundation and the National Academy of Science in the US in 2019 and the 2018 Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel Award by the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation in Germany.
2021.03.11 View 10744
Professor Mu-Hyun Baik Honored with the POSCO TJ Park Prize
Professor Mu-Hyun Baik at the Department of Chemistry was honored to be the recipient of the 2021 POSCO TJ Park Prize in Science. The POSCO TJ Park Foundation awards every year the individual or organization which made significant contribution in science, education, community development, philanthropy, and technology.
Professor Baik, a renowned computational chemist in analyzing complicated chemical reactions to understand how molecules behave and how they change. Professor Baik was awarded in recognition of his pioneering research in designing numerous organometallic catalysts with using computational molecular modelling. In 2016, he published in Science on the catalytic borylation of methane that showed how chemical reactions can be carried out using the natural gas methane as a substrate.
In 2020, he reported in Science that electrodes can be used as functional groups with adjustable inductive effects to change the chemical reactivity of molecules that are attached to them, closely mimicking the inductive effect of conventional functional groups. This constitutes a potentially powerful new way of controlling chemical reactions, offering an alternative to preparing derivatives to install electron-withdrawing functional groups.
Joined at KAIST in 2015, Professor Baik also serves as associate director at the Center for Catalytic Hydrocarbon Functionalization at the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) since 2015. Among the many recognitions and awards that he received include the Kavli Fellowship by the Kavli Foundation and the National Academy of Science in the US in 2019 and the 2018 Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel Award by the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation in Germany.
2021.03.11 View 10744 -
 Rare Mutations May Have Big Impact on Schizophrenia Pathology
- Somatic mutations found only in brain cells disrupt synaptic function. -
Schizophrenia is a neurodevelopmental disorder that disrupts brain activity, producing hallucinations, delusions, and other cognitive disturbances. Researchers have long searched for genetic influences in the disease, but genetic mutations have been identified in only a small fraction—fewer than a quarter—of sequenced patients. Now a study shows that “somatic” gene mutations in brain cells could account for some of the disease’s neuropathology.
The results of the study, led by Professor Jeong Ho Lee at the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering in collaboration with the Stanley Medical Research Institute in the US, appeared in Biological Psychiatry.
Traditional genetic mutations, called germline mutations, occur in sperm or egg cells and are passed on to offspring by their parents. Somatic mutations, in contrast, occur in an embryo after fertilization, and they can show up throughout the body or in isolated pockets of tissues, making them much harder to detect from blood or saliva samples, which are typically used for such sequencing studies.
Recently, more-advanced genetic sequencing techniques have allowed researchers to detect somatic mutations and studies have shown that even mutations present at very low levels can have functional consequences. A previous study hinted that brain somatic mutations were associated with schizophrenia, but it was not powerful enough to cement an association between brain somatic mutations and schizophrenia.
In the current study, the researchers used deep whole-exome sequencing to determine the genetic code of all exomes, the parts of genes that encode proteins. The scientists sequenced postmortem samples from brain, liver, spleen, or heart tissue of 27 people with schizophrenia and 31 control participants allowing them to compare the sequences in the two tissues. Using a powerful analytic technique, the team identified an average of 4.9 somatic single-nucleotide variants, or mutations, in brain samples from people with schizophrenia, and 5.6 somatic single-nucleotide variants in brain samples from control subjects.
Although there were no significant quantitative differences in somatic single-nucleotide variants between schizophrenia and control tissue samples, the researchers found that the mutations in schizophrenia patients were found in genes already associated with schizophrenia. Of the germline mutations that had previously been associated with schizophrenia, the genes affected encode proteins associated with synaptic neural communication, particularly in a brain region called the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex.
In the new analysis, the researchers determined which proteins might be affected by the newly identified somatic mutations. Remarkably, a protein called GRIN2B emerged as highly affected and two patients with schizophrenia carried somatic mutations on the GRIN2B gene itself. GRIN2B is a protein component of NMDA-type glutamate receptors, which are critical for neural signaling. Faulty glutamate receptors have long been suspected of contributing to schizophrenia pathology; GRIN2B ranks among the most-studied genes in schizophrenia. The somatic mutations identified in the study had a variant allele frequency of only ~1%, indicating that the mutations were rare among brain cells as a whole. Nevertheless, they have the potential to create widespread cortical dysfunction.
Professor Lee said, “Besides the comprehensive genetic analysis of brain-only mutations in postmortem tissues from schizophrenia patients, this study experimentally showed the biological consequence of identified somatic mutations, which led to neuronal abnormalities associated with schizophrenia. Thus, this study suggests that brain somatic mutations can be a hidden major contributor to schizophrenia and provides new insights into the molecular genetic architecture of schizophrenia.
John Krystal, MD, editor of Biological Psychiatry, said of the work, "The genetics of schizophrenia has received intensive study for several decades. Now a new possibility emerges, that in some cases, mutations in the DNA of brain cells contributes to the biology of schizophrenia. Remarkably this new biology points to an old schizophrenia story: NMDA glutamate receptor dysfunction. Perhaps the path through which somatic mutations contribute to schizophrenia converges with other sources of abnormalities in glutamate signaling in this disorder."
Professor Lee and the team next want to assess the functional consequences of the somatic mutations. Because of the location of the GRIN2B mutations found in schizophrenia patients, the researchers hypothesized that they might interfere with the receptors’ localization on neurons. Experiments on the cortical neurons of mice showed that the mutations indeed disrupted the receptors’ usual localization to dendrites, the “listening” ends of neurons, which in turn prevented the formation of normal synapses in the neurons. This finding suggests that the somatic mutations could disrupt neural communication, contributing to schizophrenia pathology.
- Profile:
Professor Jeong Ho Lee
Translational Neurogenetics Laboratory ( https://tnl.kaist.ac.kr/)
The Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering
KAIST
(END)
2021.03.11 View 9256
Rare Mutations May Have Big Impact on Schizophrenia Pathology
- Somatic mutations found only in brain cells disrupt synaptic function. -
Schizophrenia is a neurodevelopmental disorder that disrupts brain activity, producing hallucinations, delusions, and other cognitive disturbances. Researchers have long searched for genetic influences in the disease, but genetic mutations have been identified in only a small fraction—fewer than a quarter—of sequenced patients. Now a study shows that “somatic” gene mutations in brain cells could account for some of the disease’s neuropathology.
The results of the study, led by Professor Jeong Ho Lee at the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering in collaboration with the Stanley Medical Research Institute in the US, appeared in Biological Psychiatry.
Traditional genetic mutations, called germline mutations, occur in sperm or egg cells and are passed on to offspring by their parents. Somatic mutations, in contrast, occur in an embryo after fertilization, and they can show up throughout the body or in isolated pockets of tissues, making them much harder to detect from blood or saliva samples, which are typically used for such sequencing studies.
Recently, more-advanced genetic sequencing techniques have allowed researchers to detect somatic mutations and studies have shown that even mutations present at very low levels can have functional consequences. A previous study hinted that brain somatic mutations were associated with schizophrenia, but it was not powerful enough to cement an association between brain somatic mutations and schizophrenia.
In the current study, the researchers used deep whole-exome sequencing to determine the genetic code of all exomes, the parts of genes that encode proteins. The scientists sequenced postmortem samples from brain, liver, spleen, or heart tissue of 27 people with schizophrenia and 31 control participants allowing them to compare the sequences in the two tissues. Using a powerful analytic technique, the team identified an average of 4.9 somatic single-nucleotide variants, or mutations, in brain samples from people with schizophrenia, and 5.6 somatic single-nucleotide variants in brain samples from control subjects.
Although there were no significant quantitative differences in somatic single-nucleotide variants between schizophrenia and control tissue samples, the researchers found that the mutations in schizophrenia patients were found in genes already associated with schizophrenia. Of the germline mutations that had previously been associated with schizophrenia, the genes affected encode proteins associated with synaptic neural communication, particularly in a brain region called the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex.
