-
-
 research KAIST Uses AI to Discover Optimal New Material for Removing Radioactive Iodine Contamination
research KAIST Uses AI to Discover Optimal New Material for Removing Radioactive Iodine ContaminationManaging radioactive waste is one of the core challenges in the use of nuclear energy. In particular, radioactive iodine poses serious environmental and health risks due to its long half-life (15.7 million years in the case of I-129), high mobility, and toxicity to living organisms. A Korean research team has successfully used artificial intelligence to discover a new material that can remove io...
-
 event 2025 KAIST Global Entrepreneurship Summer School Concludes Successfully in Silicon Valley
event 2025 KAIST Global Entrepreneurship Summer School Concludes Successfully in Silicon ValleyThe “2025 KAIST Global Entrepreneurship Summer School (2025 KAIST GESS),” organized by the Office of Global Initiative of the KAIST International Office (Vice President So Young Kim), successfully concluded. Now in its fourth year, the program was designed to provide KAIST students with firsthand experience of the world’s leading startup ecosystem in Silicon Valley, USA, and to strengthen ...
-
-
-
 research KAIST Enhances Immunotherapy for Difficult-to-Treat Brain Tumors with Gut Microbiota
research KAIST Enhances Immunotherapy for Difficult-to-Treat Brain Tumors with Gut MicrobiotaAdvanced treatments, known as immunotherapies that activate T cells—our body's immune cells—to eliminate cancer cells, have shown limited efficacy as standalone therapies for glioblastoma, the most lethal form of brain tumor. This is due to their minimal response to glioblastoma and high resistance to treatment.
-
 research High-Resolution Spectrometer that Fits into Smartphones Developed by KAIST Researchers
research High-Resolution Spectrometer that Fits into Smartphones Developed by KAIST ResearchersColor, as the way light\`s wavelength is perceived by the human eye, goes beyond a simple aesthetic element, containing important scientific information like a substance\`s composition or state. Spectrometers are optical devices that analyze material properties by decomposing light into its constituent wavelengths, and they are widely used in various scientific and industrial fields, including m...
-
-
-
 research KAIST Identifies Master Regulator Blocking Immunotherapy, Paving the Way for a New Lung Cancer Treatment
research KAIST Identifies Master Regulator Blocking Immunotherapy, Paving the Way for a New Lung Cancer TreatmentKAIST researchers have discovered that \`DEAD-box helicases 54 (DDX54)\`, a type of RNA-binding protein, is the master regulator that hinders the effectiveness of immunotherapy—opening a new path for lung cancer treatment.
-
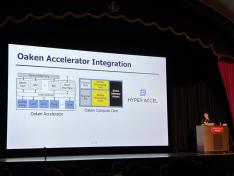 research Development of Core NPU Technology to Improve ChatGPT Inference Performance by Over 60%
research Development of Core NPU Technology to Improve ChatGPT Inference Performance by Over 60%Latest generative AI models such as OpenAI's ChatGPT-4 and Google's Gemini 2.5 require not only high memory bandwidth but also large memory capacity. This is why generative AI cloud operating companies like Microsoft and Google purchase hundreds of thousands of NVIDIA GPUs. As a solution to address the core challenges of building such high-performance AI infrastructure, Korean ...
-
-
 research KAIST Successfully Implements 3D Brain-Mimicking Platform with 6x Higher Precision
research KAIST Successfully Implements 3D Brain-Mimicking Platform with 6x Higher Precision<(From left) Dr. Dongjo Yoon, Professor Je-Kyun Park from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, (upper right) Professor Yoonkey Nam, Dr. Soo Jee Kim> Existing three-dimensional (3D) neuronal culture technology has limitations in brain research due to the difficulty of precisely replicating the brain's complex multilayered structure and the lack of a platform that can simultaneously analyze both structure and function. A KAIST research team has successfully developed an integrated platform that can implement brain-like layered neuronal structures using 3D printing technology and precisely measure neuronal activity within them. KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 16th of July that a joint research team led by Professors Je-Kyun Park and Yoonkey Nam from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering has developed an integrated platform capable of fabricating high-resolution 3D multilayer neuronal networks using low-viscosity natural hydrogels with mechanical properties similar to brain tissue, and simultaneously analyzing their structural and functional connectivity. Conventional bioprinting technology uses high-viscosity bioinks for structural stability, but this limits neuronal proliferation and neurite growth. Conversely, neural cell-friendly low-viscosity hydrogels are difficult to precisely pattern, leading to a fundamental trade-off between structural stability and biological function. The research team completed a sophisticated and stable brain-mimicking platform by combining three key technologies that enable the precise creation of brain structure with dilute gels, accurate alignment between layers, and simultaneous observation of neuronal activity. The three core technologies are: ▲ 'Capillary Pinning Effect' technology, which enables the dilute gel (hydrogel) to adhere firmly to a stainless steel mesh (micromesh) to prevent it from flowing, thereby reproducing brain structures with six times greater precision (resolution of 500 μm or less) than conventional methods; ▲ the '3D Printing Aligner,' a cylindrical design that ensures the printed layers are precisely stacked without misalignment, guaranteeing the accurate assembly of multilayer structures and stable integration with microelectrode chips; and ▲ 'Dual-mode Analysis System' technology, which simultaneously measures electrical signals from below and observes cell activity with light (calcium imaging) from above, allowing for the simultaneous verification of the functional operation of interlayer connections through multiple methods. < Figure 1. Platform integrating brain-structure-mimicking neural network model construction and functional measurement technology> The research team successfully implemented a three-layered mini-brain structure using 3D printing with a fibrin hydrogel, which has elastic properties similar to those of the brain, and experimentally verified the process of actual neural cells transmitting and receiving signals within it. Cortical neurons were placed in the upper and lower layers, while the middle layer was left empty but designed to allow neurons to penetrate and connect through it. Electrical signals were measured from the lower layer using a microsensor (electrode chip), and cell activity was observed from the upper layer using light (calcium imaging). The results showed that when electrical stimulation was applied, neural cells in both upper and lower layers responded simultaneously. When