In the new analysis, the researchers determined which proteins might be affected by the newly identified somatic mutations. Remarkably, a protein called GRIN2B emerged as highly affected and two patients with schizophrenia carried somatic mutations on the GRIN2B gene itself. GRIN2B is a protein component of NMDA-type glutamate receptors, which are critical for neural signaling. Faulty glutamate receptors have long been suspected of contributing to schizophrenia pathology; GRIN2B ranks among the most-studied genes in schizophrenia. The somatic mutations identified in the study had a variant allele frequency of only ~1%, indicating that the mutations were rare among brain cells as a whole. Nevertheless, they have the potential to create widespread cortical dysfunction.
Professor Lee said, “Besides the comprehensive genetic analysis of brain-only mutations in postmortem tissues from schizophrenia patients, this study experimentally showed the biological consequence of identified somatic mutations, which led to neuronal abnormalities associated with schizophrenia. Thus, this study suggests that brain somatic mutations can be a hidden major contributor to schizophrenia and provides new insights into the molecular genetic architecture of schizophrenia.
John Krystal, MD, editor of Biological Psychiatry, said of the work, "The genetics of schizophrenia has received intensive study for several decades. Now a new possibility emerges, that in some cases, mutations in the DNA of brain cells contributes to the biology of schizophrenia. Remarkably this new biology points to an old schizophrenia story: NMDA glutamate receptor dysfunction. Perhaps the path through which somatic mutations contribute to schizophrenia converges with other sources of abnormalities in glutamate signaling in this disorder."
Professor Lee and the team next want to assess the functional consequences of the somatic mutations. Because of the location of the GRIN2B mutations found in schizophrenia patients, the researchers hypothesized that they might interfere with the receptors’ localization on neurons. Experiments on the cortical neurons of mice showed that the mutations indeed disrupted the receptors’ usual localization to dendrites, the “listening” ends of neurons, which in turn prevented the formation of normal synapses in the neurons. This finding suggests that the somatic mutations could disrupt neural communication, contributing to schizophrenia pathology.
- Profile:
Professor Jeong Ho Lee
Translational Neurogenetics Laboratory ( https://tnl.kaist.ac.kr/)
The Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering
KAIST
(END)
2021.03.11 View 9256 -
 Provost Kwang Hyung Lee Elected as the 17th President of KAIST
Provost and Executive Vice President Kwang Hyung Lee was selected as the 17th president of KAIST during a vote of the KAIST Board of Trustees on February 18. He will succeed President Sung-Chul Shin, whose four-year term concludes on February 22.
President-elect Lee, 67, was among the three final candidates who were nominated by the Presidential Search Committee. Upon the selection, President-elect Lee said he will take up new challenges to transform KAIST into the most relevant research university in the world, fostering talents who can work with emerging technologies while pushing for innovative R&D initiatives that will benefit all of humanity.
President-elect Lee is a futurologist who pioneered multidisciplinary studies and research at KAIST. He advocated that the convergence of information, biology, and nano-technologies would be critical for future industries, playing a crucial role in establishing the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering in 2001 and the Moon Soul Graduate School of Future Strategy in 2013. He then served as the inaugural head of both faculties.
President-elect Lee has extensive administrative experience at KAIST, serving as Associate Vice President of the International Office, and Associate Vice President of Academic Affairs since early 2001. He is also serving as a member of the Korea Presidential Education Committee.
An ardent champion of entrepreneurship and startups, he has advised the first generations of KAIST startup entrepreneurs such as Nexon, Idis, Neowiz, and Olaworks. President-elect Lee, drawn to creative thinking and flipped learning, is famous for watching TV upside down. Such pioneering ideas and his unusual thinking style were modeled in the ‘eccentric professor’ role featured on the TV hit drama of ‘KAIST’ from 1999 to 2000.
An alumnus who earned his MS in industrial engineering at KAIST in 1980 after completing his undergraduate studies at Seoul National University, President-elect Lee joined the KAIST faculty in 1985 upon receiving his PhD in computer science from INSA de Lyon in France.
A computer scientist as well as fuzzy theorist whose research area extends to AI, bioinformatics, fuzzy intelligent systems, and foresight methods, Professor Lee has published more than 70 papers in international journals and textbooks on system programming, fuzzy set theory and its applications, and three-dimensional creativity. He also invented a fuzzy elevator, subway operation controller, and AI transportation controller.
A fellow at the Korea Academy of Science and Technology and the National Academy of Engineering of Korea, he was decorated by the Korean government and the French government in recognition of the innovative education and research initiatives he has pursued.
2021.02.18 View 10873
Provost Kwang Hyung Lee Elected as the 17th President of KAIST
Provost and Executive Vice President Kwang Hyung Lee was selected as the 17th president of KAIST during a vote of the KAIST Board of Trustees on February 18. He will succeed President Sung-Chul Shin, whose four-year term concludes on February 22.
President-elect Lee, 67, was among the three final candidates who were nominated by the Presidential Search Committee. Upon the selection, President-elect Lee said he will take up new challenges to transform KAIST into the most relevant research university in the world, fostering talents who can work with emerging technologies while pushing for innovative R&D initiatives that will benefit all of humanity.
President-elect Lee is a futurologist who pioneered multidisciplinary studies and research at KAIST. He advocated that the convergence of information, biology, and nano-technologies would be critical for future industries, playing a crucial role in establishing the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering in 2001 and the Moon Soul Graduate School of Future Strategy in 2013. He then served as the inaugural head of both faculties.
President-elect Lee has extensive administrative experience at KAIST, serving as Associate Vice President of the International Office, and Associate Vice President of Academic Affairs since early 2001. He is also serving as a member of the Korea Presidential Education Committee.
An ardent champion of entrepreneurship and startups, he has advised the first generations of KAIST startup entrepreneurs such as Nexon, Idis, Neowiz, and Olaworks. President-elect Lee, drawn to creative thinking and flipped learning, is famous for watching TV upside down. Such pioneering ideas and his unusual thinking style were modeled in the ‘eccentric professor’ role featured on the TV hit drama of ‘KAIST’ from 1999 to 2000.
An alumnus who earned his MS in industrial engineering at KAIST in 1980 after completing his undergraduate studies at Seoul National University, President-elect Lee joined the KAIST faculty in 1985 upon receiving his PhD in computer science from INSA de Lyon in France.
A computer scientist as well as fuzzy theorist whose research area extends to AI, bioinformatics, fuzzy intelligent systems, and foresight methods, Professor Lee has published more than 70 papers in international journals and textbooks on system programming, fuzzy set theory and its applications, and three-dimensional creativity. He also invented a fuzzy elevator, subway operation controller, and AI transportation controller.
A fellow at the Korea Academy of Science and Technology and the National Academy of Engineering of Korea, he was decorated by the Korean government and the French government in recognition of the innovative education and research initiatives he has pursued.
2021.02.18 View 10873 -
 Highly Deformable Piezoelectric Nanotruss for Tactile Electronics
With the importance of non-contact environments growing due to COVID-19, tactile electronic devices using haptic technology are gaining traction as new mediums of communication.
Haptic technology is being applied in a wide array of fields such as robotics or interactive displays. haptic gloves are being used for augmented information communication technology. Efficient piezoelectric materials that can convert various mechanical stimuli into electrical signals and vice versa are a prerequisite for advancing high-performing haptic technology.
A research team led by Professor Seungbum Hong confirmed the potential of tactile devices by developing ceramic piezoelectric materials that are three times more deformable. For the fabrication of highly deformable nanomaterials, the research team built a zinc oxide hollow nanostructure using proximity field nanopatterning and atomic layered deposition. The piezoelectric coefficient was measured to be approximately 9.2 pm/V and the nanopillar compression test showed an elastic strain limit of approximately 10%, which is more than three times greater than that of the bulk zinc oxide one.
Piezoelectric ceramics have a high piezoelectric coefficient with a low elastic strain limit, whereas the opposite is true for piezoelectric polymers. Therefore, it has been very challenging to obtain good performance in both high piezoelectric coefficients as well as high elastic strain limits. To break the elastic limit of piezoelectric ceramics, the research team introduced a 3D truss-like hollow nanostructure with nanometer-scale thin walls.
According to the Griffith criterion, the fracture strength of a material is inversely proportional to the square root of the preexisting flaw size. However, a large flaw is less likely to occur in a small structure, which, in turn, enhances the strength of the material. Therefore, implementing the form of a 3D truss-like hollow nanostructure with nanometer-scale thin walls can extend the elastic limit of the material. Furthermore, a monolithic 3D structure can withstand large strains in all directions while simultaneously preventing the loss from the bottleneck. Previously, the fracture property of piezoelectric ceramic materials was difficult to control, owing to the large variance in crack sizes. However, the research team structurally limited the crack sizes to manage the fracture properties.
Professor Hong’s results demonstrate the potential for the development of highly deformable ceramic piezoelectric materials by improving the elastic limit using a 3D hollow nanostructure. Since zinc oxide has a relatively low piezoelectric coefficient compared to other piezoelectric ceramic materials, applying the proposed structure to such components promised better results in terms of the piezoelectric activity.
“With the advent of the non-contact era, the importance of emotional communication is increasing. Through the development of novel tactile interaction technologies, in addition to the current visual and auditory communication, mankind will enter a new era where they can communicate with anyone using all five senses regardless of location as if they are with them in person,” Professor Hong said.
“While additional research must be conducted to realize the application of the proposed designs for haptic enhancement devices, this study holds high value in that it resolves one of the most challenging issues in the use of piezoelectric ceramics, specifically opening new possibilities for their application by overcoming their mechanical constraints.
The research was reported in Nano Energy and supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT, the Korea Research Foundation, and the KAIST Global Singularity Research Project.
-Profile: Professor Seungbum Hong
seungbum@kaist.ac.kr
http://mii.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
KAIST
2021.02.02 View 13004
Highly Deformable Piezoelectric Nanotruss for Tactile Electronics
With the importance of non-contact environments growing due to COVID-19, tactile electronic devices using haptic technology are gaining traction as new mediums of communication.
Haptic technology is being applied in a wide array of fields such as robotics or interactive displays. haptic gloves are being used for augmented information communication technology. Efficient piezoelectric materials that can convert various mechanical stimuli into electrical signals and vice versa are a prerequisite for advancing high-performing haptic technology.
A research team led by Professor Seungbum Hong confirmed the potential of tactile devices by developing ceramic piezoelectric materials that are three times more deformable. For the fabrication of highly deformable nanomaterials, the research team built a zinc oxide hollow nanostructure using proximity field nanopatterning and atomic layered deposition. The piezoelectric coefficient was measured to be approximately 9.2 pm/V and the nanopillar compression test showed an elastic strain limit of approximately 10%, which is more than three times greater than that of the bulk zinc oxide one.
Piezoelectric ceramics have a high piezoelectric coefficient with a low elastic strain limit, whereas the opposite is true for piezoelectric polymers. Therefore, it has been very challenging to obtain good performance in both high piezoelectric coefficients as well as high elastic strain limits. To break the elastic limit of piezoelectric ceramics, the research team introduced a 3D truss-like hollow nanostructure with nanometer-scale thin walls.
According to the Griffith criterion, the fracture strength of a material is inversely proportional to the square root of the preexisting flaw size. However, a large flaw is less likely to occur in a small structure, which, in turn, enhances the strength of the material. Therefore, implementing the form of a 3D truss-like hollow nanostructure with nanometer-scale thin walls can extend the elastic limit of the material. Furthermore, a monolithic 3D structure can withstand large strains in all directions while simultaneously preventing the loss from the bottleneck. Previously, the fracture property of piezoelectric ceramic materials was difficult to control, owing to the large variance in crack sizes. However, the research team structurally limited the crack sizes to manage the fracture properties.
Professor Hong’s results demonstrate the potential for the development of highly deformable ceramic piezoelectric materials by improving the elastic limit using a 3D hollow nanostructure. Since zinc oxide has a relatively low piezoelectric coefficient compared to other piezoelectric ceramic materials, applying the proposed structure to such components promised better results in terms of the piezoelectric activity.
“With the advent of the non-contact era, the importance of emotional communication is increasing. Through the development of novel tactile interaction technologies, in addition to the current visual and auditory communication, mankind will enter a new era where they can communicate with anyone using all five senses regardless of location as if they are with them in person,” Professor Hong said.
“While additional research must be conducted to realize the application of the proposed designs for haptic enhancement devices, this study holds high value in that it resolves one of the most challenging issues in the use of piezoelectric ceramics, specifically opening new possibilities for their application by overcoming their mechanical constraints.
The research was reported in Nano Energy and supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT, the Korea Research Foundation, and the KAIST Global Singularity Research Project.
-Profile: Professor Seungbum Hong
seungbum@kaist.ac.kr
http://mii.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
KAIST
2021.02.02 View 13004 -
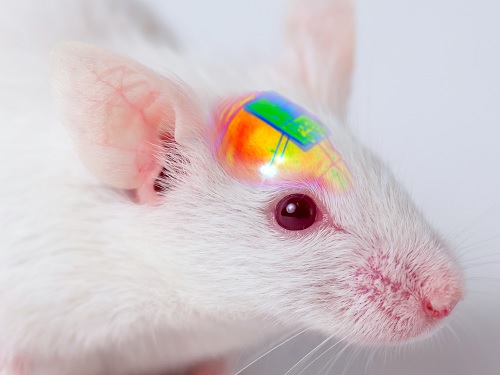 Wirelessly Rechargeable Soft Brain Implant Controls Brain Cells
Researchers have invented a smartphone-controlled soft brain implant that can be recharged wirelessly from outside the body. It enables long-term neural circuit manipulation without the need for periodic disruptive surgeries to replace the battery of the implant. Scientists believe this technology can help uncover and treat psychiatric disorders and neurodegenerative diseases such as addiction, depression, and Parkinson’s.
A group of KAIST researchers and collaborators have engineered a tiny brain implant that can be wirelessly recharged from outside the body to control brain circuits for long periods of time without battery replacement. The device is constructed of ultra-soft and bio-compliant polymers to help provide long-term compatibility with tissue. Geared with micrometer-sized LEDs (equivalent to the size of a grain of salt) mounted on ultrathin probes (the thickness of a human hair), it can wirelessly manipulate target neurons in the deep brain using light.
This study, led by Professor Jae-Woong Jeong, is a step forward from the wireless head-mounted implant neural device he developed in 2019. That previous version could indefinitely deliver multiple drugs and light stimulation treatment wirelessly by using a smartphone. For more, Manipulating Brain Cells by Smartphone.
For the new upgraded version, the research team came up with a fully implantable, soft optoelectronic system that can be remotely and selectively controlled by a smartphone. This research was published on January 22, 2021 in Nature Communications.
The new wireless charging technology addresses the limitations of current brain implants. Wireless implantable device technologies have recently become popular as alternatives to conventional tethered implants, because they help minimize stress and inflammation in freely-moving animals during brain studies, which in turn enhance the lifetime of the devices. However, such devices require either intermittent surgeries to replace discharged batteries, or special and bulky wireless power setups, which limit experimental options as well as the scalability of animal experiments.
“This powerful device eliminates the need for additional painful surgeries to replace an exhausted battery in the implant, allowing seamless chronic neuromodulation,” said Professor Jeong. “We believe that the same basic technology can be applied to various types of implants, including deep brain stimulators, and cardiac and gastric pacemakers, to reduce the burden on patients for long-term use within the body.”
To enable wireless battery charging and controls, researchers developed a tiny circuit that integrates a wireless energy harvester with a coil antenna and a Bluetooth low-energy chip. An alternating magnetic field can harmlessly penetrate through tissue, and generate electricity inside the device to charge the battery. Then the battery-powered Bluetooth implant delivers programmable patterns of light to brain cells using an “easy-to-use” smartphone app for real-time brain control.
“This device can be operated anywhere and anytime to manipulate neural circuits, which makes it a highly versatile tool for investigating brain functions,” said lead author Choong Yeon Kim, a researcher at KAIST.
Neuroscientists successfully tested these implants in rats and demonstrated their ability to suppress cocaine-induced behaviour after the rats were injected with cocaine. This was achieved by precise light stimulation of relevant target neurons in their brains using the smartphone-controlled LEDs. Furthermore, the battery in the implants could be repeatedly recharged while the rats were behaving freely, thus minimizing any physical interruption to the experiments.
“Wireless battery re-charging makes experimental procedures much less complicated,” said the co-lead author Min Jeong Ku, a researcher at Yonsei University’s College of Medicine.