a synapse-blocking agent (synaptic blocker) was introduced, the response decreased, proving that the neural cells were genuinely connected and transmitting signals. Professor Je-Kyun Park of KAIST explained, "This research is a joint development achievement of an integrated platform that can simultaneously reproduce the complex multilayered structure and function of brain tissue. Compared to existing technologies where signal measurement was impossible for more than 14 days, this platform maintains a stable microelectrode chip interface for over 27 days, allowing the real-time analysis of structure-function relationships. It can be utilized in various brain research fields such as neurological disease modeling, brain function research, neurotoxicity assessment, and neuroprotective drug screening in the future." <Figure 2. Integration process of stacked bioprinting technology and microelectrode chip> The research, in which Dr. Soo Jee Kim and Dr. Dongjo Yoon from KAIST's Department of Bio and Brain Engineering participated as co-first authors, was published online in the international journal 'Biosensors and Bioelectronics' on June 11, 2025. ※Paper: Hybrid biofabrication of multilayered 3D neuronal networks with structural and functional interlayer connectivity ※DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2025.117688
-
 research KAIST Develops Robots That React to Danger Like Humans
research KAIST Develops Robots That React to Danger Like Humans<(From left) Ph.D candidate See-On Park, Professor Jongwon Lee, and Professor Shinhyun Choi> In the midst of the co-development of artificial intelligence and robotic advancements, developing technologies that enable robots to efficiently perceive and respond to their surroundings like humans has become a crucial task. In this context, Korean researchers are gaining attention for newly implementing an artificial sensory nervous system that mimics the sensory nervous system of living organisms without the need for separate complex software or circuitry. This breakthrough technology is expected to be applied in fields such as in ultra-small robots and robotic prosthetics, where intelligent and energy-efficient responses to external stimuli are essential. KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on July15th that a joint research team led by Endowed Chair Professor Shinhyun Choi of the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST and Professor Jongwon Lee of the Department of Semiconductor Convergence at Chungnam National University (President Jung Kyum Kim) developed a next-generation neuromorphic semiconductor-based artificial sensory nervous system. This system mimics the functions of a living organism's sensory nervous system, and enables a new type of robotic system that can efficiently responds to external stimuli. In nature, animals — including humans — ignore safe or familiar stimuli and selectively react sensitively to important or dangerous ones. This selective response helps prevent unnecessary energy consumption while maintaining rapid awareness of critical signals. For instance, the sound of an air conditioner or the feel of clothing against the skin soon become familiar and are disregarded. However, if someone calls your name or a sharp object touches your skin, a rapid focus and response occur. These behaviors are regulated by the 'habituation' and 'sensitization' functions in the sensory nervous system. Attempts have been consistently made to apply these sensory nervous system functions of living organisms in order to create robots that efficiently respond to external environments like humans. However, implementing complex neural characteristics such as habituation and sensitization in robots has faced difficulties in miniaturization and energy efficiency due to the need for separate software or complex circuitry. In particular, there have been attempts to utilize memristors, a neuromorphic semiconductor. A memristor is a next-generation electrical device, which has been widely utilized as an artificial synapse due to its ability to store analog value in the form of device resistance. However, existing memristors had limitations in mimicking the complex characteristics of the nervous system because they only allowed simple monotonic changes in conductivity. To overcome these limitations, the research team developed a new memristor capable of reproducing complex neural response patterns such as habituation and sensitization within a single device. By introducing additional layer inside the memristor that alter conductivity in opposite directions, the device can more realistically emulate the dynamic synaptic behaviors of a real nervous system — for example, decreasing its response to repeated safe stimuli but quickly regaining sensitivity when a danger signal is detected. <New memristor mimicking functions of sensory nervous system such as habituation/sensitization> Using this new memristor, the research team built an artificial sensory nervous system capable of recognizing touch and pain, an applied it to a robotic hand to test its performance. When safe tactile stimuli were repeatedly applied, the robot hand, which initially reacted sensitively to unfamiliar tactile stimuli, gradually showed habituation characteristics by ignoring the stimuli. Later, when stimuli were applied along with an electric shock, it recognized this as a danger signal and showed sensitization characteristics by reacting sensitively again. Through this, it was experimentally proven that robots can efficiently respond to stimuli like humans without separate complex software or processors, verifying the possibility of developing energy-efficient neuro-inspired robots. <Robot arm with memristor-based artificial sensory nervous system> See-On Park, researcher at KAIST, stated, "By mimicking the human sensory nervous system with next-generation semiconductors, we have opened up the possibility of implementing a new concept of robots that are smarter and more energy-efficient in responding to external environments." He added, "This technology is expected to be utilized in various fusion fields of next-generation semiconductors and robotics, such as ultra-small robots, military robots, and medical robots like robotic prosthetics". This research was published online on July 1st in the international journal 'Nature Communications,' with Ph.D candidate See-On Park as the first author. Paper Title: Experimental demonstration of third-order memristor-based artificial sensory nervous system for neuro-inspired robotics DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-60818-x This research was supported by the Korea National Research Foundation's Next-Generation Intelligent Semiconductor Technology Development Project, the Mid-Career Researcher Program, the PIM Artificial Intelligence Semiconductor Core Technology Development Project, the Excellent New Researcher Program, and the Nano Convergence Technology Division, National Nanofab Center's (NNFC) Nano-Medical Device Project.