“The fact that we can control a specific behaviour of animals, by delivering light stimulation into the brain just with a simple manipulation of smartphone app, watching freely moving animals nearby, is very interesting and stimulates a lot of imagination,” said Jeong-Hoon Kim, a professor of physiology at Yonsei University’s College of Medicine. “This technology will facilitate various avenues of brain research.”
The researchers believe this brain implant technology may lead to new opportunities for brain research and therapeutic intervention to treat diseases in the brain and other organs.
This work was supported by grants from the National Research Foundation of Korea and the KAIST Global Singularity Research Program.
-Profile
Professor Jae-Woong Jeong
https://www.jeongresearch.org/
School of Electrical Engineering
KAIST
2021.01.26 View 28355
Wirelessly Rechargeable Soft Brain Implant Controls Brain Cells
Researchers have invented a smartphone-controlled soft brain implant that can be recharged wirelessly from outside the body. It enables long-term neural circuit manipulation without the need for periodic disruptive surgeries to replace the battery of the implant. Scientists believe this technology can help uncover and treat psychiatric disorders and neurodegenerative diseases such as addiction, depression, and Parkinson’s.
A group of KAIST researchers and collaborators have engineered a tiny brain implant that can be wirelessly recharged from outside the body to control brain circuits for long periods of time without battery replacement. The device is constructed of ultra-soft and bio-compliant polymers to help provide long-term compatibility with tissue. Geared with micrometer-sized LEDs (equivalent to the size of a grain of salt) mounted on ultrathin probes (the thickness of a human hair), it can wirelessly manipulate target neurons in the deep brain using light.
This study, led by Professor Jae-Woong Jeong, is a step forward from the wireless head-mounted implant neural device he developed in 2019. That previous version could indefinitely deliver multiple drugs and light stimulation treatment wirelessly by using a smartphone. For more, Manipulating Brain Cells by Smartphone.
For the new upgraded version, the research team came up with a fully implantable, soft optoelectronic system that can be remotely and selectively controlled by a smartphone. This research was published on January 22, 2021 in Nature Communications.
The new wireless charging technology addresses the limitations of current brain implants. Wireless implantable device technologies have recently become popular as alternatives to conventional tethered implants, because they help minimize stress and inflammation in freely-moving animals during brain studies, which in turn enhance the lifetime of the devices. However, such devices require either intermittent surgeries to replace discharged batteries, or special and bulky wireless power setups, which limit experimental options as well as the scalability of animal experiments.
“This powerful device eliminates the need for additional painful surgeries to replace an exhausted battery in the implant, allowing seamless chronic neuromodulation,” said Professor Jeong. “We believe that the same basic technology can be applied to various types of implants, including deep brain stimulators, and cardiac and gastric pacemakers, to reduce the burden on patients for long-term use within the body.”
To enable wireless battery charging and controls, researchers developed a tiny circuit that integrates a wireless energy harvester with a coil antenna and a Bluetooth low-energy chip. An alternating magnetic field can harmlessly penetrate through tissue, and generate electricity inside the device to charge the battery. Then the battery-powered Bluetooth implant delivers programmable patterns of light to brain cells using an “easy-to-use” smartphone app for real-time brain control.
“This device can be operated anywhere and anytime to manipulate neural circuits, which makes it a highly versatile tool for investigating brain functions,” said lead author Choong Yeon Kim, a researcher at KAIST.
Neuroscientists successfully tested these implants in rats and demonstrated their ability to suppress cocaine-induced behaviour after the rats were injected with cocaine. This was achieved by precise light stimulation of relevant target neurons in their brains using the smartphone-controlled LEDs. Furthermore, the battery in the implants could be repeatedly recharged while the rats were behaving freely, thus minimizing any physical interruption to the experiments.
“Wireless battery re-charging makes experimental procedures much less complicated,” said the co-lead author Min Jeong Ku, a researcher at Yonsei University’s College of Medicine.
“The fact that we can control a specific behaviour of animals, by delivering light stimulation into the brain just with a simple manipulation of smartphone app, watching freely moving animals nearby, is very interesting and stimulates a lot of imagination,” said Jeong-Hoon Kim, a professor of physiology at Yonsei University’s College of Medicine. “This technology will facilitate various avenues of brain research.”
The researchers believe this brain implant technology may lead to new opportunities for brain research and therapeutic intervention to treat diseases in the brain and other organs.
This work was supported by grants from the National Research Foundation of Korea and the KAIST Global Singularity Research Program.
-Profile
Professor Jae-Woong Jeong
https://www.jeongresearch.org/
School of Electrical Engineering
KAIST
2021.01.26 View 28355 -
 Expanding the Biosynthetic Pathway via Retrobiosynthesis
- Researchers reports a new strategy for the microbial production of multiple short-chain primary amines via retrobiosynthesis. -
KAIST metabolic engineers presented the bio-based production of multiple short-chain primary amines that have a wide range of applications in chemical industries for the first time. The research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering designed the novel biosynthetic pathways for short-chain primary amines by combining retrobiosynthesis and a precursor selection step.
The research team verified the newly designed pathways by confirming the in vivo production of 10 short-chain primary amines by supplying the precursors. Furthermore, the platform Escherichia coli strains were metabolically engineered to produce three proof-of-concept short-chain primary amines from glucose, demonstrating the possibility of the bio-based production of diverse short-chain primary amines from renewable resources. The research team said this study expands the strategy of systematically designing biosynthetic pathways for the production of a group of related chemicals as demonstrated by multiple short-chain primary amines as examples.
Currently, most of the industrial chemicals used in our daily lives are produced with petroleum-based products. However, there are several serious issues with the petroleum industry such as the depletion of fossil fuel reserves and environmental problems including global warming. To solve these problems, the sustainable production of industrial chemicals and materials is being explored with microorganisms as cell factories and renewable non-food biomass as raw materials for alternative to petroleum-based products. The engineering of these microorganisms has increasingly become more efficient and effective with the help of systems metabolic engineering – a practice of engineering the metabolism of a living organism toward the production of a desired metabolite. In this regard, the number of chemicals produced using biomass as a raw material has substantially increased.
Although the scope of chemicals that are producible using microorganisms continues to expand through advances in systems metabolic engineering, the biological production of short-chain primary amines has not yet been reported despite their industrial importance. Short-chain primary amines are the chemicals that have an alkyl or aryl group in the place of a hydrogen atom in ammonia with carbon chain lengths ranging from C1 to C7. Short-chain primary amines have a wide range of applications in chemical industries, for example, as a precursor for pharmaceuticals (e.g., antidiabetic and antihypertensive drugs), agrochemicals (e.g., herbicides, fungicides and insecticides), solvents, and vulcanization accelerators for rubber and plasticizers. The market size of short-chain primary amines was estimated to be more than 4 billion US dollars in 2014.
The main reason why the bio-based production of short-chain primary amines was not yet possible was due to their unknown biosynthetic pathways. Therefore, the team designed synthetic biosynthetic pathways for short-chain primary amines by combining retrobiosynthesis and a precursor selection step. The retrobiosynthesis allowed the systematic design of a biosynthetic pathway for short-chain primary amines by using a set of biochemical reaction rules that describe chemical transformation patterns between a substrate and product molecules at an atomic level.
These multiple precursors predicted for the possible biosynthesis of each short-chain primary amine were sequentially narrowed down by using the precursor selection step for efficient metabolic engineering experiments.
“Our research demonstrates the possibility of the renewable production of short-chain primary amines for the first time. We are planning to increase production efficiencies of short-chain primary amines. We believe that our study will play an important role in the development of sustainable and eco-friendly bio-based industries and the reorganization of the chemical industry, which is mandatory for solving the environmental problems threating the survival of mankind,” said Professor Lee.
This paper titled “Microbial production of multiple short-chain primary amines via retrobiosynthesis” was published in Nature Communications. This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries from the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
-Publication
Dong In Kim, Tong Un Chae, Hyun Uk Kim, Woo Dae Jang, and Sang Yup Lee. Microbial production of multiple short-chain primary amines via retrobiosynthesis. Nature Communications ( https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-020-20423-6)
-Profile
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee
leesy@kaist.ac.kr
Metabolic &Biomolecular Engineering National Research Laboratory
http://mbel.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
KAIST
2021.01.14 View 14283
Expanding the Biosynthetic Pathway via Retrobiosynthesis
- Researchers reports a new strategy for the microbial production of multiple short-chain primary amines via retrobiosynthesis. -
KAIST metabolic engineers presented the bio-based production of multiple short-chain primary amines that have a wide range of applications in chemical industries for the first time. The research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering designed the novel biosynthetic pathways for short-chain primary amines by combining retrobiosynthesis and a precursor selection step.