-
 research A KAIST Team Engineers a Microbial Platform for Efficient Lutein Production
research A KAIST Team Engineers a Microbial Platform for Efficient Lutein Production<(From Left) Ph.D. Candidate Hyunmin Eun, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, , Dr. Cindy Pricilia Surya Prabowo> The application of systems metabolic engineering strategies, along with the construction of an electron channeling system, has enabled the first gram-per-liter scale production of lutein from Corynebacterium glutamicum, providing a viable alternative to plant-derived lutein production. A research group at KAIST has successfully engineered a microbial strain capable of producing lutein at industrially relevant levels. The team, led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, developed a novel C. glutamicum strain using systems metabolic engineering strategies to overcome the limitations of previous microbial lutein production efforts. This research is expected to be beneficial for the efficient production of other industrially important natural products used in food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics. Lutein is a xanthophyll carotenoid found in egg yolk, fruits, and vegetables, known for its role in protecting our eyes from oxidative stress and reducing the risk of macular degeneration and cataracts. Currently, commercial lutein is predominantly extracted from marigold flowers; however, this approach has several drawbacks, including long cultivation times, high labor costs, and inefficient extraction yields, making it economically unfeasible for large-scale production. These challenges have driven the demand for alternative production methods. To address these issues, KAIST researchers, including Ph.D. Candidate Hyunmin Eun, Dr. Cindy Pricilia Surya Prabowo, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, applied systems metabolic engineering strategies to engineer C. glutamicum, a GRAS (Generally Recognized As Safe) microorganism widely used in industrial fermentation. Unlike Escherichia coli, which was previously explored for microbial lutein production, C. glutamicum lacks endotoxins, making it a safer and more viable option for food and pharmaceutical applications. The team’s work, entitled “Gram-per-litre scale production of lutein by engineered Corynebacterium,” was published in Nature Synthesis on 04 July , 2025. This research details the high-level production of lutein using glucose as a renewable carbon source via systems metabolic engineering. The team focused on eliminating metabolic bottlenecks that previously limited microbial lutein synthesis. By employing enzyme scaffold-based electron channeling strategies, the researchers improved metabolic flux towards lutein biosynthesis while minimizing unwanted byproducts. <Lutein production metabolic pathway engineering> To enhance productivity, bottleneck enzymes within the metabolic pathway were identified and optimized. It was determined that electron-requiring cytochrome P450 enzymes played a major role in limiting lutein biosynthesis. To overcome this limitation, an electron channeling strategy was implemented, where engineered cytochrome P450 enzymes and their reductase partners were spatially organized on synthetic scaffolds, allowing more efficient electron transfer and significantly increasing lutein production. The engineered C. glutamicum strain was further optimized in fed-batch fermentation, achieving a record-breaking 1.78 g/L of lutein production within 54 hours, with a content of 19.51 mg/gDCW and a productivity of 32.88 mg/L/h—the highest lutein production performance in any host reported to date. This milestone demonstrates the feasibility of replacing plant-based lutein extraction with microbial fermentation technology. “We can anticipate that this microbial cell factory-based mass production of lutein will be able to replace the current plant extraction-based process,” said Ph.D. Candidate Hyunmin Eun. He emphasized that the integrated metabolic engineering strategies developed in this study could be broadly applied for the efficient production of other valuable natural products used in pharmaceuticals and nutraceuticals. <Schematic diagram of microbial-based lutein production platform> “As maintaining good health in an aging society becomes increasingly important, we expect that the technology and strategies developed here will play pivotal roles in producing other medically and nutritionally significant natural products,” added Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee. This work is supported by the Development of Next-generation Biorefinery Platform Technologies for Leading Bio-based Chemicals Industry project 2022M3J5A1056072 and the Development of Platform Technologies of Microbial Cell Factories for the Next-Generation Biorefineries project 2022M3J5A1056117 from the National Research Foundation supported by the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT. Source: Hyunmin Eun (1st), Cindy Pricilia Surya Prabowo (co-1st), and Sang Yup Lee (Corresponding). “Gram-per-litre scale production of lutein by engineered Corynebacterium”. Nature Synthesis (Online published) For further information: Sang Yup Lee, Distinguished Professor of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, KAIST (leesy@kaist.ac.kr, Tel: +82-42-350-3930)
-