The research team verified the newly designed pathways by confirming the in vivo production of 10 short-chain primary amines by supplying the precursors. Furthermore, the platform Escherichia coli strains were metabolically engineered to produce three proof-of-concept short-chain primary amines from glucose, demonstrating the possibility of the bio-based production of diverse short-chain primary amines from renewable resources. The research team said this study expands the strategy of systematically designing biosynthetic pathways for the production of a group of related chemicals as demonstrated by multiple short-chain primary amines as examples.
Currently, most of the industrial chemicals used in our daily lives are produced with petroleum-based products. However, there are several serious issues with the petroleum industry such as the depletion of fossil fuel reserves and environmental problems including global warming. To solve these problems, the sustainable production of industrial chemicals and materials is being explored with microorganisms as cell factories and renewable non-food biomass as raw materials for alternative to petroleum-based products. The engineering of these microorganisms has increasingly become more efficient and effective with the help of systems metabolic engineering – a practice of engineering the metabolism of a living organism toward the production of a desired metabolite. In this regard, the number of chemicals produced using biomass as a raw material has substantially increased.
Although the scope of chemicals that are producible using microorganisms continues to expand through advances in systems metabolic engineering, the biological production of short-chain primary amines has not yet been reported despite their industrial importance. Short-chain primary amines are the chemicals that have an alkyl or aryl group in the place of a hydrogen atom in ammonia with carbon chain lengths ranging from C1 to C7. Short-chain primary amines have a wide range of applications in chemical industries, for example, as a precursor for pharmaceuticals (e.g., antidiabetic and antihypertensive drugs), agrochemicals (e.g., herbicides, fungicides and insecticides), solvents, and vulcanization accelerators for rubber and plasticizers. The market size of short-chain primary amines was estimated to be more than 4 billion US dollars in 2014.
The main reason why the bio-based production of short-chain primary amines was not yet possible was due to their unknown biosynthetic pathways. Therefore, the team designed synthetic biosynthetic pathways for short-chain primary amines by combining retrobiosynthesis and a precursor selection step. The retrobiosynthesis allowed the systematic design of a biosynthetic pathway for short-chain primary amines by using a set of biochemical reaction rules that describe chemical transformation patterns between a substrate and product molecules at an atomic level.
These multiple precursors predicted for the possible biosynthesis of each short-chain primary amine were sequentially narrowed down by using the precursor selection step for efficient metabolic engineering experiments.
“Our research demonstrates the possibility of the renewable production of short-chain primary amines for the first time. We are planning to increase production efficiencies of short-chain primary amines. We believe that our study will play an important role in the development of sustainable and eco-friendly bio-based industries and the reorganization of the chemical industry, which is mandatory for solving the environmental problems threating the survival of mankind,” said Professor Lee.
This paper titled “Microbial production of multiple short-chain primary amines via retrobiosynthesis” was published in Nature Communications. This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries from the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
-Publication
Dong In Kim, Tong Un Chae, Hyun Uk Kim, Woo Dae Jang, and Sang Yup Lee. Microbial production of multiple short-chain primary amines via retrobiosynthesis. Nature Communications ( https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-020-20423-6)
-Profile
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee
leesy@kaist.ac.kr
Metabolic &Biomolecular Engineering National Research Laboratory
http://mbel.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
KAIST
2021.01.14 View 14283 -
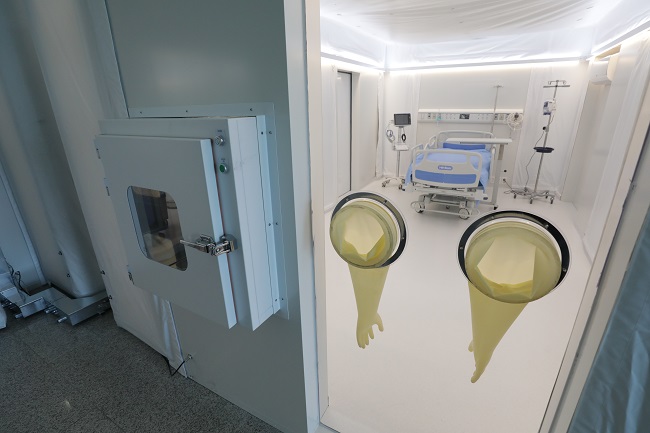 KAIST Mobile Clinic Module to Fill Negative Pressure Ward Shortage
Efficient versatile ready-for-rapid building system of MCM will serve as both a triage unit and bridge center in emergency medical situations
A team from KAIST has developed a low-cost and ready-for-rapid-production negative pressure room called a Mobile Clinic Module (MCM). The MCM is expandable, moveable, and easy to store through a combination of negative pressure frames, air tents, and multi-function panels.
The MCM expects to quickly meet the high demand for negative pressure beds in the nation and eventually many other countries where the third wave of COVID-19 is raging. The module is now ready to be rolled out after a three-week test period at the Korea Cancer Center Hospital.
Professor Tek-Jin Nam’s team swung into action, rapidly working together with researchers, engineers with expertise in mechanical design, and a team of clinical doctors to complete the MCM as one of KAIST’s New Deal R&D initiatives launched last July.
Professor Nam cites ‘expandability’ as the key feature of the MCM. Eventually, it will serve as both a triage unit and bridge center in emergency medical situations.
“The module is a very efficient and versatile unit building system. It takes approximately two hours to build the basic MCM unit, which comprises four negative pressure bed rooms, nurse’s station, locker room, and treatment room. We believe this will significantly contribute to relieving the drastic need for negative pressure beds and provide a place for monitoring patients with moderate symptoms,” said Professor Nam.
“It will also be helpful for managing less-severe patients who need to be monitored daily in quarantined rooms or as bridge stations where on-site medical staff can provide treatment and daily monitoring before hospitalization. These wards can be efficiently deployed either inside or outside existing hospitals.”
The research team specially designed the negative pressure frame to ensure safety level A for the negative pressure room, which is made of a multi-function panel wall and roofed with an air tent. The multi-function panels can hold medical appliances such as ventilators, oxygen and bio-signal monitors.
Positive air pressure devices supply fresh air from outside the tent. An air pump and controller maintain air beam pressure, while filtering exhausted air. An internal air information monitoring system efficiently controls room air pressure and purifies the air.
While a conventional negative pressure bed is reported to cost approximately 3.5 billion KRW (50 billion won for a ward), this module is estimated to cost 0.75 billion won each (10 billion won for a ward), cutting the costs by approximately 80%.
The MCM is designed to be easily transported and relocated due to its volume, weight, and maintainability. This module requires only one-fourth of the volume of existing wards and takes up approximately 40% of their weight. The unit can be transported in a 40-foot container truck.
“We believe this will significantly contribute to relieving the drastic need for negative pressure beds and provide a place for monitoring patients with moderate symptoms. We look forward to the MCM upgrading epidemic management resources around the world.”
Professor Nam’s team is also developing antiviral solutions and devices such as protective gear, sterilizers, and test kits under the KAIST New Deal R&D Initiative that was launched to promptly and proactively respond to the epidemic. More than 45 faculty members and researchers at KAIST are collaborating with industry and clinical hospitals to develop the antiviral technology that will improve preventive measures, diagnoses, and treatment.
2021.01.07 View 13681
KAIST Mobile Clinic Module to Fill Negative Pressure Ward Shortage
Efficient versatile ready-for-rapid building system of MCM will serve as both a triage unit and bridge center in emergency medical situations
A team from KAIST has developed a low-cost and ready-for-rapid-production negative pressure room called a Mobile Clinic Module (MCM). The MCM is expandable, moveable, and easy to store through a combination of negative pressure frames, air tents, and multi-function panels.
The MCM expects to quickly meet the high demand for negative pressure beds in the nation and eventually many other countries where the third wave of COVID-19 is raging. The module is now ready to be rolled out after a three-week test period at the Korea Cancer Center Hospital.
Professor Tek-Jin Nam’s team swung into action, rapidly working together with researchers, engineers with expertise in mechanical design, and a team of clinical doctors to complete the MCM as one of KAIST’s New Deal R&D initiatives launched last July.
Professor Nam cites ‘expandability’ as the key feature of the MCM. Eventually, it will serve as both a triage unit and bridge center in emergency medical situations.
“The module is a very efficient and versatile unit building system. It takes approximately two hours to build the basic MCM unit, which comprises four negative pressure bed rooms, nurse’s station, locker room, and treatment room. We believe this will significantly contribute to relieving the drastic need for negative pressure beds and provide a place for monitoring patients with moderate symptoms,” said Professor Nam.
“It will also be helpful for managing less-severe patients who need to be monitored daily in quarantined rooms or as bridge stations where on-site medical staff can provide treatment and daily monitoring before hospitalization. These wards can be efficiently deployed either inside or outside existing hospitals.”
The research team specially designed the negative pressure frame to ensure safety level A for the negative pressure room, which is made of a multi-function panel wall and roofed with an air tent. The multi-function panels can hold medical appliances such as ventilators, oxygen and bio-signal monitors.
Positive air pressure devices supply fresh air from outside the tent. An air pump and controller maintain air beam pressure, while filtering exhausted air. An internal air information monitoring system efficiently controls room air pressure and purifies the air.
While a conventional negative pressure bed is reported to cost approximately 3.5 billion KRW (50 billion won for a ward), this module is estimated to cost 0.75 billion won each (10 billion won for a ward), cutting the costs by approximately 80%.
The MCM is designed to be easily transported and relocated due to its volume, weight, and maintainability. This module requires only one-fourth of the volume of existing wards and takes up approximately 40% of their weight. The unit can be transported in a 40-foot container truck.
“We believe this will significantly contribute to relieving the drastic need for negative pressure beds and provide a place for monitoring patients with moderate symptoms. We look forward to the MCM upgrading epidemic management resources around the world.”
Professor Nam’s team is also developing antiviral solutions and devices such as protective gear, sterilizers, and test kits under the KAIST New Deal R&D Initiative that was launched to promptly and proactively respond to the epidemic. More than 45 faculty members and researchers at KAIST are collaborating with industry and clinical hospitals to develop the antiviral technology that will improve preventive measures, diagnoses, and treatment.
2021.01.07 View 13681 -
 DeepTFactor Predicts Transcription Factors
A deep learning-based tool predicts transcription factors using protein sequences as inputs
A joint research team from KAIST and UCSD has developed a deep neural network named DeepTFactor that predicts transcription factors from protein sequences. DeepTFactor will serve as a useful tool for understanding the regulatory systems of organisms, accelerating the use of deep learning for solving biological problems.
A transcription factor is a protein that specifically binds to DNA sequences to control the transcription initiation. Analyzing transcriptional regulation enables the understanding of how organisms control gene expression in response to genetic or environmental changes. In this regard, finding the transcription factor of an organism is the first step in the analysis of the transcriptional regulatory system of an organism.
Previously, transcription factors have been predicted by analyzing sequence homology with already characterized transcription factors or by data-driven approaches such as machine learning. Conventional machine learning models require a rigorous feature selection process that relies on domain expertise such as calculating the physicochemical properties of molecules or analyzing the homology of biological sequences. Meanwhile, deep learning can inherently learn latent features for the specific task.
A joint research team comprised of Ph.D. candidate Gi Bae Kim and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, and Ye Gao and Professor Bernhard O. Palsson of the Department of Biochemical Engineering at UCSD reported a deep learning-based tool for the prediction of transcription factors. Their research paper “DeepTFactor: A deep learning-based tool for the prediction of transcription factors” was published online in PNAS.
Their article reports the development of DeepTFactor, a deep learning-based tool that predicts whether a given protein sequence is a transcription factor using three parallel convolutional neural networks. The joint research team predicted 332 transcription factors of Escherichia coli K-12 MG1655 using DeepTFactor and the performance of DeepTFactor by experimentally confirming the genome-wide binding sites of three predicted transcription factors (YqhC, YiaU, and YahB).
The joint research team further used a saliency method to understand the reasoning process of DeepTFactor. The researchers confirmed that even though information on the DNA binding domains of the transcription factor was not explicitly given the training process, DeepTFactor implicitly learned and used them for prediction. Unlike previous transcription factor prediction tools that were developed only for protein sequences of specific organisms, DeepTFactor is expected to be used in the analysis of the transcription systems of all organisms at a high level of performance.
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “DeepTFactor can be used to discover unknown transcription factors from numerous protein sequences that have not yet been characterized. It is expected that DeepTFactor will serve as an important tool for analyzing the regulatory systems of organisms of interest.”
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries from the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation of Korea.
-Publication
Gi Bae Kim, Ye Gao, Bernhard O. Palsson, and Sang Yup Lee. DeepTFactor: A deep learning-based tool for the prediction of transcription factors. (https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas202117118)
-Profile
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee
leesy@kaist.ac.kr
Metabolic &Biomolecular Engineering National Research Laboratory
http://mbel.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
KAIST
2021.01.05 View 11279
DeepTFactor Predicts Transcription Factors
A deep learning-based tool predicts transcription factors using protein sequences as inputs
A joint research team from KAIST and UCSD has developed a deep neural network named DeepTFactor that predicts transcription factors from protein sequences. DeepTFactor will serve as a useful tool for understanding the regulatory systems of organisms, accelerating the use of deep learning for solving biological problems.
A transcription factor is a protein that specifically binds to DNA sequences to control the transcription initiation. Analyzing transcriptional regulation enables the understanding of how organisms control gene expression in response to genetic or environmental changes. In this regard, finding the transcription factor of an organism is the first step in the analysis of the transcriptional regulatory system of an organism.
Previously, transcription factors have been predicted by analyzing sequence homology with already characterized transcription factors or by data-driven approaches such as machine learning. Conventional machine learning models require a rigorous feature selection process that relies on domain expertise such as calculating the physicochemical properties of molecules or analyzing the homology of biological sequences. Meanwhile, deep learning can inherently learn latent features for the specific task.
A joint research team comprised of Ph.D. candidate Gi Bae Kim and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, and Ye Gao and Professor Bernhard O. Palsson of the Department of Biochemical Engineering at UCSD reported a deep learning-based tool for the prediction of transcription factors. Their research paper “DeepTFactor: A deep learning-based tool for the prediction of transcription factors” was published online in PNAS.
Their article reports the development of DeepTFactor, a deep learning-based tool that predicts whether a given protein sequence is a transcription factor using three parallel convolutional neural networks. The joint research team predicted 332 transcription factors of Escherichia coli K-12 MG1655 using DeepTFactor and the performance of DeepTFactor by experimentally confirming the genome-wide binding sites of three predicted transcription factors (YqhC, YiaU, and YahB).
The joint research team further used a saliency method to understand the reasoning process of DeepTFactor. The researchers confirmed that even though information on the DNA binding domains of the transcription factor was not explicitly given the training process, DeepTFactor implicitly learned and used them for prediction. Unlike previous transcription factor prediction tools that were developed only for protein sequences of specific organisms, DeepTFactor is expected to be used in the analysis of the transcription systems of all organisms at a high level of performance.
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “DeepTFactor can be used to discover unknown transcription factors from numerous protein sequences that have not yet been characterized. It is expected that DeepTFactor will serve as an important tool for analyzing the regulatory systems of organisms of interest.”
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries from the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation of Korea.