 research KAIST Ushers in Era of Predicting ‘Optimal Alloys’ Using AI, Without High-Temperature Experiments
research KAIST Ushers in Era of Predicting ‘Optimal Alloys’ Using AI, Without High-Temperature Experiments<Picture1.(From Left) Prof. Seungbum Hong, Ph.D candidate Youngwoo Choi> Steel alloys used in automobiles and machinery parts are typically manufactured through a melting process at high temperatures. The phenomenon where the components remain unchanged during melting is called “congruent melting.” KAIST researchers have now addressed this process—traditionally only possible through high-temperature experiments—using artificial intelligence (AI). This study draws attention as it proposes a new direction for future alloy development by predicting in advance how well alloy components will mix during melting, a long-standing challenge in the field. KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 14th of July that Professor Seungbum Hong’s research team from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, in international collaboration with Professor Chris Wolverton’s group at Northwestern University, has developed a high-accuracy machine learning model that predicts whether alloy components will remain stable during melting. This was achieved using formation energy data derived from Density Functional Theory (DFT)* calculations. *Density Functional Theory (DFT): A computational quantum mechanical method used to investigate the electronic structure of many-body systems, especially atoms, molecules, and solids, based on electron density. The research team combined formation energy values obtained via DFT with experimental melting reaction data to train a machine learning model on 4,536 binary compounds. Among the various machine learning algorithms tested, the XGBoost-based classification model demonstrated the highest accuracy in predicting whether alloys would mix well, achieving a prediction accuracy of approximately 82.5%. The team also applied the Shapley value method* to analyze the key features of the model. One major finding was that sharp changes in the slope of the formation energy curve (referred to as “convex hull sharpness”) were the most significant factor. A steep slope indicates a composition with energetically favorable (i.e., stable) formation. *Shapley value: An explainability method in AI used to determine how much each feature contributed to a prediction. The most notable significance of this study is that it predicts alloy melting behavior without performing high-temperature experiments. This is especially useful for materials such as high-entropy alloys or ultra-heat-resistant alloys, which are difficult to handle experimentally. The approach could also be extended to the design of complex multi-component alloy systems in the future. Furthermore, the physical indicators identified by the AI model showed high consistency with actual experimental results on how well alloys mix and remain stable. This suggests that the model could be broadly applied to the development of various metal materials and the prediction of structural stability. Professor Seungbum Hong of KAIST stated, “This research demonstrates how data-driven predictive materials development is possible by integrating computational methods, experimental data, and machine learning—departing from the traditional experience-based alloy design.” He added, “In the future, by incorporating state-of-the-art AI techniques such as generative models and reinforcement learning, we could enter an era where completely new alloys are designed automatically.” <Model performance and feature importance analysis for predicting melting congruency. (a) SHAP summary plot showing the impact of individual features on model predictions. (b) Confusion matrix illustrating the model’s classification performance. (c) Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve with an AUC (area under the curve) score of 0.87, indicating a strong classification performance.> Ph.D. candidate Youngwoo Choi, from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST, participated as the first author. The study was published in the May issue of APL Machine Learning, a prestigious journal in the field of machine learning published by the American Institute of Physics, and was selected as a “Featured Article.” ※ Paper title: Machine learning-based melting congruency prediction of binary compounds using density functional theory-calculated formation energy ※ DOI: 10.1063/5.0247514 This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
-
 research Professor Jung-woo' Choi ‘s Team Comes in First at the World's Top Acoustic AI Challenge