-Publication
Gi Bae Kim, Ye Gao, Bernhard O. Palsson, and Sang Yup Lee. DeepTFactor: A deep learning-based tool for the prediction of transcription factors. (https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas202117118)
-Profile
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee
leesy@kaist.ac.kr
Metabolic &Biomolecular Engineering National Research Laboratory
http://mbel.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
KAIST
2021.01.05 View 11279 -
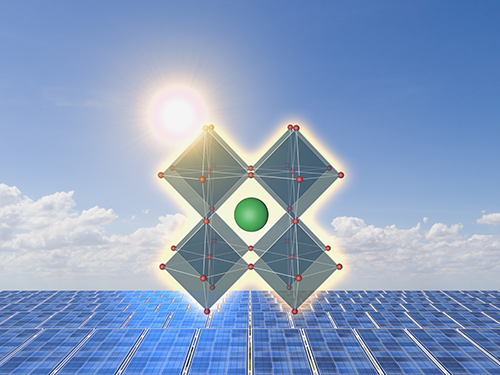 Extremely Stable Perovskite Nanoparticles Films for Next-Generation Displays
Researchers have reported an extremely stable cross-linked perovskite nanoparticle that maintains a high photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY) for 1.5 years in air and harsh liquid environments. This stable material’s design strategies, which addressed one of the most critical problems limiting their practical application, provide a breakthrough for the commercialization of perovskite nanoparticles in next-generation displays and bio-related applications.
According to the research team led by Professor Byeong-Soo Bae, their development can survive in severe environments such as water, various polar solvents, and high temperature with high humidity without additional encapsulation. This development is expected to enable perovskite nanoparticles to be applied to high color purity display applications as a practical color converting material. This result was published as the inside front cover article in Advanced Materials.
Perovskites, which consist of organics, metals, and halogen elements, have emerged as key elements in various optoelectronic applications. The power conversion efficiency of photovoltaic cells based on perovskites light absorbers has been rapidly increased. Perovskites are also great promise as a light emitter in display applications because of their low material cost, facile wavelength tunability, high (PLQY), very narrow emission band width, and wider color gamut than inorganic semiconducting nanocrystals and organic emitters. Thanks to these advantages, perovskites have been identified as a key color-converting material for next-generation high color-purity displays. In particular, perovskites are the only luminescence material that meets Rec. 2020 which is a new color standard in display industry.
However, perovskites are very unstable against heat, moisture, and light, which makes them almost impossible to use in practical applications. To solve these problems, many researchers have attempted to physically prevent perovskites from coming into contact with water molecules by passivating the perovskite grain and nanoparticle surfaces with organic ligands or inorganic shell materials, or by fabricating perovskite-polymer nanocomposites. These methods require complex processes and have limited stability in ambient air and water. Furthermore, stable perovskite nanoparticles in the various chemical environments and high temperatures with high humidity have not been reported yet.
The research team in collaboration with Seoul National University develops siloxane-encapsulated perovskite nanoparticle composite films. Here, perovskite nanoparticles are chemically crosslinked with thermally stable siloxane molecules, thereby significantly improving the stability of the perovskite nanoparticles without the need for any additional protecting layer.
Siloxane-encapsulated perovskite nanoparticle composite films exhibited a high PLQY (> 70%) value, which can be maintained over 600 days in water, various chemicals (alcohol, strong acidic and basic solutions), and high temperatures with high humidity (85℃/85%). The research team investigated the mechanisms impacting the chemical crosslinking and water molecule-induced stabilization of perovskite nanoparticles through various photo-physical analysis and density-functional theory calculation.
The research team confirmed that displays based on their siloxane-perovskite nanoparticle composite films exhibited higher PLQY and a wider color gamut than those of Cd-based quantum dots and demonstrated perfect color converting properties on commercial mobile phone screens. Unlike what was commonly believed in the halide perovskite field, the composite films showed excellent bio-compatibility because the siloxane matrix prevents the toxicity of Pb in perovskite nanoparticle.
By using this technology, the instability of perovskite materials, which is the biggest challenge for practical applications, is greatly improved through simple encapsulation method.
“Perovskite nanoparticle is the only photoluminescent material that can meet the next generation display color standard. Nevertheless, there has been reluctant to commercialize it due to its moisture vulnerability. The newly developed siloxane encapsulation technology will trigger more research on perovskite nanoparticles as color conversion materials and will accelerate early commercialization,” Professor Bae said.
This work was supported by the Wearable Platform Materials Technology Center (WMC) of the Engineering Research Center (ERC) Project, and the Leadership Research Program funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
-Publication:
Junho Jang, Young-Hoon Kim, Sunjoon Park, Dongsuk Yoo, Hyunjin Cho, Jinhyeong Jang, Han Beom Jeong, Hyunhwan Lee, Jong Min Yuk, Chan Beum Park, Duk Young Jeon, Yong-Hyun Kim, Byeong-Soo Bae, and Tae-Woo Lee. “Extremely Stable Luminescent Crosslinked Perovskite Nanoparticles under Harsh Environments over 1.5 Years” Advanced Materials, 2020, 2005255. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202005255.
Link to download the full-text paper:
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.202005255
-Profile: Prof. Byeong-Soo Bae (Corresponding author)
bsbae@kaist.ac.kr
Lab. of Optical Materials & Coating
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
2020.12.29 View 16164
Extremely Stable Perovskite Nanoparticles Films for Next-Generation Displays
Researchers have reported an extremely stable cross-linked perovskite nanoparticle that maintains a high photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY) for 1.5 years in air and harsh liquid environments. This stable material’s design strategies, which addressed one of the most critical problems limiting their practical application, provide a breakthrough for the commercialization of perovskite nanoparticles in next-generation displays and bio-related applications.
According to the research team led by Professor Byeong-Soo Bae, their development can survive in severe environments such as water, various polar solvents, and high temperature with high humidity without additional encapsulation. This development is expected to enable perovskite nanoparticles to be applied to high color purity display applications as a practical color converting material. This result was published as the inside front cover article in Advanced Materials.
Perovskites, which consist of organics, metals, and halogen elements, have emerged as key elements in various optoelectronic applications. The power conversion efficiency of photovoltaic cells based on perovskites light absorbers has been rapidly increased. Perovskites are also great promise as a light emitter in display applications because of their low material cost, facile wavelength tunability, high (PLQY), very narrow emission band width, and wider color gamut than inorganic semiconducting nanocrystals and organic emitters. Thanks to these advantages, perovskites have been identified as a key color-converting material for next-generation high color-purity displays. In particular, perovskites are the only luminescence material that meets Rec. 2020 which is a new color standard in display industry.
However, perovskites are very unstable against heat, moisture, and light, which makes them almost impossible to use in practical applications. To solve these problems, many researchers have attempted to physically prevent perovskites from coming into contact with water molecules by passivating the perovskite grain and nanoparticle surfaces with organic ligands or inorganic shell materials, or by fabricating perovskite-polymer nanocomposites. These methods require complex processes and have limited stability in ambient air and water. Furthermore, stable perovskite nanoparticles in the various chemical environments and high temperatures with high humidity have not been reported yet.
The research team in collaboration with Seoul National University develops siloxane-encapsulated perovskite nanoparticle composite films. Here, perovskite nanoparticles are chemically crosslinked with thermally stable siloxane molecules, thereby significantly improving the stability of the perovskite nanoparticles without the need for any additional protecting layer.
Siloxane-encapsulated perovskite nanoparticle composite films exhibited a high PLQY (> 70%) value, which can be maintained over 600 days in water, various chemicals (alcohol, strong acidic and basic solutions), and high temperatures with high humidity (85℃/85%). The research team investigated the mechanisms impacting the chemical crosslinking and water molecule-induced stabilization of perovskite nanoparticles through various photo-physical analysis and density-functional theory calculation.
The research team confirmed that displays based on their siloxane-perovskite nanoparticle composite films exhibited higher PLQY and a wider color gamut than those of Cd-based quantum dots and demonstrated perfect color converting properties on commercial mobile phone screens. Unlike what was commonly believed in the halide perovskite field, the composite films showed excellent bio-compatibility because the siloxane matrix prevents the toxicity of Pb in perovskite nanoparticle.
By using this technology, the instability of perovskite materials, which is the biggest challenge for practical applications, is greatly improved through simple encapsulation method.
“Perovskite nanoparticle is the only photoluminescent material that can meet the next generation display color standard. Nevertheless, there has been reluctant to commercialize it due to its moisture vulnerability. The newly developed siloxane encapsulation technology will trigger more research on perovskite nanoparticles as color conversion materials and will accelerate early commercialization,” Professor Bae said.