research Professor Jung-woo' Choi ‘s Team Comes in First at the World's Top Acoustic AI Challenge<Photo1. (From left) Ph.D candidate Yong-hoo Kwon, M.S candidate Do-hwan Kim, Professor Jung-woo Choi, Dr. Dong-heon Lee> 'Acoustic separation and classification technology' is a next-generation artificial intelligence (AI) core technology that enables the early detection of abnormal sounds in areas such as drones, fault detection of factory pipelines, and border surveillance systems, or allows for the separation and editing of spatial audio by sound source when producing AR/VR content. On the 11th of July, a research team led by Professor Jung-woo Choi of KAIST's Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering won first place in the 'Spatial Semantic Segmentation of Sound Scenes' task of the 'DCASE2025 Challenge,' the world's most prestigious acoustic detection and analysis competition. This year’s challenge featured 86 teams competing across six tasks. In this competition, the KAIST research team achieved the best performance in their first-ever participation to Task 4. Professor Jung-woo Choi’s research team consisted of Dr. Dong-heon, Lee, Ph.D. candidate Young-hoo Kwon, and M.S. candidate Do-hwan Kim. Task 4 titled 'Spatial Semantic Segmentation of Sound Scenes' is a highly demanding task requiring the analysis of spatial information in multi-channel audio signals with overlapping sound sources. The goal was to separate individual sounds and classify them into 18 predefined categories. The research team plans to present their technology at the DCASE workshop in Barcelona this October. <Figure 1. Example of an acoustic scene with multiple mixed sounds> Early this year, Dr. Dong-heon Lee developed a state-of-the-art sound source separation AI that combines Transformer and Mamba architectures. During the competition, centered around researcher Young-hoo Kwon, they completed a ‘chain-of-inference architecture' AI model that performs sound source separation and classification again, using the waveforms and types of the initially separated sound sources as clues. This AI model is inspired by human’s auditory scene analysis mechanism that isolates individual sounds by focusing on incomplete clues such as sound type, rhythm, or direction, when listening to complex sounds. Through this, the team was the only participant to achieve double-digit performance (11 dB) in 'Class-Aware Signal-to-Distortion Ratio Improvement (CA-SDRi)*,' which is the measure for ranking how well the AI separated and classified sounds, proving their technical excellence. Class-Aware Signal-to-Distortion Ratio Improvement (CA-SDRi): Measures how much clearer (less distorted) the desired sound is separated and classified compared to the original audio, in dB (decibels). A higher number indicates more accurate and cleaner sound separation. Prof. Jung-woo Choi remarked, "The research team has showcased world-leading acoustic separation AI models for the past three years, and I am delighted that these results have been officially recognized." He added, "I am proud of every member of the research team for winning first place through focused research, despite the significant increase in difficulty and having only a few weeks for development." <Figure 2. Time-frequency patterns of sound sources separated from a mixed source> The IEEE DCASE Challenge 2025 was held online, with submissions accepted from April 1 to June 15 and results announced on June 30. Since its launch in 2013, the DCASE Challenge has served as a premier global platform of IEEE Signal Processing Society for showcasing cutting-edge AI models in acoustic signal processing. This research was supported by the Mid-Career Researcher Support Project and STEAM Research Project of the National Research Foundation of Korea, funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology, as well as support from the Future Defense Research Center, funded by the Defense Acquisition Program Administration and the Agency for Defense Development.
-
 event KAIST Kicks Off the Expansion of its Creative Learning Building, a 50th Anniversary Donation Landmark
event KAIST Kicks Off the Expansion of its Creative Learning Building, a 50th Anniversary Donation LandmarkKAIST announced on July 10th that it held a groundbreaking ceremony on July 9th for the expansion of its Creative Learning Building. This project, which celebrates the university's 50th anniversary, will become a significant donation-funded landmark and marks the official start of its construction. <(From left) President Kwang Hyung Lee, Former President Sung-Chul Shin> The groundbreaking ceremony was attended by key donors who graced the occasion, including KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee, former President Sung-Chul Shin, Alumni Association President Yoon-Tae Lee, as well as parents and faculty member. The Creative Learning Building serves as a primary space where KAIST undergraduate and graduate students attend lectures, functioning as a central hub for a variety of classes and talks. It also houses student support departments, including the Student Affairs Office, establishing itself as a student-centric complex that integrates educational, counseling, and welfare functions. This expansion is more than just an increase in educational facilities; it's being developed as a "donation landmark" embodying KAIST's identity and future vision. Designed with a focus on creative convergence education, this project aims to create a new educational hub that organically combines education, exchange, and welfare functions The campaign included over 230 participants, including KAIST alumni Byung-gyu Chang, Chairman of Krafton, former Alumni Association President Ki-chul Cha, Dr. Kun-mo Chung (former Minister of Science and Technology), as well as faculty members, parents, and current students. They collectively raised 6.5 billion KRW in donations. The total cost for this expansion project is 9 billion KRW, encompassing a gross floor area of 3,222.92㎡ across five above-ground floors, with completion targeted for September 2026.
-
 event Professor Moon-Jeong Choi Appointed as an Advisor for the ITU's 'AI for Good Global Summit'
event Professor Moon-Jeong Choi Appointed as an Advisor for the ITU's 'AI for Good Global Summit'Professor Moon-Jeong Choi from KAIST’s Graduate School of Science and Technology Policy has been appointed as an advisor for "Innovate for Impact" at the AI for Good Global Summit, organized by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN). The ITU is the UN's oldest specialized agency in the field of information and communication technology (ICT) and serves as a crucial body for coordinating global ICT policies and standards. This advisory committee was formed to explore global cooperation strategies for realizing the social value of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and promoting sustainable development. Experts from around the world are participating as committee members, with Professor Choi being the sole Korean representative. <Moon-Jeong Choi from KAIST’s Graduate School of Science and Technology Policy> The AI for Good Global Summit is taking place in Geneva, Switzerland from July 8 to 11. It is organized by the ITU in collaboration with approximately 40 other UN-affiliated organizations. The summit aims to address global challenges facing humanity through the use of AI technology, focusing on key agenda items such as identifying AI application cases, discussing international policies and technical standards, and strengthening global partnerships. As an "Innovate for Impact" advisor, Professor Choi will evaluate AI application cases from various countries, participating in case analyses primarily focused on public interest and social impact. The summit will move beyond discussions of technical performance to focus on how AI can contribute to the public good, with diverse case studies from around the world being debated. Notably, during a policy panel discussion at the summit, Professor Choi will discuss policy frameworks for AI transparency, inclusivity, and fairness under the theme of "Responsible AI Development." Professor Choi commented, "I believe the social impact of technology mirrors the values and systems of each nation. As a society's core values permeate technology, the way AI is developed and used varies significantly from country to country. These differences lead to diverse manifestations of AI's impact on society." She further emphasized, "Korea's vision of becoming an AI powerhouse should not merely be about technological superiority, but rather about enhancing social capital through human-centered AI and realizing communal values that enable us to live together." Professor Moon-Jeong Choi currently serves as the Dean of the Graduate School of Science and Technology Policy. She is also an external director for the National Information Society Agency (2023-present) and chair of the Korea-OECD Digital Society Initiative (2024-present). For more information about the AI for Good Global Summit, please visit the official website: https://aiforgood.itu.int.
-
 event King Saud University and KAIST discussed Strategic AI Partnership
event King Saud University and KAIST discussed Strategic AI Partnership<From left> President Abdulla Al-Salman(King Saud University), President Kwang Hyung Lee(KAIST) KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) and King Saud University (President Abdulla Al-Salman) held a meeting on July 3 at the KAIST Campus in Seoul and agreed to pursue strategic cooperation in AI and digital platform development. The global AI landscape is increasingly polarized between closed models developed by the U.S. and China’s nationally focused technology ecosystems. In this context, many neutral countries have consistently called for an alternative third model that promotes both technological diversity and open access. President Lee has previously advocated for a "Tripartite Platform Strategy" (三分之計), proposing an international collaboration framework based on open-source principles to be free from binary digital power structures and foster cooperative coexistence. This KAIST-KSU collaboration represents a step toward developing a new, inclusive AI model. The collaboration aims to establish an innovative multilateral framework, especially within the MENA, Japan, Korea, and Southeast Asia, by building an open-source-based AI alliance. Both institutions bring complementary strengths to the table. Saudi Arabia possesses large-scale capital and digital infrastructure, while Korea leads in core AI and semiconductor technologies, applied research, and talent cultivation. Together, the two nations aim to establish a sustainable collaboration model that creates a virtuous cycle of investment, technology, and talent. This initiative is expected to contribute to the development of an open AI platform and promote diversity in the global AI ecosystem. During the meeting, the two sides discussed key areas of future cooperation, including: · Joint development of open-source AI technologies and digital platforms · Launch of a KAIST-KSU dual graduate degree program · Expansion of exchange programs for students, faculty, and researchers · Collaborative research in basic science and STEM disciplines In particular, the two institutions discussed to establish a joint AI research center to co-develop open AI models and explore practical industrial applications. The goal is to broaden access to AI technology and create an inclusive innovation environment for more countries and institutions. President Abdulla Al-Salman stated, "Under Saudi Vision 2030, we are driving innovation in science and technology through new leadership, openness, and strategic investment. This partnership with KAIST will serve as a critical foundation for building a competitive AI ecosystem in the Middle East." President Kwang Hyung Lee emphasized, "By combining Saudi Arabia's leadership, market, and investment capacity with KAIST's technological innovation and the rich talent pools from both countries, we will significantly contribute to diversifying the global AI ecosystem." Both leaders further noted, "Through joint research leading to an independent AI model, our two institutions could establish a new axis beyond the existing US-China digital order—realizing a 'Tripartite AI Strategy' that will propel us into global markets extending far beyond the MENA and ASEAN regions." KAIST and KSU plan to formalize this agreement by signing an MOU in the near future, followed by concrete actions such as launching the joint research institute and global talent development programs. This collaboration was initiated under the Korea Foundation’s Distinguished Guests Invitation Program, overseen by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, and is expected to grow into a long-term strategic partnership with continued support from KF. About King Saud University (KSU) Founded in 1957, KSU is Saudi Arabia’s first and leading national university. As a top research-oriented institution in the Middle East, it has achieved international recognition in fields such as AI, energy, and biotechnology. It plays a central role in nurturing talent and driving innovation aligned with Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030, and is expanding global partnerships to further strengthen its research capabilities. About the Korea Foundation (KF) Established in 1991 under the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, the Korea Foundation is a public diplomacy institution dedicated to strengthening international understanding and friendship with Korea. KF plays a key role in expanding Korea’s soft power through academic and cultural exchange, people-to-people networks, and global Korean studies programs. Its Distinguished Guests Invitation Program fosters strategic partnerships with global leaders in government, academia, and industry.