This work was supported by the Wearable Platform Materials Technology Center (WMC) of the Engineering Research Center (ERC) Project, and the Leadership Research Program funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
-Publication:
Junho Jang, Young-Hoon Kim, Sunjoon Park, Dongsuk Yoo, Hyunjin Cho, Jinhyeong Jang, Han Beom Jeong, Hyunhwan Lee, Jong Min Yuk, Chan Beum Park, Duk Young Jeon, Yong-Hyun Kim, Byeong-Soo Bae, and Tae-Woo Lee. “Extremely Stable Luminescent Crosslinked Perovskite Nanoparticles under Harsh Environments over 1.5 Years” Advanced Materials, 2020, 2005255. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202005255.
Link to download the full-text paper:
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.202005255
-Profile: Prof. Byeong-Soo Bae (Corresponding author)
bsbae@kaist.ac.kr
Lab. of Optical Materials & Coating
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
2020.12.29 View 16164 -
 Astrocytes Eat Connections to Maintain Plasticity in Adult Brains
Developing brains constantly sprout new neuronal connections called synapses as they learn and remember. Important connections — the ones that are repeatedly introduced, such as how to avoid danger — are nurtured and reinforced, while connections deemed unnecessary are pruned away. Adult brains undergo similar pruning, but it was unclear how or why synapses in the adult brain get eliminated.
Now, a team of KAIST researchers has found the mechanism underlying plasticity and, potentially, neurological disorders in adult brains. They published their findings on December 23 in Nature.
“Our findings have profound implications for our understanding of how neural circuits change during learning and memory, as well as in diseases,” said paper author Won-Suk Chung, an assistant professor in the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST. “Changes in synapse number have strong association with the prevalence of various neurological disorders, such as autism spectrum disorder, schizophrenia, frontotemporal dementia, and several forms of seizures.”
Gray matter in the brain contains microglia and astrocytes, two complementary cells that, among other things, support neurons and synapses. Microglial are a frontline immunity defense, responsible for eating pathogens and dead cells, and astrocytes are star-shaped cells that help structure the brain and maintain homeostasis by helping to control signaling between neurons. According to Professor Chung, it is generally thought that microglial eat synapses as part of its clean-up effort in a process known as phagocytosis.
“Using novel tools, we show that, for the first time, it is astrocytes and not microglia that constantly eliminate excessive and unnecessary adult excitatory synaptic connections in response to neuronal activity,” Professor Chung said. “Our paper challenges the general consensus in this field that microglia are the primary synapse phagocytes that control synapse numbers in the brain.”
Professor Chung and his team developed a molecular sensor to detect synapse elimination by glial cells and quantified how often and by which type of cell synapses were eliminated. They also deployed it in a mouse model without MEGF10, the gene that allows astrocytes to eliminate synapses. Adult animals with this defective astrocytic phagocytosis had unusually increased excitatory synapse numbers in the hippocampus. Through a collaboration with Dr. Hyungju Park at KBRI, they showed that these increased excitatory synapses are functionally impaired, which cause defective learning and memory formation in MEGF10 deleted animals.
“Through this process, we show that, at least in the adult hippocampal CA1 region, astrocytes are the major player in eliminating synapses, and this astrocytic function is essential for controlling synapse number and plasticity,” Chung said.
Professor Chung noted that researchers are only beginning to understand how synapse elimination affects maturation and homeostasis in the brain. In his group’s preliminary data in other brain regions, it appears that each region has different rates of synaptic elimination by astrocytes. They suspect a variety of internal and external factors are influencing how astrocytes modulate each regional circuit, and plan to elucidate these variables.
“Our long-term goal is understanding how astrocyte-mediated synapse turnover affects the initiation and progression of various neurological disorders,” Professor Chung said. “It is intriguing to postulate that modulating astrocytic phagocytosis to restore synaptic connectivity may be a novel strategy in treating various brain disorders.”
This work was supported by the Samsung Science & Technology Foundation, the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Korea Brain Research Institute basic research program.
Other contributors include Joon-Hyuk Lee and Se Young Lee, Department of Biological Sciences, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST); Ji-young Kim, Hyoeun Lee and Hyungju Park; Research Group for Neurovascular Unit, Korea Brain Research Institute (KBRI); Seulgi Noh, and Ji Young Mun, Research Group for Neural Circuit, KBRI. Kim, Noh and Park are also affiliated with the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST).
-Profile
Professor Won-Suk Chung
Department of Biological Sciences
Gliabiology Lab (https://www.kaistglia.org/)
KAIST
-Publication
"Astrocytes phagocytose adult hippocampal synapses for circuit homeostasis"
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-03060-3
2020.12.24 View 13368
Astrocytes Eat Connections to Maintain Plasticity in Adult Brains
Developing brains constantly sprout new neuronal connections called synapses as they learn and remember. Important connections — the ones that are repeatedly introduced, such as how to avoid danger — are nurtured and reinforced, while connections deemed unnecessary are pruned away. Adult brains undergo similar pruning, but it was unclear how or why synapses in the adult brain get eliminated.
Now, a team of KAIST researchers has found the mechanism underlying plasticity and, potentially, neurological disorders in adult brains. They published their findings on December 23 in Nature.
“Our findings have profound implications for our understanding of how neural circuits change during learning and memory, as well as in diseases,” said paper author Won-Suk Chung, an assistant professor in the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST. “Changes in synapse number have strong association with the prevalence of various neurological disorders, such as autism spectrum disorder, schizophrenia, frontotemporal dementia, and several forms of seizures.”
Gray matter in the brain contains microglia and astrocytes, two complementary cells that, among other things, support neurons and synapses. Microglial are a frontline immunity defense, responsible for eating pathogens and dead cells, and astrocytes are star-shaped cells that help structure the brain and maintain homeostasis by helping to control signaling between neurons. According to Professor Chung, it is generally thought that microglial eat synapses as part of its clean-up effort in a process known as phagocytosis.
“Using novel tools, we show that, for the first time, it is astrocytes and not microglia that constantly eliminate excessive and unnecessary adult excitatory synaptic connections in response to neuronal activity,” Professor Chung said. “Our paper challenges the general consensus in this field that microglia are the primary synapse phagocytes that control synapse numbers in the brain.”
Professor Chung and his team developed a molecular sensor to detect synapse elimination by glial cells and quantified how often and by which type of cell synapses were eliminated. They also deployed it in a mouse model without MEGF10, the gene that allows astrocytes to eliminate synapses. Adult animals with this defective astrocytic phagocytosis had unusually increased excitatory synapse numbers in the hippocampus. Through a collaboration with Dr. Hyungju Park at KBRI, they showed that these increased excitatory synapses are functionally impaired, which cause defective learning and memory formation in MEGF10 deleted animals.
“Through this process, we show that, at least in the adult hippocampal CA1 region, astrocytes are the major player in eliminating synapses, and this astrocytic function is essential for controlling synapse number and plasticity,” Chung said.
Professor Chung noted that researchers are only beginning to understand how synapse elimination affects maturation and homeostasis in the brain. In his group’s preliminary data in other brain regions, it appears that each region has different rates of synaptic elimination by astrocytes. They suspect a variety of internal and external factors are influencing how astrocytes modulate each regional circuit, and plan to elucidate these variables.
“Our long-term goal is understanding how astrocyte-mediated synapse turnover affects the initiation and progression of various neurological disorders,” Professor Chung said. “It is intriguing to postulate that modulating astrocytic phagocytosis to restore synaptic connectivity may be a novel strategy in treating various brain disorders.”
This work was supported by the Samsung Science & Technology Foundation, the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Korea Brain Research Institute basic research program.
Other contributors include Joon-Hyuk Lee and Se Young Lee, Department of Biological Sciences, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST); Ji-young Kim, Hyoeun Lee and Hyungju Park; Research Group for Neurovascular Unit, Korea Brain Research Institute (KBRI); Seulgi Noh, and Ji Young Mun, Research Group for Neural Circuit, KBRI. Kim, Noh and Park are also affiliated with the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST).
-Profile
Professor Won-Suk Chung
Department of Biological Sciences
Gliabiology Lab (https://www.kaistglia.org/)
KAIST
-Publication
"Astrocytes phagocytose adult hippocampal synapses for circuit homeostasis"
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-03060-3
2020.12.24 View 13368