-
 event KAIST to Lead the Way in Nurturing Talent and Driving S&T Innovation for a G3 AI Powerhouse
event KAIST to Lead the Way in Nurturing Talent and Driving S&T Innovation for a G3 AI Powerhouse* Focusing on nurturing talent and dedicating to R&D to become a G3 AI powerhouse (Top 3 AI Nations). * Leading the realization of an "AI-driven Basic Society for All" and developing technologies that leverage AI to overcome the crisis in Korea's manufacturing sector. * 50 years ago, South Korea emerged as a scientific and technological powerhouse from the ashes, with KAIST at its core, contributing to the development of scientific and technological talent, innovative technology, national industrial growth, and the creation of a startup innovation ecosystem. As public interest in AI and science and technology has significantly grown with the inauguration of the new government, KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced its plan, on June 24th, to transform into an "AI-centric, Value-Creating Science and Technology University" that leads national innovation based on science and technology and spearheads solutions to global challenges. At a time when South Korea is undergoing a major transition to a technology-driven society, KAIST, drawing on its half-century of experience as a "Starter Kit" for national development, is preparing to leap beyond being a mere educational and research institution to become a global innovation hub that creates new social value. In particular, KAIST has presented a vision for realizing an "AI-driven Basic Society" where all citizens can utilize AI without alienation, enabling South Korea to ascend to the top three AI nations (G3). To achieve this, through the "National AI Research Hub" project (headed by Kee Eung Kim), led by KAIST representing South Korea, the institution is dedicated to enhancing industrial competitiveness and effectively solving social problems based on AI technology. < KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee > KAIST's research achievements in the AI field are garnering international attention. In the top three machine learning conferences (ICML, NeurIPS, ICLR), KAIST ranked 5th globally and 1st in Asia over the past five years (2020-2024). During the same period, based on the number of papers published in top conferences in machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision (ICML, NeurIPS, ICLR, ACL, EMNLP, NAACL, CVPR, ICCV, ECCV), KAIST ranked 5th globally and 4th in Asia. Furthermore, KAIST has consistently demonstrated unparalleled research capabilities, ranking 1st globally in the average number of papers accepted at ISSCC (International Solid-State Circuits Conference), the world's most prestigious academic conference on semiconductor integrated circuits, for 19 years (2006-2024). KAIST is continuously expanding its research into core AI technologies, including hyper-scale AI models (Korean LLM), neuromorphic semiconductors, and low-power AI processors, as well as various application areas such as autonomous driving, urban air mobility (UAM), precision medicine, and explainable AI (XAI). In the manufacturing sector, KAIST's AI technologies are also driving on-site innovation. Professor Young Jae Jang's team has enhanced productivity in advanced manufacturing fields like semiconductors and displays through digital twins utilizing manufacturing site data and AI-based prediction technology. Professor Song Min Kim's team developed ultra-low power wireless tag technology capable of tracking locations with sub-centimeter precision, accelerating the implementation of smart factories. Technologies such as industrial process optimization and equipment failure prediction developed by INEEJI Co., Ltd., founded by Professor Jaesik Choi, are being rapidly applied in real industrial settings, yielding results. INEEJI was designated as a national strategic technology in the 'Explainable AI (XAI)' field by the government in March. < Researchers performing data analysis for AI research > Practical applications are also emerging in the robotics sector, which is closely linked to AI. Professor Jemin Hwangbo's team from the Department of Mechanical Engineering garnered attention by newly developing RAIBO 2, a quadrupedal robot usable in high-risk environments such as disaster relief and rough terrain exploration. Professor Kyoung Chul Kong's team and Angel Robotics Co., Ltd. developed the WalkOn Suit exoskeleton robot, significantly improving the quality of life for individuals with complete lower body paralysis or walking disabilities. Additionally, remarkable research is ongoing in future core technology areas such as AI semiconductors, quantum cryptography communication, ultra-small satellites, hydrogen fuel cells, next-generation batteries, and biomimetic sensors. Notably, space exploration technology based on small satellites, asteroid exploration projects, energy harvesting, and high-speed charging technologies are gaining attention. Particularly in advanced bio and life sciences, KAIST is collaborating with Germany's Merck company on various research initiatives, including synthetic biology and mRNA. KAIST is also contributing to the construction of a 430 billion won Merck Bio-Center in Daejeon, thereby stimulating the local economy and creating jobs. Based on these cutting-edge research capabilities, KAIST continues to expand its influence not only within the industry but also on the global stage. It has established strategic partnerships with leading universities worldwide, including MIT, Stanford University, and New York University (NYU). Notably, KAIST and NYU have established a joint campus in New York to strengthen human exchange and collaborative research. Active industry-academia collaborations with global companies such as Google, Intel, and TSMC are also ongoing, playing a pivotal role in future technology development and the creation of an innovation ecosystem. These activities also lead to a strong startup ecosystem that drives South Korean industries. The flow of startups, which began with companies like Qnix Computer, Nexon, and Naver, has expanded to a total of 1,914 companies to date. Their cumulative assets amount to 94 trillion won, with sales reaching 36 trillion won and employing approximately 60,000 people. Over 90% of these are technology-based startups originating from faculty and student labs, demonstrating a model that makes a tangible economic contribution based on science and technology. < Students at work > Having consistently generated diverse achievements, KAIST has already produced approximately 80,000 "KAISTians" who have created innovation through challenge and failure, and is currently recruiting new talent to continue driving innovation that transforms South Korea and the world. President Kwang Hyung Lee emphasized, "KAIST will establish itself as a global leader in science and technology, designing the future of South Korea and humanity and creating tangible value." He added, "We will focus on talent nurturing and research and development to realize the new government's national agenda of becoming a G3 AI powerhouse." He further stated, "KAIST's vision for the AI field, in which it places particular emphasis, is to strive for a society where everyone can freely utilize AI. We will contribute to significantly boosting productivity by recovering manufacturing competitiveness through AI and actively disseminating physical AI, AI robots, and AI mobility technologies to industrial sites."
-
 people Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee Wins 2025 Global Metabolic Engineering Award
people Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee Wins 2025 Global Metabolic Engineering Award< Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee (Senior Vice President for Research) from the Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering > KAIST announced on the 20th that Professor Sang Yup Lee, who serves as the Vice President for Research and a Distinguished Professor at our university, has been awarded the '2025 Gregory N. Stephanopoulos Award for Metabolic Engineering' by the International Metabolic Engineering Society (IMES). Professor Lee delivered his award lecture at the 16th Metabolic Engineering Conference (ME16), held in Copenhagen, Denmark, from June 15th to 19th. This award was established through contributions from the American Institute of Chemical Engineers (AIChE) Foundation, as well as fellow colleagues and acquaintances, to honor the achievements of Dr. Gregory Stephanopoulos, widely recognized as one of the pioneers of metabolic engineering. Presented biennially, the award recognizes scientists who have successfully commercialized fundamental research in metabolic engineering or have made outstanding contributions to the quantitative analysis, design, and modeling of metabolic pathways. Professor Sang Yup Lee boasts an impressive record of over 770 journal papers and more than 860 patents. His groundbreaking research in metabolic engineering and biochemical engineering is highly acclaimed globally. Throughout his 31 years as a professor at KAIST, Professor Lee has developed various metabolic engineering-based technologies and strategies. These advancements have been transferred to industries, facilitating the production of bulk chemicals, polymers, natural products, pharmaceuticals, and health functional foods. He has also founded companies and actively engages in advisory roles with various enterprises. The International Metabolic Engineering Society (IMES) defines metabolic engineering as the manipulation of metabolic pathways in microorganisms or cells to produce useful substances (such as pharmaceuticals, biofuels, and chemical products). It utilizes tools like systems biology, synthetic biology, and computational modeling with the aim of enhancing the economic viability and sustainability of bio-based processes. Furthermore, Professor Lee previously received the Merck Metabolic Engineering Award, a prominent international award in the field, in 2008. In 2018, he was honored with the Eni Award, often referred to as the Nobel Prize in energy, presented by the President of Italy. Professor Sang Yup Lee remarked, "Metabolic engineering is a discipline that leads the current and future of biotechnology. It is a tremendous honor to receive this meaningful award at a time when the transition to a bio-based economy is accelerating. Together with my students and fellow researchers, we have generated numerous patents and transferred technologies to industry, and also established startups in the fields of biofuels, wound healing, and cosmetics. I will continue to pursue research that encompasses both fundamental research and technological commercialization." The 'International Metabolic Engineering Society (IMES)' is a specialized society under the American Institute of Chemical Engineers. Its mission is to enable the production of various bio-based products, including pharmaceuticals, food additives, chemicals, and fuels, through metabolic engineering. The society hosts the Metabolic Engineering Conference biennially, offering researchers opportunities for knowledge exchange and collaboration.
-
 Nature Conferences The two-way relationship between AI and materials was reflected a Nature Conference ‘M...
Nature Conferences The two-way relationship between AI and materials was reflected a Nature Conference ‘M...https://www.nature.com/articles/d42473-025-00107-9
2025.02.05 -
 Nature Portfolio Nature Conference: Materials for AI, AI for Materials
Nature Portfolio Nature Conference: Materials for AI, AI for Materialshttps://youtu.be/W92YYMHNjj8?si=lBQPn3LK5lz_sowb
2025.02.05 -
 CNN Tech for Good: Students craft beetle-bot hybrids and six-legged flying drones
CNN Tech for Good: Students craft beetle-bot hybrids and six-legged flying droneshttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3k1TqmMcTPQ
2024.11.25 -
 CNN Tech for Good: Racing against the world’s fastest four-legged robot
CNN Tech for Good: Racing against the world’s fastest four-legged robothttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gUhpe_72y2k
2024.11.22 -
 Nature Women in chemistry: Q&A with Professor Hyunjoo Lee
Nature Women in chemistry: Q&A with Professor Hyunjoo Leehttps://www.nature.com/articles/s42004-024-01291-3
2024.09.25